Abstract
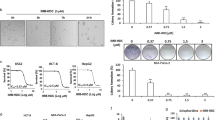
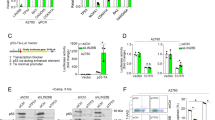
Tumor suppressor p53 is stabilized in response to γ-irradiation or treatment with DNA-damaging agents, and as a result p53 transcriptionally activates its targets leading to cell-cycle arrest or apoptosis. P-TEFb (positive transcription elongation factor b) inhibitors such as flavopiridol or 4-amino-6-hydrazino-7-b-d-ribofuranosyl-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]-pyrimidine-5-carboxamide (ARC) upregulate p53 protein levels, but inhibit the expression of its targets p21 and hdm2. DNA-damaging agents, doxorubicin and cisplatin are being used in combination with P-TEFb inhibitor flavopiridol in clinical trials for the treatment of some cancer patients. In this study, we found that P-TEFb inhibitors block the phosphorylation of p53 induced by doxorubicin. Furthermore, treatment of cells with P-TEFb inhibitors together with doxorubicin inhibits doxorubicin-induced binding of p53 to DNA and p53 transcriptional activity. These data suggest that P-TEFb inhibitors may antagonize the activation of p53 by DNA-damaging agents in tumors with wild-type p53.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashcroft M, Kubbutat MH, Vousden KH . (1999). Regulation of p53 function and stability by phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 19: 1751–1758.
Bible KC, Lensing JL, Nelson SA, Lee YK, Reid JM, Ames MM et al. (2005). Phase 1 trial of flavopiridol combined with cisplatin or carboplatin in patients with advanced malignancies with the assessment of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic end points. Clin Cancer Res 11: 5935–5941.
Brooks CL, Gu W . (2003). Ubiquitination, phosphorylation and acetylation: the molecular basis for p53 regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15: 164–171.
Bunz F, Hwang PM, Torrance C, Waldman T, Zhang Y, Dillehay L et al. (1999). Disruption of p53 in human cancer cells alters the responses to therapeutic agents. J Clin Invest 104: 263–269.
Demidenko ZN, Blagosklonny MV . (2004). Flavopiridol induces p53 via initial inhibition of Mdm2 and p21 and, independently of p53, sensitizes apoptosis-reluctant cells to tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Res 64: 3653–3660.
Dunkern TR, Wedemeyer I, Baumgartner M, Fritz G, Kaina B . (2003). Resistance of p53 knockout cells to doxorubicin is related to reduced formation of DNA strand breaks rather than impaired apoptotic signaling. DNA Repair (Amst) 2: 49–60.
Gomes NP, Bjerke G, Llorente B, Szostek SA, Emerson BM, Espinosa JM . (2006). Gene-specific requirement for P-TEFb activity and RNA polymerase II phosphorylation within the p53 transcriptional program. Genes Dev 20: 601–612.
Guillot C, Falette N, Paperin MP, Courtois S, Gentil-Perret A, Treilleux I et al. (1997). p21(WAF1/CIP1) response to genotoxic agents in wild-type TP53 expressing breast primary tumours. Oncogene 14: 45–52.
Jack MT, Woo RA, Motoyama N, Takai H, Lee PW . (2004). DNA-dependent protein kinase and checkpoint kinase 2 synergistically activate a latent population of p53 upon DNA damage. J Biol Chem 279: 15269–15273.
Radhakrishnan SK, Bhat UG, Hughes DE, Wang IC, Costa RH, Gartel AL . (2006). Identification of a chemical inhibitor of the oncogenic transcription factor forkhead box m1. Cancer Res 66: 9731–9735.
Radhakrishnan SK, Feliciano CS, Najmabadi F, Haegebarth A, Kandel ES, Tyner AL et al. (2004). Constitutive expression of E2F-1 leads to p21-dependent cell cycle arrest in S phase of the cell cycle. Oncogene 23: 4173–4176.
Radhakrishnan SK, Gartel AL . (2006a). CDK9 phosphorylates p53 on serine residues 33, 315 and 392. Cell Cycle 5: 519–521.
Radhakrishnan SK, Gartel AL . (2006b). A novel transcriptional inhibitor induces apoptosis in tumor cells and exhibits antiangiogenic activity. Cancer Res 66: 3264–3270.
Thompson T, Tovar C, Yang H, Carvajal D, Vu BT, Xu Q et al. (2004). Phosphorylation of p53 on key serines is dispensable for transcriptional activation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279: 53015–53022.
Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ . (2000). Surfing the p53 network. Nature 408: 307–310.
Vousden KH, Woude GF . (2000). The ins and outs of p53. Nat Cell Biol 2: E178–E180.
Wang S, Konorev EA, Kotamraju S, Joseph J, Kalivendi S, Kalyanaraman B . (2004). Doxorubicin induces apoptosis in normal and tumor cells via distinctly different mechanisms. Intermediacy of H(2)O(2) and p53-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem 279: 25535–25543.
Wang Y, Prives C . (1995). Increased and altered DNA binding of human p53 by S and G2/M but not G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Nature 376: 88–91.
Woo RA, McLure KG, Lees-Miller SP, Rancourt DE, Lee PW . (1998). DNA-dependent protein kinase acts upstream of p53 in response to DNA damage. Nature 394: 700–704.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Sergei Nekhai for providing purified P-TEFb protein. This work was supported by the start-up funds from the UIC Department of Medicine, award from UIC Campus Research Board and by DOD Grant BC052816 to ALG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radhakrishnan, S., Bhat, U., Halasi, M. et al. P-TEFb inhibitors interfere with activation of p53 by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene 27, 1306–1309 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210737
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210737
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Salinomycin, a p-glycoprotein inhibitor, sensitizes radiation-treated cancer cells by increasing DNA damage and inducing G2 arrest
Investigational New Drugs (2012)