Abstract
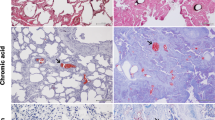
CHRONIC intoxication of dogs by the γ-isomer of hexachlorocyclohexane was induced by repeated intramuscular injections of 10–30 mgm. of this substance in 10 per cent oily solution per kgm body-weight, until a total dose of 130–475 mgm./kgm. was reached. The dogs died or were killed seven to forty-four days after the first injection. The intoxication resulted in abnormal intracellular deposits of fat in most tissues and organs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GEREBTZOFF, M., DALLEMAGNE, M. & PHILIPPOT, E. Histochemical Study of Fat Deposits in Chronic Intoxication of the Dog by γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane. Nature 165, 572–573 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1038/165572b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/165572b0
This article is cited by
-
Chronische Lebererkrankungen nach beruflicher Einwirkung von Dichlordiphenyltrichlor�than (DDT) und Hexachlorcyclohexan (HCH)
Internationales Archiv f�r Gewerbepathologie und Gewerbehygiene (1968)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.