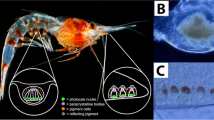
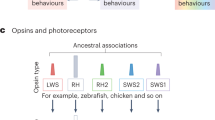
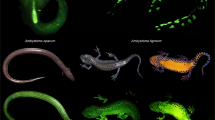
Abstract
IN a broad sense the absorbance spectra of the rhodopsins of fishes seem to vary to suit the spectral energy distributions of the lights reaching them through the water1–6. Thus bathypelagic fishes, living in an environment where the ambient daylight (and the light from bioluminescent organisms) is maximal between 460 and 490 nm7, have rhodopsins of λmax between 472 and 487 nm (refs. 1–5). Similarly, coastal fishes, which live in light environments with peak radiation between 490 and 550 nm7, have rhodopsins that range correspondingly in λmax between 495 and 512 nm (refs. 3–5, 8).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denton, E. J., and Warren, F. J., Nature, 178, 1059 (1956).
Denton, E. J., and Warren, F. J., J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK, 36, 651 (1957).
Munz, F. W., thesis Univ. of California, Los Angeles (1957).
Munz, F. W., Science, 125, 1142 (1957).
Munz, F. W., J. Physiol., 140, 220 (1958).
Wald, G., Brown, P. K., and Brown, P. S., Nature, 180, 969 (1957).
Jerlov, N. G., Optical Oceanography (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1968).
Munz, F. W., J. Gen. Physiol., 42, 445 (1958).
Saito, Z., Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 32, 432 (1938).
Harrison, R. J., and Tomlinson, J. D. W., Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond., 126, 205 (1956).
Dearborn, J. H., J. Mammology, 46, 37 (1965).
Laws, R. M., Falkland Islands Dependencies Surveys, Sci. Rep., 13, 1 (1956).
de Vries, A. L., and Wohlschlag, D. E., Science, 145, 292 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LYTHGOE, J., DARTNALL, H. A “Deep Sea Rhodopsin” in a Mammal. Nature 227, 955–956 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/227955a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/227955a0
This article is cited by
-
First observations of Weddell seals foraging in sponges in Erebus Bay, Antarctica
Polar Biology (2023)
-
Three-dimensional space use during the bottom phase of southern elephant seal dives
Movement Ecology (2017)
-
Basic mechanisms in pinniped vision
Experimental Brain Research (2009)
-
Visual pigments of marine carnivores: pinnipeds, polar bear, and sea otter
Journal of Comparative Physiology A (2006)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.