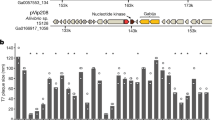
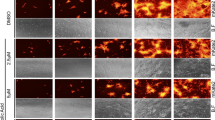
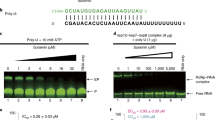
Abstract
RIFAMPICIN1 inhibits the replication of vaccinia virus in infected cells in vitro when added at 100 µg/ml. immediately after infection3,4 or at a late stage of the virus latent period4. In the presence of the drug the translation of late viral mRNA spacies was found to be markedly inhibited 8 h after infection5; the rate of late viral protein synthesis declined6; the synthesis of the particulate viral RNA polymerase molecules, induced late in infection, was prevented7; and the assembly of virions was affected8,9. Rifampicin did not affect the synthesis of viral mRNA molecules nor their association with ribosomos to form polyribosomes5. The inability of rifampicin to inhibit in vitro the activity of the three different species of poxvirus specific DNA dependent RNA polymerases7 suggested that the mode of antiviral activity of rifampicin differed from its antimicrobial activity. The latter was attributed10 to the macrocyclic ring of the rifamycin SV molecule which binds to the microbial DNA dependent RNA polymerase and inhibits the initiation of RNA synthesis. Using Shope fibroma virus (SFV), a poxvirus which causes localized tumours in rabbits11–13, and several rifamycin SV derivatives, we have obtained results which indicate that the anti-poxvirus activity resides in the hydrazone side chain of rifampicin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maggi, N., Pasqualucci, C. R., Ballotta, R., and Sensi, P., Chemotherapia, 11, 285 (1966).
Maggi, N., Pallanza, R., and Sensi, P., Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 765 (1965).
Heller, E., Argaman, M., Levy, H., and Goldblum, N., Nature, 222, 273 (1969).
Subak-Sharpe, J. H., Timbury, M. C., and Williams, J. F., Nature, 222, 341 (1969).
Ben-Ishai, Z., Heller, E., Goldblum, N., and Becker, Y., Nature, 224, 29 (1969).
Moss, B., Katz, E., and Rosenblum, E. N., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 36, 858 (1969).
McAuslan, B., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 37, 289 (1969).
Moss, B., Rosenblum, E. N., Katz, E., and Grimley, P. M., Nature, 224, 1280 (1969).
Nagayama, A., Pogo, B. G., and Dales, S., Virology, 40, 1039 (1970).
Wehrli, W., and Staehelin, M., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 182, 24 (1969).
Shope, R. E., J. Exp. Med., 63, 43 (1936).
Ewton, D., and Hodes, M. E., Virology, 33, 77 (1967).
Chang, L. M. S., and Hodes, M. E., Virology, 36, 323 (1968).
Bauer, D. J., and Sadler, P. W., Brit. J. Pharmacol., 15, 101 (1960).
Becker, Y., and Zakay-Rones, Z., Nature, 222, 851 (1969).
Becker, Y., Asher, Y., Himmel, N., Zakay-Rones, Z., and Maythar, B., Nature, 224, 33 (1969).
Becker, Y., Asher, Y., Himmel, N., and Zakey-Rones, Z., Nature, 225, 454 (1970).
Woodson, B., and Joklik, W. K., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 54, 946 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ZAKAY-RONES, Z., BECKER, Y. Anti-poxvirus Activity of Rifampicin associated with Hydrazone Side Chain. Nature 226, 1162–1163 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/2261162a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2261162a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.