Abstract
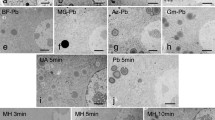
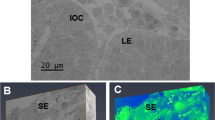
IT was recently reported1 that collagen fibrils appeared tubular in electron micrographs of ‘Epon’ sections stained with Karnovsky's2 alkaline lead hydroxide solution, and it was speculated that mucopolysaccharide might be present within the fibrils. The colloidal iron method for demonstrating acid mucopolysaccharides3,4 has been adapted for the electron microscope5,6, and although it confirms that acid mucopolysaccharide is present in the ground-substance coating the fibril (Fig. 1) it provides no evidence for the presence of mucopolysaccharides within the fibril. It seems that two factors, which may be interrelated, contribute to the tubular appearance of the fibrils: (1) ‘Epon’ penetrates collagen fibrils poorly and sometimes not at all; (2) the lead hydroxide solution tends to have a stronger affinity for ground-substance than for collagen fibrils (Figs. 1 and 2). Nevertheless, longitudinal sections still show the characteristic banding of collagen (Fig. 3), which means that the ground-substance coating each fibril is acting like a stained replica of the fibril's surface. This affinity of lead for ground-substance is found after fixation in osmium-sucrose solution, formalin, glutar-aldehyde and Luft's solution. Oddly enough, it can be influenced by the process of section-cutting, and wherever the ‘Epon’ has been compressed during cutting there are occasional areas in which the image is reversed, with dark-stained collagen fibres and pale ground-substance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curran, R. C., and Clark, A. E., Nature, 198, 798 (1963).
Karnovsky, M. J., J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol., 11, 729 (1961).
Hale, C. W., Nature, 157, 802 (1946).
Mowry, R. W., Lab. Invest., 7, 566 (1958).
Curran, R. C., and Clark, A. E., Biochem. Soc. Proc., 90, 2, p (1964).
Curran, R. C., and Clark, A. E., J. Cell Biol. (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CLARK, A., CURRAN, R. Staining Reactions of Collagen in ‘Epon’ Sections. Nature 202, 912–913 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1038/202912a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/202912a0
This article is cited by
-
Hepatic fibrosis—a study on hepatic collagen and acid mucopolysaccharide
Gastroenterologia Japonica (1970)
-
Zur Verteilung Hale-reaktiver Substanzen im Bindegewebe normaler menschlicher Haut
Archiv f�r Klinische und Experimentelle Dermatologie (1965)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.