Abstract
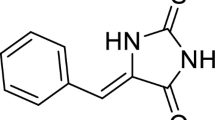
IN a long series of aminoazobenzene derivatives tested for hepatocarcinogenicity in the rat only those compounds with at least one N-methyl group are markedly active1. The hypothesis has been advanced that the actual carcinogen is a derivative of the parent dye and that its production may be hindered or enhanced under different dietary conditions, or in different species. The N-methyl group is thought to undergo stepwise oxidation in the liver to formaldehyde, the first product being an N-methylol derivative, hydroxymethylaminoazobenzene (I) in the case of methylaminoazobenzene2. Such compounds are reactive species and are capable of alkylating thiol groups, amino-groups, phenolic residues and so on by a Mannich condensation. It has been suggested that reactions of this type account to some extent for the formation of protein bound dye in vivo in the case of dimethylaminoazobenzene (butter yellow) and certain of its derivatives1,3,4. In view of the importance of DNA and RNA in cellular metabolism, an investigation has been carried out to determine whether such methylol derivatives are capable of reacting with nucleic acids in vitro.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller, J. A., and Miller, E. C., Advances in Cancer Research, 1, 339 (Academic Press, New York, 1953).
Mueller, G. C., and Miller, J. A., Cancer Res., 11, 271 (1951).
Terayama, H., Kusama, K., and Aoki, T., Gann, 49, 97 (1958).
Miller, E. C., and Miller, J. A., Cancer Res., 12, 547 (1952).
Berenbom, M., Cancer Res., 19, 1045 (1959).
Magee, P. N., and Farber, E., Biochem. J., 83, 114 (1962).
Culvenor, C. C. J., Dann, A. T., and Dick, A. T., Nature, 195, 570 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ROBERTS, J., WARWICK, G. Azo Dye Liver Carcinogenesis: Reaction of Hydroxymethylaminoazobenzene with Nucleic Acids in vitro. Nature 197, 87–88 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/197087a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/197087a0
This article is cited by
-
Organotrope carcinogene Wirkungen bei 65 verschiedenen N-Nitroso-Verbindungen an BD-Ratten
Zeitschrift f�r Krebsforschung (1967)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.