Abstract
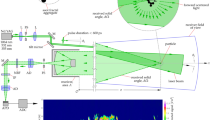
ONE method of measuring atmospheric molecular pollutants at remote locations uses the Raman backscatter from a laser beam: the scattered wavelengths are characteristic of each pollutant, and their intensities give a measure of the respective concentrations1–3. But, because of the isotropic nature of the scatter, large telescopes are required to collect even a small fraction of the total scatter, and so the probing distance is small.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leonard, D. A., Nature, 216, 142 (1967).
Melfi, S. H., Lawrence, J. D., and McCormick, M. P., Appl. Phys. Lett., 15, 295 (1969).
Kobayashi, T., and Inaba, H., Proc. IEEE, 58, 1568 (1970).
Weast, R. C., Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, F-147 (Chemical Rubber Co., 1970).
Hinkley, E. D., and Kelly, P. L., Science, 171, 635 (1971).
Schorygin, P. P., J. Chim. Phys., 50, D31 (1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
FONTANA, J., HASSIN, G. & KINCAID, B. Remote Sensing of Molecular Pollutants in the Atmosphere by Stimulated Raman Emission. Nature 234, 292–293 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/234292a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/234292a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.