Summary:
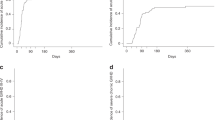
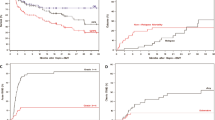
Using non-total body irradiation (TBI) containing preparative regimens, 13 patients with severe aplastic anemia (SAA) were transplanted from an alternative donor in a single institute. In total, 12 donors were unrelated volunteers and one was an HLA one-locus mismatched sibling. Median time from diagnosis of SAA to bone marrow transplantation (BMT) was 10.1 months (range, 1.6–180.1). Nine patients had received immunosuppressive treatment with ATG before BMT, while four had not. Preparative regimens consisted of cyclophosphamide plus ATG in nine patients, cyclophosphamide plus fludarabine in two patients, and cyclophosphamide plus fludarabine plus ATG in two patients. All patients received non-T-cell depleted bone marrow from the donor. Cyclosporine plus methotrexate were given for GVHD prophylaxis. All patients engrafted on a median of day 21 (range, 15–27). Grade III–IV acute GVHD developed in three (23%) of 13 patients and extensive chronic GVHD in four (31%) of 12 evaluable patients. With a median follow-up duration of 1138 days (range, 118–1553), 10 patients are alive with durable engraftment showing 74.6% (95% confidence interval, 49.5–99.7%) of survival rate. Cause of the deaths was CNS bleeding in one and chronic GVHD in two. In conclusion, non-TBI containing preparative regimen could ensure durable engraftment in alternative donor BMT for SAA and showed promising results.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marsh JC, Gordon-Smith EC . Treatment options in severe aplastic anaemia. Lancet 1998; 351: 1830–1831.
Young NS, Barrett AJ . The treatment of severe acquired aplastic anemia. Blood 1995; 85: 3367–3377.
Frickhofen N, Kaltwasser JP, Schrezenmeier H et al. Treatment of aplastic anemia with antilymphocyte globulin and methylprednisolone with or without cyclosporine. The German Aplastic Anemia Study Group. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 1297–1304.
Bacigalupo A, Broccia G, Corda G et al. Antilymphocyte globulin, cyclosporin, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with acquired severe aplastic anemia (SAA): a pilot study of the EBMT SAA Working Party. Blood 1995; 85: 1348–1353.
Margolis DA, Casper JT . Alternative-donor hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Semin Hematol 2000; 37: 43–55.
Margolis D, Camitta B, Pietryga D et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation to treat severe aplastic anaemia in children and young adults. Br J Haematol 1996; 94: 65–72.
Kojima S, Inaba J, Kondo M et al. Unrelated donor marrow transplantation for severe acquired aplastic anemia using cyclophosphamide, antithymocyte globulin, and total body irradiation. Blood 1995; 85: 291–292.
Wagner JL, Deeg HJ, Seidel K et al. Bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia from genotypically HLA-nonidentical relatives. An update of the Seattle experience. Transplantation 1996; 61: 54–61.
Hows JM, Yin JL, Marsh J et al. Histocompatible unrelated volunteer donors compared with HLA nonidentical family donors in marrow transplantation for aplastic anemia and leukemia. Blood 1986; 68: 1322–1328.
Gluckman E, Horowitz MM, Champlin RE et al. Bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: influence of conditioning and graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis regimens on outcome. Blood 1992; 79: 269–275.
Curtis RE, Rowlings PA, Deeg HJ et al. Solid cancers after bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med 1997; 336: 897–904.
Storb R, Deeg HJ . Failure of allogeneic canine marrow grafts after total-body irradiation. Allogeneic ‘resistance’ versus transfusion-induced sensitization. Transplantation 1986; 42: 571–580.
Storb R, Thomas ED, Buckner CD et al. Marrow transplantation in thirty ‘untransfused’ patients with severe aplastic anemia. Ann Intern Med 1980; 92: 30–36.
Anasetti C, Doney KC, Storb R et al. Marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Long-term outcome in fifty ‘untransfused’ patients. Ann Intern Med 1986; 104: 461–466.
Doney K, Leisenring W, Storb R, Appelbaum FR . Primary treatment of acquired aplastic anemia: outcomes with bone marrow transplantation and immunosuppressive therapy. Seattle Bone Marrow Transplant Team. Ann Intern Med 1997; 126: 107–115.
Champlin RE, Horowitz MM, van Bekkum DW et al. Graft failure following bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: risk factors and treatment results. Blood 1989; 73: 606–613.
Bean MA, Storb R, Graham T et al. Prevention of transfusion-induced sensitization to minor histocompatibility antigens on DLA-identical canine marrow grafts by gamma irradiation of marrow donor blood. Transplantation 1991; 52: 956–960.
Bean MA, Graham T, Appelbaum FR et al. Gamma-irradiation of pretransplant blood transfusions from unrelated donors prevents sensitization to minor histocompatibility antigens on dog leukocyte antigen-identical canine marrow grafts. Transplantation 1994; 57: 423–426.
Bean MA, Graham T, Appelbaum FR et al. Gamma radiation of blood products prevents rejection of subsequent DLA-identical marrow grafts. Tolerance versus abrogation of sensitization to non-DLA antigens. Transplantation 1996; 61: 334–335.
Storb R, Bean MA, Appelbaum FR et al. Treatment of marrow donor blood products with gamma-irradiation prevents transfusion-induced sensitization to DLA-identical marrow grafts. Transplant Proc 1991; 23: 1697–1698.
Georges GE, Storb R . Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for aplastic anemia. In: Blume KG, Forman SJ, Appelbaum FR (eds) Thomas’ Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Blackwell Publishing, Inc.: Malden, 2004, pp 981–1001.
