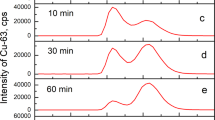
Abstract
ALTHOUGH the toxic effects of mercury and its derivatives are well known1–7 relatively little is known about the transport mechanisms involved in its distribution throughout the body. One possible means could be the serum lipoproteins through reactions involving lipids and proteins. Various metal ions bind with phospholipids8; for example, calcium ions bind to anionic sites of phospholipids in lipid monolayers9. In addition, phospholipids provide negatively charged sites for calcium ion exchanges in biomembranes10 and contribute to the transport of ferrous ions in biphasic systems11. These findings, together with the fact that mercurials bind with negative sites of proteins, led us to explore the possibility that mercurials are actively sequestered by the serum lipoproteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corner, E. D. S., and Sparrow, B. W., J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K., 35, 531 (1956).
Aberg, B., Ekman, L., Falk, R., Greitz, U., Persson, G., and Snihs, J., Arch. environ. Health, 19, 478 (1969).
Vallee, B. L., and Ulmer, D. D., A. Rev. Biochem., 41, 91 (1972).
Scott, K. M., Knight, V. A., Settlemire, C. T., and Brierly, G. P., Biochemistry, 9, 714 (1970).
Fowler, B. A., Science, N. Y., 175, 18 (1972).
Blake, C. A., and Sawyer, C. H., Science, N. Y., 177, 621 (1972).
Brubaker, P. E., Lucier, G. W., and Klein, R., Biochim. biophys. Acta, 44, 1552 (1971).
Cerejido, M., and Rotunno, C. A., Introduction to the Study of Biological Membranes (Gordon and Breach, New York and London, 1970).
Seimiya, T., and Ohki, S., Nature, 239, 26 (1972).
Rojas, E., and Tobias, J. M., Biochim. biophys. Acta, 94, 394 (1965).
Agate, A. D., and Vishniac, W., Chem. Phys. Lipids, 9, 245 (1972).
Freeman, N. K., Lindgren, F. T., and Nichols, A. V., in Holman, R. T., Lunderg, W. O., and Malkin, T., Progress in the Chemistry of Fats and Other Lipids, 218 (Pergamon, New York, 1963).
Scanu, A. M., and Edelstein, C., Anal. Biochem., 44, 576 (1971).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J., J. biol. Chem., 193, 265 (1951).
Malins, D. C. >, in Progress in the Chemistry of Fats and Other Lipids, 8, part 3, 343 (Pergamon, Oxford, 1966).
Gottfried, E. L., J. Lipid Res., 8, 321 (1967).
Hanson, S. W. F., and Olley, J., Biochem. J., 89, 101 (1963).
Huges, W. L., Ann. Acad. N. Y. Sci., 65, 454 (1957).
Gotto, A. M., Levy, R. I., Lux, S. E., Birnbaum, M. E., and Frederickson, D. S., Biochem. J., 133, 369 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
REICHERT, W., MALINS, D. Interaction of Mercurials with Salmon Serum Lipoproteins. Nature 247, 569–570 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/247569a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/247569a0
This article is cited by
-
Fundamental roles of biological barriers in mercury accumulation and transfer in freshwater ecosystems (analysis at organism, organ, cell and molecular levels)
Water Air & Soil Pollution (1991)
-
Electron spin resonance study of serum lipoproteins of salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch): Structural alterations produced in high density lipoproteins by mercury and cadmium
Lipids (1975)
-
The behaviour of mercury in the system water-fish
Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (1975)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.