Abstract
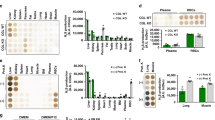
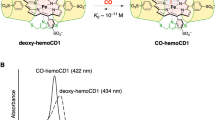
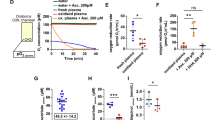
IN an earlier communication1, an account was given of investigations indicating that carbon monoxide can be formed in blood on incubation at 38° C., especially at acid or alkaline pH's or after addition of sodium azide. These observations formed the basis for further investigation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sjöstrand, T., Nature [168, 729 (1951)].
Lemberg, R., Legge, J. W., and Lockwood, W. H., Biochem. J., 33, 754 (1939); 35, 339 (1941).
Lemberg, R., Biochem. J., 29, 1322 (1935).
Sjöstrand, T., Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest., 1, 201 (1949).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SJÖSTRAND, T. Formation of Carbon Monoxide in Connexion with Hæmoglobin Catabolism. Nature 168, 1118–1119 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1038/1681118a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1681118a0
This article is cited by
-
Kinetic effects of carbon monoxide inhalation on tissue protection in ventilator-induced lung injury
Laboratory Investigation (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.