Abstract
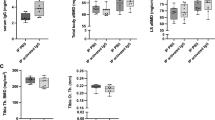
THE 19S alpha-2 globulin isolated by us from the alpha-2 globulin fraction of human serum (obtained from Mann Res. Lab., New York) by the procedure of Schonenberger et al.1 and identified by electrophoresis on poly aery lamide gel2 and ultracentrifugation was found to stimulate the regeneration of bone marrow cells in X-irradiated mice (C57Bl/6). A sample (0.5 mg) of the 19S alpha-2 globulin injected intraperitoneally into 33–35 day old mice within an hour of exposure to 170 r. produced a significant speeding up in the incorporation of 3H-thymidine into bone marrow cells, as compared with that in irradiated animals injected with saline (Fig. 1). Seven days after irradiation 19S alpha-2 globulin-injected animals showed an actual overshoot in number of cells of femoral and tibial bone marrow (55 × 106/mouse), as compared with unirradiated controls (42 × 106/mouse) and irradiated but saline-injected controls (41 × 106/mouse), respectively. The total DNA content of bone marrow cells at this stage showed a similar picture, the femoral and tibial bone marrow cells of mice injected with 19S alpha-2 globulin containing 527 µg of DNA, while the irradiated (saline-injected) controls contained 410 µg and the non-irradiated controls contained 414 µg of DNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schönenberger, M., Schmidtberger, R., and Schultze, H. E., Z. Natur forschung, 13 B, 761 (1958).
Davis, B. J., Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 121, 404 (1964).
Trainin, N., Burger, M., and Kaye, A. M., Biochem. Pharmacol., 16, 711 (1967).
Cividalli, G., and Knyszynski, A., Radiat. Res., 30, 148 (1967).
Berenblum, I., Cividalli, G., and Hodes, M. E., Nature, 202, 973 (1964).
Berenblum, I., Cividalli, G., and Hodes, M. E., Blood, 26, 8 (1965).
Berenblum, I., Trainin, N., Cividalli, G., Boiato-Chen, L., and Knyszynski, A., Tumori, 53, 5 (1967).
Berenblum, I., Burger, M., Cividalli, G., Knyszynski, A., and Trainin, N., Abstr. Proc. Symp. on Perspectives in Leukemia, New Orleans, Louisiana, December 1966 (in the press).
Hanna, jun., M. G., Nettesheim, P., Fisher, W. D., Peters, L. C., and Francis, M. W., Science, 157, 1458 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BERENBLUM, I., BURGER, M. & KNYSZYNSKI, A. Regeneration of Bone Marrow Cells and Thymus induced by 19S Alpha-2 Globulin in Irradiated Mice. Nature 217, 857–858 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/217857a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/217857a0
This article is cited by
-
Effect of neutral proteases from human granulocytes on colony forming cells in vitro
Blut (1978)
-
The values of alpha 2-macroglobulin in the serum of persons at work with X-rays
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics (1977)
-
The inhibitory effect of α-2-macroglobulin on tumour growth
Experientia (1973)
-
Phythämagglutinin (PHA) und Serumproteine in der Lymphocytenkultur
Zeitschrift für Die Gesamte Experimentelle Medizin einschließlich experimentelle Chirurgie (1970)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.