Abstract
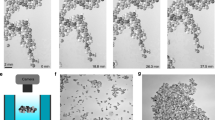
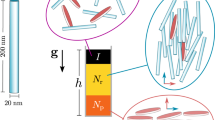
THE dependence of hydraulic and aerodynamic drag on particle shape has been of interest for a considerable time but theoretical work has greatly exceeded experimental results, especially for submicron particles. Fuchs1 gave a concise summary of the position and Preining2 and Vomela and Whitby3 have published mainly theoretical articles. Kunkel4 determined the drag on various configurations of steel balls glued together and falling in oil, and Megaw and Wiffen5 compared the diffusion coefficient of single and clustered submicron polystyrene spheres. Stöber et al.6 deduced that the Stokes diameter dn of a cluster containing n spheres should be related to the diameter d1 of a single sphere by the expression  and confirmed its validity in an experiment in which single particles and clusters of submicron polystyrene spheres were centrifuged out of a spinning air stream. Stöber et al. also showed that, when expressed in terms of the Stokes diameter, Kunkel's results (in which the unit sphere was 0.12 cm diameter) agreed very well with those for submicron spheres in air.
and confirmed its validity in an experiment in which single particles and clusters of submicron polystyrene spheres were centrifuged out of a spinning air stream. Stöber et al. also showed that, when expressed in terms of the Stokes diameter, Kunkel's results (in which the unit sphere was 0.12 cm diameter) agreed very well with those for submicron spheres in air.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fuchs, N. A., The Mechanics of Aerosols (Pergamon, Oxford, 1964).
Preining, O., Atm. Env., 1, 3, 271 (1967).
Vomela, R. A., and Whitby, K. T., J. Coll. Intern. Sci., 25, 4, 568 (1967).
Kunkel, W. B., J. Appl. Phys., 19, 1056 (1948).
Megaw, W. J., and Wiffen, R. D., J. Rech. Atmos., 2, 2, 69 (1966).
Stöber, W., Berner, A., and Blaschke, R., J. Coll. Intern. Sci., 29, 4, 710 (1969).
Megaw, W. J., J. Rech. Atmos., 2, 2, 53 (1966).
Megaw, W. J., and Wells, A. C., Nature, 219, 259 (1968).
Megaw, W. J., and Wells, A. C., J. Sci. Instrum., 2, 1013 (1969).
Fuchs, N. A., and Stechkina, I. B., Trans. Faraday Soc., 58, 1949 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MEGAW, W., WELLS, A. Drag on Clusters of Submicron Spheres in Gravitational and Electrical Fields. Nature 229, 624–626 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/229624a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/229624a0
This article is cited by
-
�ber die orientierung und den dynamischen formfaktor von kettenf�rmigen aerosolteilchen in ladungsspektrometern
Water, Air, and Soil Pollution (1974)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.