Abstract
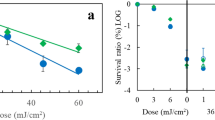
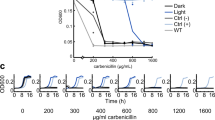
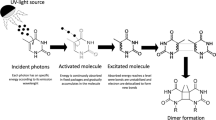
WE suggested recently that nucleic acid precursors, altered in vivo by ultra-violet light, are involved as chemical intermediates in the induction of mutation1. We have since reported that, in the absence of an adequate source of nitrogen, an immediate and rapid decline in the frequency of mutations induced by ultra-violet light occurs (‘mutation frequency decline’)2. We demonstrated that the prevention of this decline depends on the availability immediately following exposure to radiation of a supply of amino-acids, and suggested that the amino-acids are involved in a process of temporary ‘stabilization’ of the ‘potential mutation’ (the modified purine or pyrimidine) in the cell prior to its effect in the induction of mutation (‘mutation stabilization’)2. The potential mutation is ultimately ‘fixed’ into the cell and is no longer subject to those conditions which previously resulted in decline in mutation frequency (‘mutation fixation’)2. Recently we have reported that the progression of ‘mutation fixation’ is closely correlated with the synthesis of ribonucleic acid in the culture, and suggested that the initial mutagenic event involves the incorporation of the modified nucleic acid precursor into ribonucleic acid3. We wish to report here experiments which determine the effect of certain purine and pyrimidine analogues on reversion induced by ultra-violet light in an auxotrophic strain of Escherichia coli.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haas, F. L., and Doudney, C. O., Proc. U.S. Nat. Acad. Sci., 45, 871 (1957).
Doudney, C. O., and Haas, F. L., Proc. U.S. Nat. Acad. Sci., 44, 390 (1958).
Doudney, C. O., and Haas, F. L., J. Mol. Biol. (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DOUDNEY, C., HAAS, F. Effect of Purine and Pyrimidine Analogues on Reversion of a Tryptophan-requiring Strain of Escherichia coli . Nature 184, 114–115 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1038/184114a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/184114a0
This article is cited by
-
Does caffeine induce dominant lethal mutations in mice?
Human Genetics (1969)
-
Enhancement of ultraviolet-induced mutation in bacteria by caffeine
Zeitschrift f�r Vererbungslehre (1961)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.