Abstract
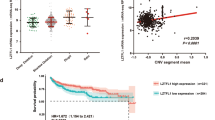
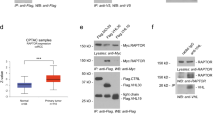
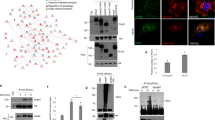
TRC8/RNF139 and von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) both encode E3 ubiquitin (Ub) ligases mutated in clear-cell renal carcinomas (ccRCC). VHL, inactivated in nearly 70% of ccRCCs, is a tumor suppressor encoding the targeting subunit for a Ub ligase complex that downregulates hypoxia-inducible factor-α. TRC8/RNF139 is a putative tumor suppressor containing a sterol-sensing domain and a RING-H2 motif essential for Ub ligase activity. Here we report that human kidney cells are growth inhibited by TRC8. Inhibition is manifested by G2/M arrest, decreased DNA synthesis and increased apoptosis and is dependent upon the Ub ligase activity of the RING domain. Tumor formation in a nude mouse model is inhibited by TRC8 in a RING-dependent manner. Expression of TRC8 represses genes involved in cholesterol and fatty acid biosynthesis that are transcriptionally regulated by the sterol response element binding proteins (SREBPs). Expression of activated SREBP-1a partially restores the growth of TRC8-inhibited cells. These data suggest that TRC8 modulation of SREBP activity comprises a novel regulatory link between growth control and the cholesterol/lipid homeostasis pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ciechanover A . (2006). The ubiquitin proteolytic system: from a vague idea, through basic mechanisms, and onto human diseases and drug targeting. Neurology 66: S7–S19.
Clayman RV, Bilhartz LE, Buja LM, Spady DK, Dietschy JM . (1986). Renal cell carcinoma in the Wistar–Lewis rat: a model for studying the mechanisms of cholesterol acquisition by a tumor in vivo. Cancer Res 46: 2958–2963.
Clifford SC, Astuti D, Hooper L, Maxwell PH, Ratcliffe PJ, Maher ER . (2001). The pVHL-associated SCF ubiquitin ligase complex: molecular genetic analysis of elongin B and C, Rbx1 and HIF-1alpha in renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 20: 5067–5074.
Cohen AJ, Li FP, Berg S, Marchetto DJ, Tsai S, Jacobs SC et al. (1979). Hereditary renal-cell carcinoma associated with a chromosomal translocation. N Engl J Med 301: 592–595.
Ettinger SL, Sobel R, Whitmore TG, Akbari M, Bradley DR, Gleave ME et al. (2004). Dysregulation of sterol response element-binding proteins and downstream effectors in prostate cancer during progression to androgen independence. Cancer Res 64: 2212–2221.
Falck J, Mailand N, Syljuasen RG, Bartek J, Lukas J . (2001). The ATM-Chk2-Cdc25A checkpoint pathway guards against radioresistant DNA synthesis. Nature 410: 842–847.
Fang S, Ferrone M, Yang C, Jensen JP, Tiwari S, Weissman AM . (2001). The tumor autocrine motility factor receptor, gp78, is a ubiquitin protein ligase implicated in degradation from the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 14422–14427.
Gebhard RL, Clayman RV, Prigge WF, Figenshau R, Staley NA, Reesey C et al. (1987). Abnormal cholesterol metabolism in renal clear cell carcinoma. J Lipid Res 28: 1177–1184.
Gemmill RM, Bemis LT, Lee JP, Sozen MA, Baron A, Zeng C et al. (2002). The TRC8 hereditary kidney cancer gene suppresses growth and functions with VHL in a common pathway. Oncogene 21: 3507–3516.
Gemmill RM, Lee JP, Chamovitz DA, Segal D, Hooper JE, Drabkin HA . (2005). Growth suppression induced by the TRC8 hereditary kidney cancer gene is dependent upon JAB1/CSN5. Oncogene 24: 3503–3511.
Gemmill RM, West JD, Boldog F, Tanaka N, Robinson LJ, Smith DI et al. (1998). The hereditary renal cell carcinoma 3;8 translocation fuses FHIT to a patched-related gene, TRC8. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 9572–9577.
Goldstein JL, DeBose-Boyd RA, Brown MS . (2006). Protein sensors for membrane sterols. Cell 124: 35–46.
Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS . (2002). SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest 109: 1125–1131.
