Abstract
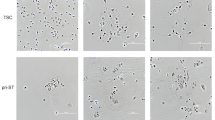
WHILE investigating the antigenicity of human trophoblast and its possible role in the toxaemias of pregnancy, we wished to set up pure tissure cultures of trophoblast. Placental tissue in explant and monolayer culture gives rise to a mixed population of cells, the identification of which is difficult because they undergo morphological and physiological changes in vitro. Existing methods for identifying trophoblast in vitro include cytology1,2, enzyme histochemistry1 and the demonstration of chorionic gonadotrophin production3,4. Thiede1 distinguished three cell types in cultures of chorionic villi: fibroblasts, epithelioid cells and giant multinucleated cells. He suggested that these originated from mesenchyme, cytotrophoblast and syncytio-trophoblast respectively, but emphasized the unreliability of morphological criteria. The histochemical localization of alkaline phosphatase in epithelioid and multinucleate cell types1 is considered compatible with an origin from trophoblast in view of the distribution of this enzyme in the placenta found by several workers5–9. Soma, Ehrmann and Hertig3 found that the goriadotrophic activity of the culture medium declined in concert with the disappearance of giant multinucleated cells, suggesting that these might be trophoblastic in origin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thiede, H. A., Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec., 79, 636 (1960).
Thiede, H. A., Clin. Obstet. Gynec., 6, 110 (1963).
Soma, H., Ehrmann, R. L., Hertig, A. T., Obstet. Gynec., 18, 704 (1961).
Currie, G. A., J. Obstet. Gynec. Brit. Commonwealth, 74, 84 (1967).
Wislocki, G. B., and Dempsey, E. W., Endocrinology, 38, 90 (1946).
Botello, J., Cano, A., Arch. Med. Exp. (Madrid), 13, 45 (1950).
Dumont, M., Presse Med., 65, 535 (1957).
Thomsen, K., Geburtsh Frauenheilk, 18, 354 (1958).
Curzen, P., J. Obstet. Gynec. Brit. Commonwealth, 74, 385 (1967).
Curzen, P., J. Obstet. Gynec. Brit. Commonwealth, 75, 1128 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RIGBY, P., CURZEN, P. Identification of Human Trophoblast in vitro. Nature 222, 1062–1063 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1038/2221062b0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2221062b0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.