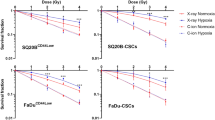
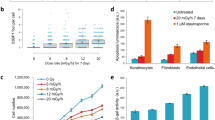
Abstract
The initiation and propagation of the early processes of bystander signaling induced by low-dose α-particle irradiation are very important for understanding the underlying mechanism of the bystander process. Our previous investigation showed that the medium collected from cell culture exposed to low-dose α-particle rapidly induced phosphorylated form of H2AX protein foci formation among the non-irradiated medium receptor cells in a time-dependent manner. Using NG-methyl-L-arginine, 4-amino-5-methylamino-2′,7′-difluorofluorescein diacetate and Nω-nitro-L-arginine (L-NNA) treatment before exposure to 1 cGy α-particle, we showed in the present study that nitric oxide (NO•) produced in the irradiated cells was important and necessary for the DNA double strand break inducing activity (DIA) of conditioned medium and the generation of NO• in irradiated confluent AG1522 cells is in a time-dependent manner and that almost all NO• was generated within 15 min post-irradiation. Concurrently, the kinetics of NO• production in the medium of irradiated cells after irradiation was rapid and in a time-dependent manner as well, with a maximum yield observed at 10 min after irradiation with electron spin resonance analysis. Furthermore, our results that 7-Nitroindazole and L-NNA, but not aminoguanidine hemisulfate, treatment before exposure to 1 cGy α-particle significantly decrease the DIA of the conditioned medium suggested that constitutive NO• from the irradiated cells possibly acted as an intercellular signaling molecule to initiate and activate the early process (⩽30 min) of bystander response after low-dose irradiation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AG:
-
aminoguanidine hemisulfate
- c-PTIO:
-
2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide
- DAF-FM diacetate:
-
4-amino-5-methylamino-2′,7′-difluorofluorescein diacetate
- DIA:
-
DSB-inducing activity (of conditioned medium collected from the irradiated culture)
- D-NMMA:
-
NG-methyl-D-arginine
- DSBs:
-
DNA double strand breaks
- ESR:
-
electron spin resonance
- γ-H2AX:
-
phosphorylated form of H2AX protein
- L-NMMA:
-
NG-methyl-L-arginine
- L-NNA:
-
Nω-nitro-L-arginine
- 7-Ni:
-
7-Nitroindazole
- NO•:
-
nitric oxide
- NO2−:
-
nitrite
- NOS:
-
nitric oxide synthase
- ONOO−:
-
peroxynitrite
- RIBE:
-
radiation-induced bystander effects
- RNS:
-
reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
References
Aten JA, Stap J, Krawczyk PM, Van Oven CH, Hoebe RA, Essers J et al. (2004). Dynamics of DNA double-strand breaks revealed by clustering of damaged chromosome domains. Science 303: 92–95.
Azzam EI, De Toledo SM, Little JB . (2001). Direct evidence for the participation of gap-junction mediated intercellular communication in the transmission of damage signals from alpha-particle irradiated to non-irradiated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 473–478.
Azzam EI, De Toledo SM, Little JB . (2004). Stress signaling from irradiated to non-irradiated cells. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4: 53–64.
Azzam EI, Little JB . (2003). The radiation induced bystander effect: evidence and significance. Biol Eff low Level Exposures Newslett 11: 2–6.
Beckman JS, Beckman TW, Chen J, Marshall PA, Freeman BA . (1990). Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 1620–1624.
Beckman JS, Koppenol WH . (1996). Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, the bad, and ugly. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 271: C1424–C1437.
Burma S, Chen BP, Murphy M, Kurimasa A, Chen DJ . (2001). ATM phosphorylates histone H2AX in response to DNA double strand breaks. J Biol Chem 276: 42462–42467.
Chen HT, Bhandoola A, Difilippantonio MJ, Zhu J, Brown MJ, Tai X et al. (2000). Response to RAG-mediated VDJ cleavage by NBS1 and gamma-H2AX. Science 290: 1962–1965.
