Abstract
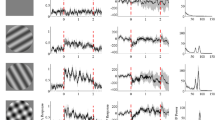
LIGHT striking the eye is absorbed by three types of pigment preferentially sensitive to either red, green or blue light. The resulting neurophysiological signals are ultimately pooled before they activate the neural mechanism that underlies the perception of photometric brightness. On the other hand, the role of colour might be different when viewing coloured scenes containing fine detail (pattern vision) compared with standard photometric stimulus fields; colour signals may not be pooled as when perceiving brightness1,2. There is evidence that the human visual system handles red patterns in parallel with green and blue patterns1,2. I have attempted to determine spectral sensitivity curves for the red-sensitive and green-sensitive channels of human pattern vision. This was done objectively by measuring brain activity electrophysiologically.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCollough, C., Science, 149, 1115 (1965).
Regan, D., Vision Res., 11, 1203 (1971); in The Visual System (edit. by Arden, G. B.) (Plenum Press, New York, 1972).
Regan, D., Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 20, 238–248 (1966); Med. Elect. biol. Eng., 4, 169–177 (1966); Evoked Potentials in Psychology, Sensory Physiology and Clinical Medicine (Chapman and Hall, London, 1972).
Regan, D., Invest. Ophthal., 12, 669–679 (1973).
Regan, D., Vision Res. (in the press).
Campbell, F. W., and Maffei, L., J. Physiol., Lond., 207, 635–652 (1970).
Regan, D., Vision Res., 13, 2381–2402 (1973).
Spekreijse, H., Tweel, L. H., van der, and Zuidma, Th., Vision Res., 13, 1577–1601 (1973).
Regan, D., J. opt. Soc. Am., 60, 856–859 (1970).
Wyszecki, G., and Stiles, W. S., Colour Sci., (Wiley, New York, 1967).
Brindley, G. S., Physiology of the Retina and Visual Pathway, 2nd ed., (Arnold, London, 1970).
Brown, P. K., and Wald, G., Science, 144, 45–52 (1964).
Marks, W. B., Dobel, W. H., and MacNichol, E. F., Science, 143, 1181–1183 (1964).
Baker, H. D., and Rushton, W. A. H., J. Physiol., Lond., 176, 56–72 (1965).
Weale, R. A., Optica Acta, 6, 158–174 (1959).
Wald, G., Science, 145, 1007–1017 (1964).
Pitt, F. H. G., Proc. R. Soc. B, 132, 101–117 (1944).
Thomson, L. C., and Wright, W. D., J. opt. Soc. Am., 43, 890–894 (1953).
Stiles, W. S., Proc. R. Soc. B, 133, 418–434 (1946); Docum. Ophthal., 3, 138–163 (1949); Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 45, 100–114 (1959).
Regan, D., and Sperling, H. G., Vision Res., 11, 173–176 (1971).
Regan, D., and Spekreijse, H., Vision Res., 14, 89–95 (1974).
Green, D. G., J. Physiol., Lond., 196, 415–429 (1968).
McKee, S. P., and Westheimer, G., J. Physiol., Lond., 206, 117–128 (1970).
Kelly, D. H., J. Physiol., Lond., 228, 55–72 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
REGAN, D. Electrophysiological evidence for colour channels in human pattern vision. Nature 250, 437–439 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/250437a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/250437a0
This article is cited by
-
Understanding individual face discrimination by means of fast periodic visual stimulation
Experimental Brain Research (2014)
-
Identification of a novel dynamic red blindness in human by event-related brain potentials
Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology [Medical Sciences] (2010)
-
Independence of channels in colour contrast perception
Nature (1975)
-
Recent advances in electrical recording from the human brain
Nature (1975)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.