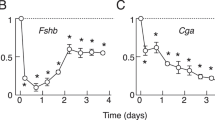
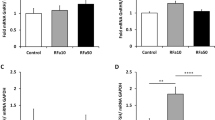
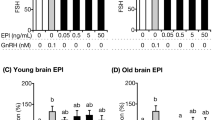
Abstract
SINCE the discovery of a gonadotrophin inhibitor in urinaiy extracts from children1 and adults2, there has been some controversy as to its mode of action. Because a constituent of human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG), N-acetyl-D-neuraminic acid, reduced the uterine weight response to HCG, it was suggested that the inhibitor competes with the gonadotrophin for the site of hormone action3. It has also been postulated that the inhibitor suppresses secretion of endogenous gonadotrophin. This hypothesis was based on the similarity between the increased doses of gonadotrophins required for the production of a response in hypophysectomized animals compared with those given an inhibitor4. The possibility that the urinary inhibitor is an antagonistic substance which combines with HCG without affecting the pituitary–ovarian axis of the assay animal has also been considered5. I report here the effect of the urinary inhibitor on the pituitary content of gonadotrophin. Possible direct antagonism of HCG by the inhibitor has also been tested in vitro and in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landau, B., Schwartz, H. S., and Soffer, L. J., Metabolism, 9, 85 (1960).
Futterweit, W., Margolis, S. A., Soffer, L. J., and Dorfman, R. I., Endocrinology, 72, 903 (1963).
Amir, S. M., Barker, S. A., Butt, W. R., and Crooke, A. C., Nature, 211, 975 (1966).
Hipkin, L. J., Acta Endocrinol., 59, 417 (1968).
Ota, M., Dronkert, A., and Gates, A. H., Metabolism, 17, 181 (1968).
Loraine, J., and Brown, J. B., J. Endocrinol., 18, 77 (1959).
Brown, P. S., J. Endocrinol., 13, 59 (1955).
Johnsen, S. G., Acta Endocrinol., 28, 69 (1958).
Klastersky, J., and Herlant, M., Ann. Endocrinol., 28, 127 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HIPKIN, L. Effect of the Urinary Gonadotrophin Inhibitor on Endogenous and Exogenous Gonadotrophin. Nature 221, 473–474 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1038/221473a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/221473a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.