Dahm-Daphi J, Sass C, Albert W . (2000). Comparison of biological effects of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation and hydrogen peroxide in CHO cells. Int J Radiat Biol 76: 67–75.
Dawson VL, Dawson TM, London ED, Bred DS, Snyder SH . (1991). Nitric oxide mediates glutamate neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 6368–6371.
Fagagna FA, Reaper PM, Clay-Farrace L, Fiegler H, Carr P, Zglinicki TV et al. (2003). A DNA damage checkpoint response in telomere-initiated senescence. Nature 426: 194–198.
Fernandes E, Gomes A, Costa D, Lima JLFC . (2005). Pindolol is a potent scavenger of reactive nitrogen species. Life Sci 77: 1983–1992.
Han W, Wu L, Hu B, Zhang L, Chen S, Bao L et al. (2007) The early and initiation process of radiation-induced bystander effects involving in the induction of DNA double strand breaks in non-irradiated cultures. Br J Radiol (special issue, in press).
Hoeijmakers JH . (2001). Genome maintenance mechanisms for preventing cancer. Nature 411: 366–374.
Hu B, Han W, Wu L, Feng H, Liu X, Zhang L et al. (2005). In situ visualization of DSBs to assess the extranuclear/extracellular effects induced by low dose α-particle irradiation. Radiat Res 164: 286–293.
Hu B, Wu L, Han W, Zhang L, Chen S, Xu A et al. (2006). The time and spatial effects of bystander response in mammalian cells induced by low dose radiation. Carcinogenesis 27: 245–251.
Iyer R, Lehnert BE . (2000). Factors underlying the cell growth-related bystander responses to alpha particles. Cancer Res 60: 1290–1298.
Janssen YM, Soultanakis R, Steece K, Heerdt E, Singh RJ, Joseph J et al. (1998). Depletion of nitric oxide causes cell cycle alterations, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in pulmonary cells. Am J Physiol 275: 1100–1109.
Jourd'heuil D, Kang D, Grisham MB . (1997). Interactions between superoxide and nitric oxide: implications in DNA damage and mutagenesis. Front Biosci 2: 189–196.
Kiang JG, McClain DE, Warke VG, Krishnan S, Tsokos GC . (2003). Constitutive NO synthase regulates the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in human T cells: role of [Ca2+]i and tyrosine phosphorylation. J Cell Biol 89: 1030–1043.
Kojima H, Nakatsubo N, Kikuchi K, Urano Y, Higuchi T, Tanaka J et al. (1998). Direct evidence of NO production in rat hippocampus and cortex using a new fluorescent indicator: DAF-2 DA. Neuroreport 9: 3345–3348.
Kojima H, Urano Y, Kikuchi K, Higuchi T, Hirata Y, Nagano T . (1999). Fluorescent indicators for imaging nitric oxide production. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 38: 3209–3212.
Lacza Z, Snipe JA, Zhang J, Horv'ath EM, Figueroa JP, Szab'o C et al. (2003). Mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase is not eNOS, nNOS or iNOS. Free Radic Biol Med 35: 1217–1228.
Leach JK, Black SM, Schmidt-Ullrich RK, Mikkelsen RB . (2002). Activation of constitutive nitric-oxide synthase activity is an early signaling event induced by ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem 277: 15400–15406.
Lewis DA, Mayhugh BM, Qin Y, Trott K, Mendonca MS . (2001). Production of delayed death and neoplastic transformation in CGL1 cells by radiation-induced bystander effects. Radiat Res 156: 251–258.
Li N, Sul JY, Haydon PG . (2003). A calcium-induced calcium influx factor, nitric oxide, modulates the refilling of calcium stores in astrocytes. J Neurosci 23: 10302–10310.
