Abstract
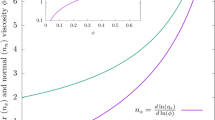
THE observation of Mieras and Van Rijn1 that the steady shear flow compliance of polymer melts is dependent only on the width of the molecular weight distribution, characterized by M̄z/M̄w, is in accord with our similar measurements on polydimethylsiloxane melts. The shear stress p12 and first normal stress difference p11–p22 were measured with a Weissenberg cone and plate viscometer as a function of shear rate ɣ̇ for fractions and blends of polydimethylsiloxane. (With the usual convention 1 is the flow direction, and 2 is normal to the measuring surface.) The Newtonian viscosity η and the limiting value of the normal stress coefficient θ (defined by p11–p22/ɣ̇2) were found, for molecular weights greater than the “entanglement” molecular weight Me (55,000), to vary according to the equations  where G and L are constants. The steady shear compliance J was therefore given by
where G and L are constants. The steady shear compliance J was therefore given by  The experimental values of J are shown in Fig. 1, together with data from the tensile stress relaxation of anionically polymerized polystyrenes2,3. There are different constants G for the two polymers, and the values of G correlate well with the shear modulus of a rubber network with a molecular weight between cross-links equal to Me
The experimental values of J are shown in Fig. 1, together with data from the tensile stress relaxation of anionically polymerized polystyrenes2,3. There are different constants G for the two polymers, and the values of G correlate well with the shear modulus of a rubber network with a molecular weight between cross-links equal to Me where ρ is the polymer density, R the gas constant and T the absolute temperature.
where ρ is the polymer density, R the gas constant and T the absolute temperature.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mieras, H. J. M. A., and Van Rijn, C. F. H., Nature, 218, 865 (1968).
Akovaldi, G., J. Polymer Sci., A-2, 5, 875 (1967).
Ueno, T., and Murakami, K., J. Soc. Mat. Sci., Japan, 16, 498 (1967).
Rouse, P. E., J. Chem. Phys., 21, 1272 (1953).
Bueche, F., J. Chem. Phys., 22, 603 (1954).
Lodge, A. S., Elastic Liquids (Academic Press, London, 1964).
Ferry, J. D., Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers (Wiley, New York, 1961).
Porter, R. S., and Johnson, J. F., Chem. Rev., 66, 1 (1966).
Mills, N. J., Rheol. Acta (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MILLS, N. Elasticity of Polydimethylsiloxane Melts. Nature 219, 1249–1250 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/2191249a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2191249a0
This article is cited by
-
Optimum processing conditions for the maximum crystallization rate of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Viscoelastic properties of copolycarbonates comprising isosorbide and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol
Colloid and Polymer Science (2023)
-
Rheology of Ziegler–Natta and metallocene high-density polyethylenes: broad molecular weight distribution effects
Rheologica Acta (2011)
-
Rubber elasticity and viscoelasticity of polymer melts and solutions in shear flow
Polymer Mechanics (1976)
-
The measurement of constrained elastic recovery in polymeric solutions
Rheologica Acta (1970)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.