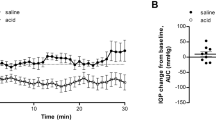
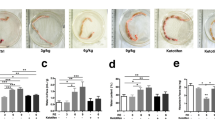
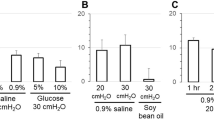
Abstract
WHEN an aqueous solution of either iodoacetamide or N-ethyl maleimide, in suitable concentration, is applied topically to the mucosa of a canine Heiden-hain pouch half an hour before the injection of hist-amine, the hydrochloric acid secretory activity of the pouch is inhibited completely, though reversibly1. This inhibitory action may be presumed to involve a competitive inhibition of one or more enzymes within the parietal cells, though Davenport's assumption2 that these enzymes contain sulphydryl still awaits confirmation. Instead of the water-like solution of hydrochloric acid ordinarily obtained in response to histamine stimulation, the pouch now pours out a mucinous cell-free liquid of pH greater than 7, and sometimes even as high as 8. Flow of this viscous liquid continues for many hours after drainage of the iodoacetamide or N-ethyl maleimide solution from the pouch, whereas the acid-secretory response to subcutaneously administered histamine usually lasts for no more than 1–1½hr. Further evidence that this mucinous material bears no relation to the parietal secretion is given by the fact that the same response is obtained when the instillation of iodoacetamide or N-ethyl maleimide into the pouch is not followed by the subcutaneous administration of histamine.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hollander, F., Amer. J. Physiol., 187, 231 (1956).
Davenport, H. W., Chavre, V. J., and Davenport, V. D., Amer. J. Physiol., 182, 221 (1954).
Janowitz, H. D., Hollander, F., and Jackson, C., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 76, 578 (1951).
Hollander, F., and Lauber, F. U., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 67, 34 (1948).
Hollander, F., Gastroenterology, 20, 512 (1952).
Hollander, F., Lauber, F. U., and Stein, J., Amer. J. Physiol., 149, 724 (1947).
Janowitz, H. D., and Hollander, F., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 95, 320 (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HOLLANDER, F. ‘Gastric Para-Mucus’. Nature 181, 847–848 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1038/181847b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/181847b0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.