Limoli CL, Giedzinski E, Bonner WM, Cleaver JE . (2002). UV-induced replication arrest in the xeroderma pigmentosum variant leads to DNA double-strand breaks, gamma -H2AX formation, and Mre11 relocalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 233–238.
Liu SX, Davidson MM, Tang X, Walker WF, Athar M, Ivanov V et al. (2005). Mitochondrial damage mediates genotoxicity of arsenic in mammalian cells. Cancer Res 65: 3236–3242.
Lyng FM, Seymour CB, Mothersill C . (2000). Production of a signal by irradiated cells which leads to a response in non-irradiated cells characteristic of initiation of apoptosis. Br J Cancer 83: 1223–1230.
Mahadevaiah SK, Turner JM, Baudat F, Rogakou EP, Boer P, Blanco-Rodriguez J et al. (2001). Recombinational DNA double-strand breaks in mice precede synapsis. Nat Genet 27: 271–276.
Matsumoto H, Hayashi S, Hatashita M, Ohnishi K, Shioura H, Ohtsubo T et al. (2001). Induction of radioresistance by a nitric oxide-mediated bystander effect. Radiat Res 155: 387–396.
Matsumoto H, Hayashi S, Hatashita M, Shioura H, Ohisubo T, Kitai R et al. (2000). Induction of radioresistance to accelerated carbon-ion beams in recipient cells by nitric oxide excreted from irradiated donor cells of human glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Biol 76: 1649–1657.
Minetti M, Mallozzi C, Di Stasi AM . (2002). Peroxynitrite activates kinases of the Src family and upregulates tyrosine phosphorylation signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 33: 744–754.
Mothersill C, Seymour C . (1997). Medium from irradiated human epithelial cells but not human fibroblasts reduces the clonogenic survival of non-irradiated cells. Int J Radiat Biol 71: 421–427.
Mothersill C, Seymour CB . (1998). Cell–cell contact during gamma irradiation is not required to induce a bystander effect in normal kidney keratinocytes: evidence for release during irradiation of a signal controlling survival into the medium. Radiat Res 149: 256–262.
Murad F . (1998). Nitric oxide signaling: would you believe that a simple free radical could be a second messenger, autacoid, paracrine substance, neurotransmitter, and hormone? Recent Prog Horm Res 53: 43–60.
Nagar S, Smith LE, Morgan WF . (2003). Characterization of a novel epigenetic effect of ionizing radiation: the death-inducing effect. Cancer Res 63: 324–328.
Petersen S, Casellas R, Reina-San-Martin B, Chen HT, Difilippantonio MJ, Wilson PC et al. (2001). AID is required to initiate Nbs1/gamma-H2AX focus formation and mutations at sites of class switching. Nature 414: 660–665.
Pfeiffer S, Leopold E, Hemmens B, Schmidt K, Werner ER, Mayer B . (1997). Interference of carboxy-PTIO with nitric oxide- and peroxynitrite-mediated reactions. Free Radic Biol Med 22: 787–794.
Qu XW, Wang H, Plaen IGD, Rozenfeld RA, Hsueh W . (2001). Neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS) regulates the expression of inducible NOS in rat small intestine via modulation of nuclear factor kappa B. FASEB J 15: 439–446.
Rao CV, Indranie C, Simi B, Manning PT, Connor JR, Reddy BS . (2002). Chemopreventive properties of a selective inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in colon carcinogenesis, administered alone or in combination with celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Cancer Res 62: 165–170.
Rogakou EP, Pilch DR . (1999). Megabase chromatin domains involved in DNA double-strand breaks in vivo. J Cell Biol 146: 905–915.
Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS, Bonner WM . (1998). DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J Biol Chem 273: 5858–5868.
Rothkamm K, Lobrich M . (2003). Evidence for a lack of DNA double strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low x-ray doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 5057–5062.
