Abstract
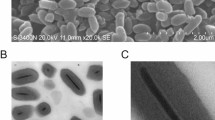
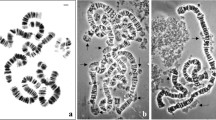
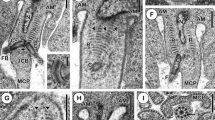
THERE have been conflicting reports in the literature about the chemical nature and origin of chromatoid and related bodies found in the cytoplasm of certain protozoa1–8 and in the spermatogenic cells of certain crustaceans9, insects10–11, cyclostomes9, reptiles12, birds9, and mammals13–15. Of special importance is the recent work of Barker1,16. This investigator has shown in his cytochemi-cal and electron microscope studies that chromatoid bodies in Entamoeba invadens, a parasite of snakes, are composed of ribonucleic acid and protein and that chromatoid bodies arise by a process of aggregation tof small groups of 250–300 Å units which form polycrystalline masses in precysts and early cysts. The purposes of this report are to show: (A) that the chromatoid bodies are also found in axenically grown trophozoites, where there is no cyst formation, and (B) that the ribonucleoproteins within the chromatoid bodies are arranged in a helical pattern.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker, D. C., Z. Zellforschung, 58, 641 (1963).
MacLennan, R. F., in Protozoa in Biological Research, edit. by Calkins, G. N., and Summers, F. M., 111 (Columbia Univ. Press, New York, 1941).
Hartmann, M., Arch. Protistenk., 24, 163 (1912).
Hertwig, R., Arch. Protistenk., 1, 1 (1902).
James, W. M., Ann. Trap. Med. Parasit., 8, 133 (1914).
Meyers, A., Bot. Ztg., 62, 113 (1904).
Minchin, E. A., Quart. J. Micro. Sci., 53, 755 (1909).
Schaudinn, F., Arb. Gesundh. Amte (Berlin), 19, 547 (1903).
Wilson, E. B., The Cell in Development and Heredity, third ed. (Macmillan Co., New York, 1925).
Plough, H. H., Biol. Bull., 32, 1 (1917).
Wilson, E. B., Biol. Bull., 24, 392 (1913).
Sud, B. N., Quart. J. Micro. Sci., 102, 273 (1961).
Moore, J. E. S., Anat. Anz. (Jena), 8, 683 (1893).
Niessing, G., Arch. Mikr. Anat., 48, 111 (1897).
Regaud, C., Arch. Anat. Micro., 4, 101 (1901).
Barker, D. C., Proc. Fifth Intern. Cong. Electron Microscopy, Philadelphia, UU-9 (1962).
Diamond, L. S., J. Parasitol., 46, 484 (1960).
Kushida, H., J. Electron Micro., 10, 194 (1961).
Karnovsky, M. J., J.B.B.C., 11, 729 (1961).
Watson, J. D., and Crick, F. H. C., Nature, 171, 737 (1953).
Davies, D. R., Nature, 186, 1030 (1960).
Spencer, M., Fuller, W., Wilkins, M. H. F., and Brown, G. L., Nature, 194, 1014 (1962).
Brown, G. L., and Zubay, G., J. Mol. Biol., 2, 287 (1960).
Fuller, W., J. Mol. Biol., 3, 175 (1961).
Langridge, R., Science, 140, 1000 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SIDDIQUI, W., RUDZINSKA, M. A Helical Structure in Ribonucleoprotein Bodies of Entamoeba invadens. Nature 200, 74–75 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/200074a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/200074a0
This article is cited by
-
Submicrosocpic structure of the chromatoid body of Entamoeba invadens and Entamoeba moshkovskii
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (1967)
-
�ber Kontakt und Verzweigung der Protein-Schrauben
�sterreichische Botanische Zeitschrift (1965)
-
�ber die Modifikationen der Schraubenrotation im Protoplasma
�sterreichische Botanische Zeitschrift (1964)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.