Abstract
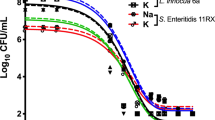
IT has been shown1 that suspensions of Escherichia coli which had been treated with phenol gave lower counts on membrane filters than on the surface of nutrient agar. Many workers2 have observed that bacteria which have been exposed to bactericides or heat exhibit a marked sensitivity to the nature of the subculture medium, and both Flett et al.2 and Jacobs and Harris3 have shown that when ferric chloride was added to the medium it exerted a beneficial effect, demonstrated by longer extinction times than in control media, on the growth of phenol-treated organisms. The latter workers found that the rate and extent of the death of phenol-treated cells of E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus which occurred in nutrient broth4 was reduced by the inclusion of 5 × 10−3M of magnesium chloride, and that the inclusion of ferric chloride and other metal chlorides in nutrient agar gave surface-viable counts of such cells greater than were obtained on nutrient agar without metals5. In view of the present widespread use of membrane filters, and suggestions that these filters should be used to recover damaged cells from a variety of harmful environments, for example, in sterility tests, it was thought useful to examine the effect of adding salts to the nutrient broth on which the membranes are incubated.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris, N. D., and Richards, J. P., J. App. Bact., 21, 86 (1958).
Curran, H. R., and Evans, F. R., J. Bact., 34, 179 (1937). Nelson, F. E., ibid., 45, 395 (1943). Flett, L. H., et al., ibid., 50, 591 (1945). Jacobs, S. E., and Harris, N. D., Congr. Intern. Microbiol., Rome, 1, 603 (1953).
Jacobs, S. E., and Harris, N. D., J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 6, 877 (1954).
Jacobs, S. E., and Harris, N. D., J. App. Bact., 23, 294 (1960).
Harris, N. D., and Jacobs, S. E., J. App. Bact., 23, (3), viii (1960). Richards, J. P., thesis (London, 1959).
Gale, E. F., and Taylor, E. S., J. Gen. Microbiol., 1, 77 (1947). Bean, H. S., and Walters, V., J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 7, 661 (1955). Beckett, A. H., Patki, S. J., and Robinson, A. E., Nature, 181, 712 (1958).
Haydon, D. A., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 145, 383 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HARRIS, N., RICHARDS, J. Influence of adding Salts to the Medium on Counts of Phenol-treated Escherichia coli on Membrane Filters. Nature 192, 87–88 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1038/192087a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/192087a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.