Abstract
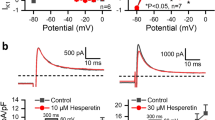
THE action potential of cardiac fibres differs from that of most other cell types: the fast rising phase is followed by a plateau lasting a few 100 msec. The results of voltage clamp analysis in Purkinje fibres1 show that a depolarizing voltage step elicits a large sodium current, which has a slow component which declines for several hundred milliseconds. The potassium current falls after depolarization with a similar time constant. The slow decline of both currents can explain the plateau of the cardiac action potential. The sodium current was identified by comparing the membrane currents in Tyrode solution with those in a sodium-free solution1. An independent check of this procedure would be useful; we therefore investigated the effect of tetrodotoxin (TTX) on short Purkinje fibres of sheep. TTX at concentrations of 10−8 to 10−7 g/ml. is known to block selectively the excitatory inward sodium current in invertebrate axons2,3. We recorded membrane potentials in fourteen preparations and passed current through a second intracellular glass microelectrode. Details of the preparation and of the electronic apparatus are given elsewhere4.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deck, K. A., and Trautwein, W., Pflügers Arch. Ges. Physiol., 280, 63 (1964).
Nakamura, Y., Nakajima, S., and Grundfest, H., J. Gen. Physiol., 48, 985 (1965).
Narahashi, T., Moore, J. W., and Scott, D. R., J. Gen. Physiol., 47, 965 (1964).
Trautwein, W., Dudel, J., and Peper, K., J. Cell. Comp. Physiol., 66, Suppl. 2, 79 (1965).
Weidmann, S., J. Physiol. (Lond.), 127, 213 (1955).
Hagiwara, S., and Nakajima, S., Science, 149, 1254 (1965).
Dudel, J., Peper, K., and Trautwein, W., Pflügers Arch. Ges. Physiol., 288, 262 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DUDEL, J., PEPER, K., RÜDEL, R. et al. Effect of Tetrodotoxin on Membrane Currents in Mammalian Cardiac Fibres. Nature 213, 296–297 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/213296a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/213296a0
This article is cited by
-
Field-stimulus response of guinea-pig atria as influenced by the peptides angiotensin, bradykinin, and substance P
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (1980)
-
Action of Iontophoretically Applied Tetrodotoxin on Cortical Nerve Cells
Nature (1968)
-
Effects of Droperidol on sheep Purkinje fibers
Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archiv f�r Pharmakologie und Experimentelle Pathologie (1968)
-
Comparison between Tetrodotoxin Effects on Excitation in Mammalian Cardiac Fibres and Squid Giant Axons
Nature (1967)
-
The effect of tetrodotoxin on the membrane current in cardiac muscle (Purkinje fibers)
Pflügers Archiv für die Gesamte Physiologie des Menschen und der Tiere (1967)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.