Abstract
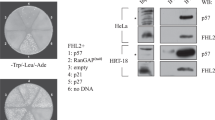
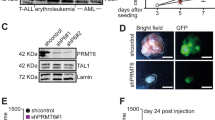
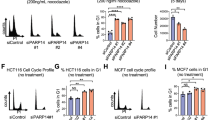
Prohibitin, a tumor suppresser protein, plays an important role in the transcriptional regulation of various genes involved in cell-cycle control and proliferation. Recent studies have reported that the growth-suppressive property of the prohibitin protein is exhibited in its physical interaction with E2F family proteins and its subsequent repression of their transcriptional activity. Herein, we report that prohibitin interacts with RING finger protein 2 (RNF2), a member of the PcG (polycomb-group) family of proteins, and that the two proteins regulate the activity of E2F1 via dual pathways: the direct, prohibitin-mediated pathway and the indirect, p16-mediated pathway of E2F1 transcriptional regulation. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments showed that endogenous prohibitin interacts with endogenous RNF2. Interestingly, the expressed amounts of RNF2 and prohibitin were interdependently affected at the post-translational level. Furthermore, the depletion of either endogenous RNF2 or prohibitin using the RNA interference technique increased the level of p16 protein expression, resulting in a decrease in the transcriptional activity of E2F1 via the p16–CDK4–Rb pathway. In addition, chromatin immunoprecipitation assays showed that RNF2 was recruited to E2F1-response promoters along with prohibitin to inhibit the transcriptional activity of E2F1. Cell proliferation was also regulated by the prohibitin–RNF2 interaction. These results suggest that the RNF2–prohibitin complex regulates the activity of E2F1 via dual pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell LA, Ryan KM . (2004). Life and death decisions by E2F-1. Cell Death Differ 11: 137–142.
Fusaro G, Dasgupta P, Rastogi S, Joshi B, Chellappan S . (2003). Prohibitin induces the transcriptional activity of p53 and is exported from the nucleus upon apoptotic signaling. J Biol Chem 278: 47853–47861.
Harbour JW, Dean DC . (2000). Chromatin remodeling and Rb activity. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12: 685–689.
Kim H, Jeong W, Ahn K, Ahn C, Kang S . (2004). Siah-1 interacts with the intracellular region of polycystin-1 and affects its stability via the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 2042–2049.
Lee SJ, Choi D, Rhim H, Kang S . (2005). E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF2 interacts with the S6′ proteasomal ATPase subunit and increases the ATP hydrolysis activity of S6′. Biochem J 389: 457–463.
Lee SJ, Choi JY, Sung YM, Park H, Rhim H, Kang S . (2001). E3 ligase activity of RING finger proteins that interact with Hip-2, a human ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. FEBS Lett 503: 61–64.
Luo RX, Postigo AA, Dean DC . (1998). Rb interacts with histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Cell 92: 463–473.
Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Groisman R, Naguibneva I, Robin P, Lorain S, Le Villain JP et al. (1998). Retinoblastoma protein represses transcription by recruiting a histone deacetylase. Nature 391: 601–605.
Sato T, Sakamoto T, Takita K, Saito H, Okui K, Nakamura Y . (1993). The human prohibitin (PHB) gene family and its somatic mutations in human tumors. Genomics 17: 762–764.
Shang Y, Hu X, DiRenzo J, Lazar MA, Brown M . (2000). Cofactor dynamics and sufficiency in estrogen receptor-regulated transcription. Cell 103: 843–852.
Sherr CJ . (2000). The Pezcoller lecture: cancer cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res 60: 3689–3695.
Voncken JW, Roelen BA, Roefs M, de Vries S, Verhoeven E, Marino S et al. (2003). Rnf2 (Ring1b) deficiency causes gastrulation arrest and cell cycle inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 2468–2473.
Wang H, Wang L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Vidal M, Tempst P, Jones RS et al. (2004). Role of histone H2A ubiquitination in Polycomb silencing. Nature 431: 873–878.
Wang S, Nath N, Adlam M, Chellappan S . (1999a). Prohibitin, a potential tumor suppressor, interacts with RB and regulates E2F function. Oncogene 18: 3501–3510.
Wang S, Nath N, Fusaro G, Chellappan S . (1999b). Rb and prohibitin target distinct regions of E2F1 for repression and respond to different upstream signals. Mol Cell Biol 19: 7447–7460.
Wang S, Zhang B, Faller DV . (2002). Prohibitin requires Brg-1 and Brm for the repression of E2F and cell growth. EMBO J 21: 3019–3028.
Yoo YA, Kim MJ, Park JK, Chung YM, Lee JH, Chi SG et al. (2005). Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L41 suppresses cell growth in association with p53 and p27Kip1. Mol Cell Biol 25: 6603–6616.
Zhu L . (2005). Tumour suppressor retinoblastoma protein Rb: a transcriptional regulator. Eur J Cancer 41: 2415–2427.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation grant funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD) (KRF-2005-C00350) and Korea University (K0401401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, D., Lee, SJ., Hong, S. et al. Prohibitin interacts with RNF2 and regulates E2F1 function via dual pathways. Oncogene 27, 1716–1725 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210806
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210806
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RNF2 mediates pulmonary fibroblasts activation and proliferation by regulating mTOR and p16-CDK4-Rb1 signaling pathway
Inflammation Research (2022)
-
Expression pattern of phb2 and its potential function in spermatogenesis of scallop (Chlamys farreri)
Journal of Ocean University of China (2015)
-
Prohibitin is required for transcriptional repression by the WT1–BASP1 complex
Oncogene (2014)
-
Follicular stage-dependent regulation of apoptosis and steroidogenesis by prohibitin in rat granulosa cells
Journal of Ovarian Research (2013)
-
Dynamic Change of Prohibitin2 Expression in Rat Sciatic Nerve After Crush
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2013)