Abstract
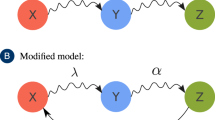
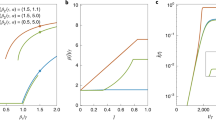
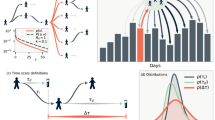
Goffman and Newill1 have directed attention to the analogy between the spreading of an infectious disease and the dissemination of information. We have recently examined the spreading of a rumour from the point of view of mathematical epidemiology and wish to report very briefly here on work to be published in detail elsewhere2. In particular, we must emphasize that a mathematical model for the spreading of rumours can be constructed in a number of different ways, depending on the mechanism postulated to describe the growth and decay of the actual spreading process. In all these models the mathematical techniques familiar in mathematical epidemiology can be applied, but even the qualitative results so obtained need not necessarily be as expected on the basis of the formal analogy with epidemics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Goffman, W., and Newill, V. A., Nature, 204, 225 (1964).
Daley, D. J., and Kendall, D. G. (unpublished).
Bailey, N. T. J., The Mathematical Theory of Epidemics (Griffin, 1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DALEY, D., KENDALL, D. Epidemics and Rumours. Nature 204, 1118 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1038/2041118a0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2041118a0
This article is cited by
-
Gender-specific homophily on Instagram and implications on information spread
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Rumor spreading model with a focus on educational impact and optimal control
Nonlinear Dynamics (2024)
-
On a Rumor Propagation Model with Spatial Heterogeneity
Qualitative Theory of Dynamical Systems (2024)
-
Mathematical modeling of disinformation and effectiveness of mitigation policies
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Dynamic analysis of rumor propagation model with media report and time delay on social networks
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computing (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.