Abstract
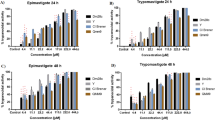
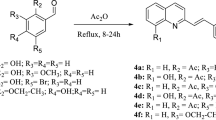
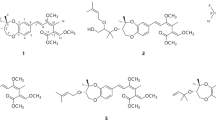
SINCE Babès in 1885 claimed the complete inhibition of cholera vibrio by an old culture of Micrococcus prodigiosus there have been numerous descriptions1–3 of antibiotic properties associated with the bacterium Chromobacterium prodigiosum (Serratia marcescens) and the bipyrrolylpyrrolylmethene prodigiosin (I), which occurs in the red bacterial pigment. The purity of the metabolite4,5 used in the earlier investigations is suspect and the earlier claims like those for the bacterium lack definition of the true causative factor. In this regard the prodigiosin used has been considered too toxic for therapeutic use, although it has evidently been used in the clinical treatment of some cases of disseminated coccidioidomycosis (San Joaquin Valley fever)6. Goble and Boyd7 examined a number of porphyrins, bilirubinoids, pyrroles and congeners against Trypanosoma congolese in mice and found chlorophyllins, containing either magnesium or copper, and haematoporphyrin to be effective in delaying death and curative with prolonged treatment. We have investigated the antimalarial properties of purified prodigiosin (I), the cyclotetradepsipeptide serratamolide (II)4,8,9, an ethyl alcoholic extract of Serratia marcescens (III) from which I, II and other metabolites can be derived4, and two dipyrrolylmethenes (IV a and b) against Plasmodium berghei in mice. Prodigiosin showed definite activity (Table 1) against the parasite, which took about twice as long to kill the mice as compared with untreated infections, whereas the other materials exhibited only weak activity at the same or comparable concentrations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Florey, H. W., et al., Antibiotics, 1, 558 (Oxford University Press, London,1949).
Burger, A., et al., Medicinal Chemistry, 857, 949, 1013 (Interscience Publishers, Inc. New York, second edition, 1960).
Castro, A. J., Gale, G. R., Means, G. E., and Tertzakian, G., J. Med. Chem., 10, 29 (1967).
Castro, A. J., Corwin, A. H., Waxham, F. J., and Beilby, A. L., J. Org.Chem., 24, 455 (1959).
Castro, A. J., Deck, J. F., Hugo, M. T., Lowe, E. J., Marsh, jun, J. P., and Pfeiffer, R. J., J. Org. Chem., 28, 857 (1963).
Weir, R. H., Egeberg, R. O., Lack, A. R., and Leiby, G. M., Amer. J. Med. Sci., 224, 70 (1952).
Goble, F. C., and Boyd, J. L., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 100, 745 (1959).
Wasserman, H. H., Keggi, J. J., and MeKeon, J. E., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 84, 2978 (1962).
Shemyakin, M. M., Ovchinnikov, Y. A., Antonov, V. K., Kiryushkin, A. A., Ivanov, V. T., Shchelokov, V. I., and Shkroh, A. M., Tetrahedron Lett., 47 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CASTRO, A. Antimalarial Activity of Prodigiosin. Nature 213, 903–904 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/213903a0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/213903a0
This article is cited by
-
The Golgi stacking protein GRASP55 is targeted by the natural compound prodigiosin
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Prodigiosin inhibits cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via suppressing SNAREs-dependent autophagy
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
Biovalorization of agro-industrial waste soybean meal for the production of prodigiosin by Serratia marcescens
Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery (2021)
-
Production of prodigiosin by a drug-resistant Serratia rubidaea HB01 isolated from sewage
Environmental Sustainability (2020)
-
Recent advancements in high-level synthesis of the promising clinical drug, prodigiosin
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.