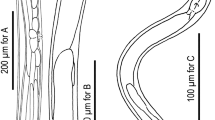
Abstract
SINCE the description of Rhopalomyces elegans by Corda1, numerous investigators have unsuccessfully attempted to germinate its spores and to grow it in pure culture. As a consequence, the systematic position of this fungus has been in doubt, and the repeated suggestion that R. elegans is parasitic on nematodes or their eggs could not be proved. Martin2 has published a useful summary. Based on studies of material found on various substrata, Boedijn3 recently erected the family Helicocephalidaceae to include this fungus in the Mucorales. Rhopalomyces minor, a new species reported by Windisch4, is not considered by us to be a member of the genus sensu Corda, because R. minor has regularly septate mycelia and conidiophores. He is, therefore, not the first to have a member of this genus in pure culture for study.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corda, A. C. J., Prachtflora, 3, pl. 2 (1839).
Martin, G. W., Proc. Iowa Acad. Sci., 67, 139 (1960).
Boedijn, K. B., Sydowia Ann. Mycolo., Ser. II, 12, 321 (1958).
Windisch, S., Zentr. Bakteriol. Parasitenk., II, Abt., 113, 679 (1960).
Ling-Young, M., Rev. Gén. Botan., 42, 551 (1930).
Lendner, A., Bull. Soc. Botan. Genève, 13, 8 (1921).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ELLIS, J., HESSELTINE, C. Rhopalomyces and Spinellus in Pure Culture and the Parasitism of Rhopalomyces on Nematode Eggs. Nature 193, 699–700 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/193699a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/193699a0
This article is cited by
-
Early-diverging fungal phyla: taxonomy, species concept, ecology, distribution, anthropogenic impact, and novel phylogenetic proposals
Fungal Diversity (2021)
-
Spinellus in Pure Culture
Nature (1963)
-
Culture of Spinellus
Nature (1962)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.