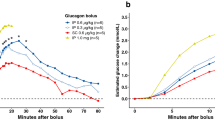
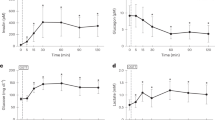
Abstract
IN earlier work the effect of a prolonged intravenous infusion of insulin on the utilization and production of circulating glucose was investigated in the trained, unanæsthetized normal dog in the post-absorptive state with the aid of intravenously administered 14C-glucose1. The plasma glucose concentration and specific activity were determined at frequent intervals, and from these values were calculated the rates of production of hepatic 12C -glucose and total glucose-uptake by the tissues2. It was shown that insulin brought about a hypoglycæmia primarily by increasing the uptake of glucose by the tissues. The rate of production of hepatic 12C-glucose, although temporarily somewhat reduced soon after the insulin infusion was begun, usually rose during the course of the infusion to higher than normal levels, but not sufficiently to restore the plasma glucose concentration to its pre-insulin level. When the insulin infusion was stopped, there was a marked further increase in the production of hepatic 12C-glucose which restored the plasma glucose concentration to its control-level. From these findings it was concluded that, during the period of insulin infusion, the production of 12C-glucose was restrained in spite of severe hypoglycæmia1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Bodo, R. C., Steele, R., Altszuler, N., Dunn, A., Armstrong, D. T., and Bishop, J. S., Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 82, 431 (1959).
Steele, R., Wall, J. S., de Bodo, R. C., and Altszuler, N., Amer. J. Physiol., 187, 15 (1956).
Dunn, A., Steele, R., Altszuler, N., Armstrong, D. T., Bishop, J. S., and de Bodo, R. C., Fed. Proc., 19, 163 (1960).
Cori, C. F., Physiol. Reviews, 11, 143 (1931).
Leloir, L. F., and Goldemberg, S. H., J. Biol. Chem., 235, 919 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DUNN, A., de BODO, R., STEELE, R. et al. An Effect of Insulin on Production of Glucose during Hepatic Glycogenolysis. Nature 188, 236–237 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1038/188236a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/188236a0
This article is cited by
-
The influences of insulin on the hepatic metabolism of glucose
Ergebnisse der Physiologie Biologischen Chemie und Experimentellen Pharmakologie (1966)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.