Horton JD, Shah NA, Warrington JA, Anderson NN, Park SW, Brown MS et al. (2003). Combined analysis of oligonucleotide microarray data from transgenic and knockout mice identifies direct SREBP target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 12027–12032.
Hughes AL, Todd BL, Espenshade PJ . (2005). SREBP pathway responds to sterols and functions as an oxygen sensor in fission yeast. Cell 120: 831–842.
Ito K, Hirao A, Arai F, Matsuoka S, Takubo K, Hamaguchi I et al. (2004). Regulation of oxidative stress by ATM is required for self-renewal of haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 431: 997–1002.
Kaelin Jr WG . (2004). The von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor gene and kidney cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10: 6290S–6295S.
Kaelin Jr WG . (2005). The von Hippel–Lindau protein, HIF hydroxylation, and oxygen sensing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338: 627–638.
Katoh S, Hong C, Tsunoda Y, Murata K, Takai R, Minami E et al. (2003). High precision NMR structure and function of the RING-H2 finger domain of EL5, a rice protein whose expression is increased upon exposure to pathogen-derived oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem 278: 15341–15348.
Li FP, Decker HJ, Zbar B, Stanton Jr VP, Kovacs G, Seizinger BR et al. (1993). Clinical and genetic studies of renal cell carcinomas in a family with a constitutional chromosome 3;8 translocation. Genetics of familial renal carcinoma. Ann Intern Med 118: 106–111.
Lorick KL, Jensen JP, Fang S, Ong AM, Hatakeyama S, Weissman AM . (1999). RING fingers mediate ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2)-dependent ubiquitination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 11364–11369.
Ma D, Nutt CL, Shanehsaz P, Peng X, Louis DN, Kaetzel DM . (2005). Autocrine platelet-derived growth factor-dependent gene expression in glioblastoma cells is mediated largely by activation of the transcription factor sterol regulatory element binding protein and is associated with altered genotype and patient survival in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 65: 5523–5534.
Mandriota SJ, Turner KJ, Davies DR, Murray PG, Morgan NV, Sowter HM et al. (2002). HIF activation identifies early lesions in VHL kidneys: evidence for site-specific tumor suppressor function in the nephron. Cancer Cell 1: 459–468.
Martel PM, Bingham CM, McGraw CJ, Baker CL, Morganelli PM, Meng ML et al. (2006). S14 protein in breast cancer cells: direct evidence of regulation by SREBP-1c, superinduction with progestin, and effects on cell growth. Exp Cell Res 312: 278–288.
Matsuoka S, Huang M, Elledge SJ . (1998). Linkage of ATM to cell cycle regulation by the Chk2 protein kinase. Science 282: 1893–1897.
Ohira T, Gemmill RM, Ferguson K, Kusy S, Roche J, Brambilla E et al. (2003). WNT7a induces E-cadherin in lung cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 10429–10434.
Todd BL, Stewart EV, Burg JS, Hughes AL, Espenshade PJ . (2006). Sterol regulatory element binding protein is a principal regulator of anaerobic gene expression in fission yeast. Mol Cell Biol 26: 2817–2831.
Zheng N, Wang P, Jeffrey PD, Pavletich NP . (2000). Structure of a c-Cbl-UbcH7 complex: RING domain function in ubiquitin–protein ligases. Cell 102: 533–539.
Acknowledgements
We thank H Schulze for expression plasmids, A Kraft for vectors and 293FI cells. This investigation used the DNA Sequencing, Flow Cytometry and Biostatistics Cores of the University of Colorado Cancer Center. We thank J Jacobsen, C Korch, K Helm, M Ashton, C Childs and C Zeng for technical assistance. KLL, YCT and AMW are supported by the Intramural Research Program of the Center for Cancer Research, NCI, NIH. HAD and RMG are supported by NIH RO1 CA076035.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncology website (http://www.nature.com/ncponc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brauweiler, A., Lorick, K., Lee, J. et al. RING-dependent tumor suppression and G2/M arrest induced by the TRC8 hereditary kidney cancer gene. Oncogene 26, 2263–2271 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210017
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210017
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
An E3 Ubiquitin Ligase RNF139 Serves as a Tumor-Suppressor in Glioma
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2021)
-
Porcine JAB1 significantly enhances apoptosis induced by staurosporine
Cell Death & Disease (2013)
-
TRC8 suppresses tumorigenesis through targeting heme oxygenase-1 for ubiquitination and degradation
Oncogene (2013)
-
Lipid Synthesis in Lactation: Diet and the Fatty Acid Switch
Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia (2007)