Abstract
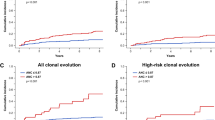
To identify a correlation between metaphase cytogenetics and relapse after reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) allotransplant for patients with multiple myeloma, data on 60 patients (median age 52) who received grafts from a sibling (n=49) or unrelated donor (n=11) were analyzed. Fifty-three patients (88%) showed chromosomal abnormalities (CA) before the allotransplant, including 42 with abnormalities involving 13q (CA13). Twenty-two patients (41%) relapsed post-allotransplant at a median of 165 days. Of these, 11 patients showed abnormal cytogenetics at the time of post-allotransplant relapse at a median of 167 days. Of 54 patients who developed graft-versus-host disease, relapse occurred in 19 of 48 patients (43%) with CA present before RCI allotransplant, versus 1 of 6 without CA (17%) (P=0.06). Loss of CA before RIC allotransplant and disease status>PR after RIC allotransplant were significantly associated with a lower risk of post-allotransplant relapse with cytogenetic abnormalities; 5.2 vs 36%, and 18 vs 53%, (both P<0.05), respectively. The current data suggests that myeloma associated with persistent clonal cytogenetic abnormalities is an entity which most likely escapes the effects of a graft versus myeloma activity, maybe because of acquisition of resistance to immunologic manipulations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bensinger W, Maloney D, Storb R . Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. Semin Hematol 2001; 38: 243–249.
Barlogie B, Shaughnessy J, Tricot G, Jacobson J, Zangari M, Anaissie E et al. Treatment of multiple myeloma. Blood 2004; 103: 20–32.
Gahrton G, Svensson H, Cavo M, Apperly J, Bacigalupo A, Bjorkstrand B et al. Progress in allogenic bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma: a comparison between transplants performed 1983–93 and 1994–8 at European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation centres. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: 209–216.
Crawley C, Lalancette M, Szydlo R, Gilleece M, Peggs K, Mackinnon S et al. Outcomes for reduced intensity allogeneic transplantation for multiple myeloma: an analysis of prognostic factors from the chronic leukemia working party of the EBMT. Blood 2005; 105: 4532–4539.
Kroger N, Perez-Simon JA, Myint H, Klingemann H, Shimoni A, Nagler A et al. Relapse to prior autograft and chronic graft-versus-host disease are the strongest prognostic factors for outcome of melphalan/fludarabine-based dose-reduced allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2004; 10: 698–708.
Lee CK, Badros A, Barlogie B, Morris C, Zangari M, Fassas A et al. Prognostic factors in allogeneic transplantation for patients with high-risk multiple myeloma after reduced intensity conditioning. Exp Hematol 2003; 31: 73–80.
Kroger N, Sayer HG, Schwerdtfeger R, Kiehl M, Nagler A, Renges H et al. Unrelated stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma after a reduced-intensity conditioning with pretransplantation antithymocyte globulin is highly effective with low transplantation-related mortality. Blood 2002; 100: 3919–3924.
Attal M, Harousseau JL, Facon T, Guilhot F, Doyen C, Fuzibet JG et al. Single versus double autologous stem-cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 2495–2502.
Shaughnessy J, Jacobson J, Sawyer J, McCoy J, Fassas A, Zhan F et al. Continuous absence of metaphase-defined cytogenetic abnormalities, especially of chromosome 13 and hypodiploidy, ensures long-term survival in multiple myeloma treated with Total Therapy I: interpretation in the context of global gene expression. Blood 2003; 101: 3849–3856.
Barlogie B, Jagannath S, Desikan KR, Mattox S, Vesole D, Siegel D et al. Total therapy with tandem transplants for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood 1999; 93: 55–65.
Badros A, Barlogie B, Siegel E, Cottler-Fox M, Zangari M, Fassas A et al. Improved outcome of allogeneic transplantation in high-risk multiple myeloma patients after nonmyeloablative conditioning. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 1295–1303.
Sawyer JR, Lukacs JL, Munshi N, Desikan KR, Singhal S, Mehta J et al. Identification of new nonrandom translocations in multiple myeloma with multicolor spectral karyotyping. Blood 1998; 92: 4269–4278.
Gooley TA, Leisenring W, Crowley J, Storer BE . Estimation of failure probabilities in the presence of competing risks: new representations of old estimators. Stat Med 1999; 18: 695–706.
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observation. JASA 1958; 53: 457–481.
Collett D . Modeling Survival Data in Medical Research. Chapman and Hall: London, 1994.
Lokhorst HM, Wu K, Verdonck LF, Laterveer LL, van de Donk NW, van Oers MH, et al. The occurrence of graft-versus-host disease is the major predictive factor for response to donor lymphocyte infusions in multiple myeloma. Blood 2004; 103: 4362–4364.
Alyea E, Weller E, Schlossman R, Canning C, Webb I, Doss D et al. T-cell–depleted allogeneic bone marrow transplantation followed by donor lymphocyte infusion in patients with multiple myeloma: induction of graft-versus-myeloma effect. Blood 2001; 98: 934–939.
Schmaltz C, Alpdogan O, Kappel BJ, Muriglan SJ, Rotolo JA, Ongchin J et al. T cells require TRAIL for optimal graft-versus-tumor activity. Nat Med 2002; 8: 1433–1437.
Schmaltz C, Alpdogan O, Horndasch KJ, Muriglan SJ, Kappel BJ, Teshima T et al. Differential use of Fas ligand and perforin cytotoxic pathways by donor T cells in graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-leukemia effect. Blood 2001; 97: 2886–2895.
Fonseca R, Barlogie B, Bataille R, Bastard C, Bergsagel PL, Chesi M et al. Genetics and cytogenetics of multiple myeloma: A workshop report. Cancer Research 2004; 64: 1546–1558.
Desikan R, Barlogie B, Sawyer J, Ayers D, Tricot G, Badros A et al. Results of high-dose therapy for 1000 patients with multiple myeloma: durable complete remissions and superior survival in the absence of chromosome 13 abnormalities. Blood 2000; 95: 4008–4010.
Smadja NV, Bastard C, Brigaudeau C, Leroux D, Fruchart C . Hypodiploidy is a major prognostic factor in multiple myeloma. Blood 2001; 98: 2229–2238.
Fassas AB, Spencer T, Sawyer J, Zangari M, Lee CK, Anaissie E et al. Both hypodiploidy and deletion of chromosome 13 independently confer poor prognosis in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 2002; 118: 1041–1047.
Kroger N, Schilling G, Einsele H, Liebisch P, Shimoni A, Nagler A et al. Deletion of chromosome band 13q14 detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization is a prognostic factor in patients with multiple myeloma who are receiving allogeneic dose reduced stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004; 103: 4056–4061.
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Richardson PG, McMullan C, Poulaki V, Fanourakis G et al. Molecular sequelae of histone deacetylase inhibition in human malignant B cells. Blood 2003; 101: 4055–4062.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CK., Zangari, M., Fassas, A. et al. Clonal cytogenetic changes and myeloma relapse after reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 37, 511–515 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705267
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705267