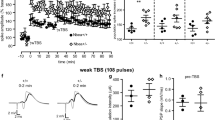
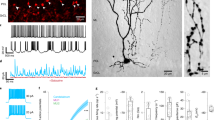
Abstract
THE laminar organisation of neurones in the brain of the homozygous ‘reeler’ mutant mouse1 is grossly disrupted, especially in the cerebellum, hippocampus and neocortex2–6. Although a number of histological studies on synaptic organisation in the cerebellum of various mutants have been reported7–9, the effect of such disorganisation on interneuronal connections has not been investigated electrophysiologically, either in the cerebellum or elsewhere.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Falconer, D. S., J. Genet., 50, 192–201 (1951).
Caviness, V. S., and Sidman, R. L., J. comp. Neurol., 145, 85–104 (1972).
Caviness, V. S., and Sidman, R. L., J. comp. Neurol., 147, 235–254 (1973).
Hamburgh, M., Experientia, 16, 460–461 (1960).
Hamburgh, M., Devl Biol., 8, 165–185 (1963).
Meier, H., and Hoag, W. G., J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol., 21, 649–654 (1962).
Rakic, P., and Sidman, R. L., J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol., 31, 192 (1972).
Rakic, P., and Sidman, R. L., J. comp. Neurol., 152, 133–162 (1973).
Sotelo, C., and Changeux, J.-P., Brain Res., 67, 519–526 (1974).
Lorente de Nó, R., J. Psychol. Neurol., Lpz., 46, 113–177 (1934).
Andersen, P., Bliss, T. V. P., and Skrede, K. K., Expl Brain Res., 13, 222–238 (1971).
Lømo, T., Expl Brain Res., 12, 18–45 (1971).
Angevine, jun., J. B., Expl Neurol., Suppl. 2, 1–70 (1965).
Bliss, T. V. P., Chung, S. H., and Stirling, R. V., J. Physiol., Lond., 239, 92–94P (1974).
Caviness, V. S., J. comp. Neurol., 151, 113–120 (1973).
DeLong, G. R., Devl Biol., 22, 563–583 (1970).
DeLong, G. R., and Sidman, R. L., Devl. Biol., 22, 584–600 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BLISS, T., CHUNG, S. An electrophysiological study of the hippocampus of the ‘reeler’ mutant mouse. Nature 252, 153–155 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/252153a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/252153a0
This article is cited by
-
Neonatla vestibular stimulation and mating in cerebellar mutants
Behavior Genetics (1993)
-
An early development defect in the cerebral cortex of the reeler mouse
Anatomy and Embryology (1979)
-
Redirected perforant and commissural connections of eutopic and ectopic neurons in the hippocampus of methylazoxymethanol-acetate treated rats
Acta Neuropathologica (1978)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.