Kojima S, Matsuyama T, Kato S et al. Outcome of 154 patients with severe aplastic anemia who received transplants from unrelated donors: the Japan Marrow Donor Program. Blood 2002; 100: 799–803.
Deeg HJ, Amylon ID, Harris RE et al. Marrow transplants from unrelated donors for patients with aplastic anemia: minimum effective dose of total body irradiation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2001; 7: 208–215.
Deeg HJ, Seidel K, Casper J et al. Marrow transplantation from unrelated donors for patients with severe aplastic anemia who have failed immunosuppressive therapy. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 1999; 5: 243–252.
Horowitz MM . Current status of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in acquired aplastic anemia. Semin Hematol 2000; 37: 30–42.
Kojima S, Inaba J, Yoshimi A et al. Unrelated donor marrow transplantation in children with severe aplastic anaemia using cyclophosphamide, anti-thymocyte globulin and total body irradiation. Br J Haematol 2001; 114: 706–711.
Chan KW, Li CK, Worth LL et al. A fludarabine-based conditioning regimen for severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 27: 125–128.
Elebute MO, Ball SE, Gordon-Smith EC et al. Autologous recovery following non-myeloablative unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anaemia. Ann Hematol 2002; 81: 378–381.
Vassiliou GS, Webb DK, Pamphilon D et al. Improved outcome of alternative donor bone marrow transplantation in children with severe aplastic anaemia using a conditioning regimen containing low-dose total body irradiation, cyclophosphamide and Campath. Br J Haematol 2001; 114: 701–705.
Lee JH, Lee JH, Lee JS et al. Cyclophosphamide and antithymocyte globulin conditioning may be sufficient for Korean patients with early stage severe aplastic anemia transplanted with marrow from donors other than HLA-identical siblings. Haematologica 2001; 86: 434–435.
Camitta BM, Rappeport JM, Parkman R, Nathan DG . Selection of patients for bone marrow transplantation in severe aplastic anemia. Blood 1975; 45: 355–363.
Hopkins KA . Basic microlymphocytotoxicity test. In: Zachary AA, Teresi GA (ed.). Laboratory Manual. American Society of Histocompatibility and Immunogenetics: Lenexa, 1990, pp 195–201.
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL et al. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med 1980; 69: 204–217.
Tutschka PJ, Beschorner WE, Hess AD, Santos GW . Cyclosporin-A to prevent graft-versus-host disease: a pilot study in 22 patients receiving allogeneic marrow transplants. Blood 1983; 61: 318–325.
Przepiorka D, Anderlini P, Saliba R et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation. Blood 2001; 98: 1695–1700.
Przepiorka D, Khouri I, Ippoliti C et al. Tacrolimus and minidose methotrexate for prevention of acute graft-versus-host disease after HLA-mismatched marrow or blood stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 763–768.
McDonald GB, Hinds MS, Fisher LD et al. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver and multiorgan failure after bone marrow transplantation: a cohort study of 355 patients. Ann Intern Med 1993; 118: 255–267.
Bearman SI . The syndrome of hepatic veno-occlusive disease after marrow transplantation. Blood 1995; 85: 3005–3020.
Gleaves CA, Smith TF, Shuster EA, Pearson GR . Comparison of standard tube and shell vial cell culture techniques for the detection of cytomegalovirus in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1985; 21: 217–221.
Pancholi P, Wu F, Della-Latta P . Rapid detection of cytomegalovirus infection in transplant patients. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 2004; 4: 231–242.
St George K, Rinaldo Jr CR . Comparison of cytomegalovirus antigenemia and culture assays in patients on and off antiviral therapy. J Med Virol 1999; 59: 91–97.
Choi SJ, Lee KH, Lee JH et al. Prognostic value of hematopoietic chimerism in patients with acute leukemia after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: a prospective study. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 327–332.
Deeg HJ, Anasetti C, Petersdorf E et al. Cyclophosphamide plus ATG conditioning is insufficient for sustained hematopoietic reconstitution in patients with severe aplastic anemia transplanted with marrow from HLA-A, B, DRB matched unrelated donors. Blood 1994; 83: 3417–3418.
Hows J, Szydlo R, Anasetti C et al. Unrelated donor marrow transplants for severe acquired aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 1992; 10 (Suppl 1): 102–106.
Petersdorf EW, Gooley TA, Anasetti C et al. Optimizing outcome after unrelated marrow transplantation by comprehensive matching of HLA class I and II alleles in the donor and recipient. Blood 1998; 92: 3515–3520.
Morishima Y, Kodera Y, Hirabayashi N et al. Low incidence of acute GVHD in patients transplanted with marrow from HLA-A,B,DR-compatible unrelated donors among Japanese. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 235–239.
Lin MT, Storer B, Martin PJ et al. Relation of an interleukin-10 promoter polymorphism to graft-versus-host disease and survival after hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 2201–2210.
Deeg HJ, Spitzer TR, Cottler-Fox M et al. Conditioning-related toxicity and acute graft-versus-host disease in patients given methotrexate/cyclosporine prophylaxis. Bone Marrow Transplant 1991; 7: 193–198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JH., Choi, SJ., Lee, JH. et al. Non-total body irradiation containing preparative regimen in alternative donor bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 35, 755–761 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704880
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704880
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Retrospective study of alemtuzumab vs ATG-based conditioning without irradiation for unrelated and matched sibling donor transplants in acquired severe aplastic anemia: a study from the British Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Comparison of matched-sibling donor BMT and unrelated donor BMT in children and adolescent with acquired severe aplastic anemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2010)