Abstract
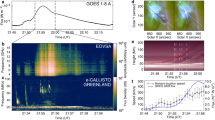
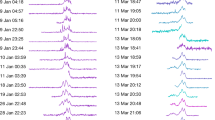
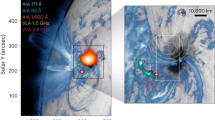
A CURIOUS but rare feature of the metre–wave continuum (type IV) radiation received from certain large solar flares is the pulsating structure which modulates the intensity in a periodic or quasi-periodic manner1,2. The modulation may persist for about l min or more and the period of the pulsation is typically of the order of 1 s. Of various explanations suggested, we consider the most satisfactory to be that of Rosenberg, in which the radiation is attributed to synchrotron radiation emitted by electrons in a magnetic flux tube embedded in the solar corona and the pulsations are attributed to modulation by standing magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) waves set up within the tube. We now present further evidence of this phenomenon and outline a model which accounts both for the acceleration of the emitting electrons and for the pulsations themselves. There is also evidence to suggest that energetic protons may be accelerated by the same process. We consider that the phenomenon affords a possible observational clue to a physical process by which solar cosmic rays can be generated high in the solar corona.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrami, A., Solar Phys., 11, 104 (1970).
Rosenberg, H., Astron. Astrophys., 9, 159 (1970).
Wild, J. P., Smerd, S. F., and Weiss, A. A., Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys., 1, 291 (1963).
Parker, E. N., Phys. Rev., 109, 1328 (1958).
Wentzel, D. G., Astrophys. J., 140, 1013 (1964).
Wild, J. P., and Hill, E. R., Austral. J. Phys., 24, 43 (1971).
ESSA Bulletin of Solar-Geophysical Data (US Department of Commerce).
Wild, J. P., Solar Phys., 9, 260 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McLEAN, D., SHERIDAN, K., STEWART, R. et al. Regular Pulses from the Sun and a Possible Clue to the Origin of Solar Cosmic Rays. Nature 234, 140–142 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/234140a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/234140a0
This article is cited by
-
Magnetohydrodynamic Fast Sausage Waves in the Solar Corona
Space Science Reviews (2020)
-
Loss-cone instability modulation due to a magnetohydrodynamic sausage mode oscillation in the solar corona
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Location of Decimetric Pulsations in Solar Flares
Solar Physics (2011)
-
Electron acceleration and type II radio emission at quasi-parallel shock waves
Radiophysics and Quantum Electronics (1998)
-
Time signatures of impulsively generated waves in a coronal plasma
Solar Physics (1994)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.