Sedelnikova OA, Panyutin IV, Neumann RD, Bonner WM, Panyutin IG . (2004). Assessment of DNA damage produced by 125I-triplex-forming oligonucleotides in cells. Int J Radiat Biol 80: 927–931.
Sedelnikova OA, Rogakou EP, Panyutin IG . (2002). Quantitative detection of 125IdU-induced DNA double-strand breaks with g-H2AX antibody. Radiat Res 158: 486–492.
Seymour CB, Mothersill C . (1997). Delayed expression of lethal mutations and genomic instability in the progeny of human epithelial cells that survived in a bystander killing environment. Radiat Oncol Investig 5: 106–110.
Shao C, Folkardn M, Michael BD, Prise KM . (2004). Targeted cytoplasmic irradiation induces bystander responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 13495–13500.
Shao C, Furusawa Y, Aoki M, Matsumoto H, Ando K . (2002). Nitric oxide-mediated bystander effect induced by heavy-ions in human salivary gland tumour cells. Int J Radiat Biol 78: 837–844.
Shao C, Furusawa Y, Kobayashi Y, Funayama T, Wada S . (2003b). Bystander effect induced by counted high-LET particles in confluent human fibroblasts: a mechanistic study. FASEB J 17: 1422–1427.
Shao C, Stewart V, Folkardn M, Michael BD, Prise KM . (2003a). Nitric oxide-mediated signaling in the bystander response of individually targeted glioma cells. Cancer Res 63: 8437–8442.
Stefano GB . (1998). Autoimmunovascular regulation: morphine and anandamide stimulated nitric oxide release. J Neuroimmunol 83: 70–76.
Stefano GB, Goumon Y, Bilfinger TV, Welters ID, Cadet P . (2000). Basal nitric oxide limits immune, nervous and cardiovascular excitation: human endothelia express a mu opiate receptor. Progress Neurobiol 60: 513–530.
Stefano GB, Hartman A, Bilfinger TV, Magazine HI, Liu Y, Casares F et al. (1995). Presence of the m3 opiate receptor in endothelial cells: coupling to nitric oxide production and vasodilation. J Biol Chem 270: 30290–30293.
Van Gent DC, Hoeijmakers JH, Kanaar R . (2001). Chromosomal stability and the DNA double-stranded break connection. Nat Rev Genet 2: 196–206.
Vodovotz Y, Chesler L, Chong H, Kim SJ, Simpson JT, DeGraff W et al. (1999). Regulation of Transforming Growth Factor b1 by Nitric Oxide. Cancer Res 59: 2142–2149.
Xiong Q, Shi Q, Le X, Wang B, Xie K . (2001). Regulation of interleukin-8 expression by nitric oxide in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Interferon Cytokine Res 21: 529–537.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Mohammad Athar, Hari Bhat and Vladimir Ivanov for critical reading of the paper and their helpful discussions, and Dr Haiying Hang for his technical assistance with DSB detection. This work was funded by National Nature Science Foundation of China under Grant nos. 10225526 and 30570435, Grant KSCX2-SW-324 of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and US National Institutes of Health Grants ES 012888 and Environmental Center Grant ES09089.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, W., Wu, L., Chen, S. et al. Constitutive nitric oxide acting as a possible intercellular signaling molecule in the initiation of radiation-induced DNA double strand breaks in non-irradiated bystander cells. Oncogene 26, 2330–2339 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210024
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210024
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The emerging role of exosomes in radiotherapy
Cell Communication and Signaling (2022)
-
Intercellular communications-redox interactions in radiation toxicity; potential targets for radiation mitigation
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2019)
-
Integrated Modelling of Cell Responses after Irradiation for DNA-Targeted Effects and Non-Targeted Effects
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Reduction–oxidation (redox) system in radiation-induced normal tissue injury: molecular mechanisms and implications in radiation therapeutics
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2018)
-
Bystander autophagy mediated by radiation-induced exosomal miR-7-5p in non-targeted human bronchial epithelial cells
Scientific Reports (2016)