Abstract
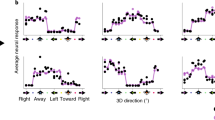
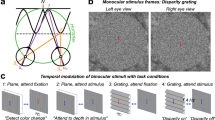
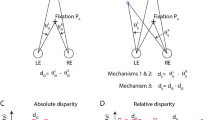
STEREOPSIS is the perception of relative depth by means of the disparate retinal stimulation which occurs when horizontally separated eyes are fixed on a common point. The stimulus conditions which produce stereopsis in humans have been studied thoroughly, but only recently has it been possible to study the neural mechanisms1–4. We have been able to demonstrate stereoscopic vision in the cat, a result which complements neurophysiological data demonstrating the presence of cells in cat visual cortex with receptive field geometry which is specialized for the detection of retinal disparity1,2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlow, H. B., Blakemore, C., and Pettigrew, J. D., J. Physiol., 193, 327 (1967).
Joshua, O. E., and Bishop, P. O., Exp. Brain Res., 10, 389 (1970).
Hubel, D. H., and Wiesel, T. N., Nature, 255, 41 (1970).
Bough, E. W., Nature, 255, 42 (1970).
Estes, W. K., and Skinner, B. F., J. Exp. Psychol., 29, 390 (1941).
Brady, J. V., and Conrad, D. G., J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 54, 149 (1961).
Kamin, L. J., J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 53, 128 (1960).
Hoffman, H. S., Selekman, W. L., and Fleshler, M., J. Exp. Anal. Behav., 9, 659 (1966).
Sidman, M., Ray, B., Sidman, R., and Klinger, J., Exp. Neurol., 16, 377 (1966).
Hendricks, J., J. Exp. Anal. Behav., 9, 501 (1966).
Shumake, S. A., Smith, J. C., and Tucker, D., J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 67, 64 (1969).
Hefner, H., and Masterton, R. B., J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 71, 175 (1970).
Gregory, R. L., Nature, 203, 1407 (1964).
Lee, D. N., Vision Res., 9, 145 (1969).
Templeton, W. B., and Green, F. A., Quart. J. Exp. Psychol., 20, 200 (1968).
Julesz, B., Science, 145, 356 (1964).
Anonymous neurophysiological correspondent, Nature, 216, 1067 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
FOX, R., BLAKE, R. Stereoscopic Vision in the Cat. Nature 233, 55–56 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/233055a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/233055a0
This article is cited by
-
The primary visual cortex of Cetartiodactyls: organization, cytoarchitectonics and comparison with perissodactyls and primates
Brain Structure and Function (2022)
-
Single unit receptive fields in rabbit primary binocular cortex
Experimental Brain Research (1982)
-
Stereopsis in toads
Nature (1977)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.