Abstract
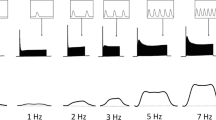
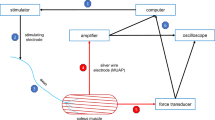
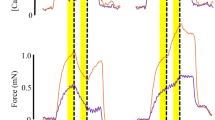
THE influence of temperature on isometric contractions of rat skeletal muscles in vitro has been determined for fast extensor digitorum longus muscles (EDL) and slow soleus muscles (SOL) from 4 week old female Wistar rats. Isometric contractions were recorded with the long axis of the muscle vertical, with one tendon tied to the frame below and the other tendon tied to a short steel wire connexion which linked it with the tension transducer above. The compliance of the transducer (Statham, Gl-80-350) and the steel wire connexion to the muscle was 4.5 × 10−5 cm/g and the natural frequency of vibration was 2 kHz. The muscle was immersed in about 100 ml. of fluid (137 mM Nacl; 5 mM KCl; 2 mM CaCl2; 1 mM MgCl2; 1 mM NaH2PO4; 2 g/l. of NaHCO3 and 2 g/l. of glucose) which was bubbled continuously with 95 per cent O2 and 5 per cent CO2. Neuromuscular transmission was blocked by adding 2.0 × 10−5 g of tubocurarine chloride/ml. of bath fluid. The muscles were stimulated directly by a transverse electrical field of 15 V/cm for 0.2 or 0.3 ms applied to the bath fluid by “massive” bright platinum electrodes set about 1 cm apart1. All recordings were made with the muscle set at the optimal length determined for twitch contractions at 20° C.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gutmann, E., and Sandow, A., Life Sci., 4, 1149 (1965).
Truong, X. T., Wall, B. J., and Walker, S. M., Amer. J. Physiol., 207, 393 (1964).
Hill, A. V., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 138, 349 (1951).
Close, R., J. Physiol., 180, 542 (1965).
Brown, G. L., and von Euler, U. S., J. Physiol., 93, 39 (1938).
Ramsey, R. W., and Street, S. F., Biol. Symp., 3, 9 (1941).
Colomo, F., and Rocchi, P., Arch. Fisiol., 64, 189 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CLOSE, R., HOH, J. Influence of Temperature on Isometric Contractions of Rat Skeletal Muscles. Nature 217, 1179–1180 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/2171179a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2171179a0
This article is cited by
-
Potential role of passively increased muscle temperature on contractile function
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2022)
-
High-performance phosphorene electromechanical actuators
npj Computational Materials (2020)
-
Hot ambient conditions shift the Force / EMG relationship
SpringerPlus (2013)
-
Myosin phosphorylation and force potentiation in skeletal muscle: evidence from animal models
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (2013)
-
Effects of hydrostatic pressure on fatiguing frog muscle fibres
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.