Abstract
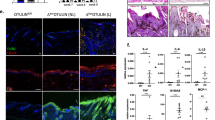
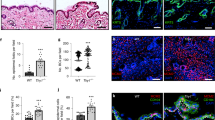
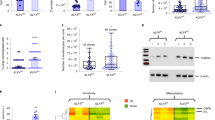
Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) is an important regulator of epidermal homeostasis and repair. Therefore, the identification of KGF target genes in keratinocytes should contribute to our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying these processes. In a search for KGF-regulated genes, we identified the gene encoding the nucleoside diphosphate kinase NM23-H1. Apart from a housekeeping function, NM23 proteins are involved in the regulation of many cellular processes as well as in tumor metastasis, but their functions in epidermal homeostasis and repair are largely unknown. Here, we show a high expression of NM23-H1 and NM23-H2 in the KGF-responsive keratinocytes of the hyperproliferative epidermis of mouse skin wounds and of patients suffering from the skin disease psoriasis. To determine if this overexpression is functionally important, we generated HaCaT keratinocyte cell lines overexpressing NM23-H1 and/or -H2. Whereas the enhanced levels of NM23 did not affect cell proliferation in monoculture, NM23-H2 and double transfectants but not NM23-H1 transfectants formed a strongly hyperthickened epithelium in three-dimensional organotypic cultures. The abnormal epithelial morphology resulted from enhanced proliferation, reduced apoptosis and alterations in the differentiation pattern. These findings suggest that epidermal homeostasis depends on a tight regulation of the levels of NM23 isoforms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auf dem Keller U, Huber M, Beyer TA, Siemes C, Kümin A, Braun S et al. (2006). Mol Cell Biol 26: 3773–3784.
Beer H-D, Munding C, Dubois N, Mamie C, Hohl D, Werner S . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 20740–20749.
Bernard BA, Asselineau D, Schaffar-Deshayes L, Darmon MY . (1988). J Invest Dermatol 90: 801–805.
Boukamp P, Petrussevska RT, Breitkreutz D, Hornung J, Markham A, Fusenig NE . (1988). J Cell Biol 106: 761–771.
Braun S, Hanselmann C, Gassmann MG, auf dem Keller U, Born-Berclaz C, Chan K et al. (2002). Mol Cell Biol 22: 5492–5505.
Chang CL, Strahler JR, Thoraval DH, Qian MG, Hinderer R, Hanash SM . (1996). Oncogene 12: 659–667.
Chen CA, Okayama H . (1988). Biotechniques 6: 632–638.
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N . (1987). Anal Biochem 162: 156–159.
Finch PW, Murphy F, Cardinale I, Krueger JG . (1997). Am J Pathol 151: 1619–1628.
Finch PW, Rubin JS . (2004). Adv Cancer Res 91: 69–136.
Fournier HN, Albiges-Rizo C, Block MR . (2003). J Bioenerg Biomembr 35: 81–87.
Frank S, Munz B, Werner S . (1997). Oncogene 14: 915–921.
Gassmann MG, Stanzel A, Werner S . (1999). Oncogene 18: 6667–6676.
Gassmann MG, Werner S . (2000). Exp Cell Res 258: 23–32.
Gilles AM, Presecan E, Vonica A, Lascu I . (1991). J Biol Chem 266: 8784–8789.
Gromov P, Skovgaard GL, Palsdottir H, Gromova I, Ostergaard M, Celis JE . (2003). Mol Cell Proteom 2: 70–84.
Grotendorst GR, Soma Y, Takehara K, Charette M . (1989). J Cell Physiol 139: 617–623.
Hailat N, Keim DR, Melhem RF, Zhu XX, Eckerskorn C, Brodeur GM et al. (1991). J Clin Invest 88: 341–345.
Igawa M, Rukstalis DB, Tanabe T, Chodak GW . (1994). Cancer Res 54: 1313–1318.
Kadunce DP, Krueger GG . (1995). Pathogenesis of psoriasis Dermatol Clin 13: 723–737.
Kanitakis J, Euvrard S, Bourchany D, Fauvre M, Claudy A . (1997). J Cutan Pathol 24: 151–156.
Keim D, Hailat N, Melhem R, Zhu XX, Lascu I, Veron M et al. (1992). J Clin Invest 89: 919–924.
Kimura N, Shimada N, Fukuda M, Ishijima Y, Miyazaki H, Ishii A et al. (2000). J Bioenerg Biomembr 32: 309–315.
King Jr LE, Gates RE, Stoscheck CM, Nanney LB . (1990). J Invest Dermatol 95: 10S–12S.
Krampert M, Bloch W, Sasaki T, Bugnon P, Rülicke T, Wolf E et al. (2004). Mol Biol Cell 15: 5242–5254.
Lacombe ML, Milon L, Munier A, Mehus JG, Lambeth DO . (2000). J Bioenerg Biomembr 32: 247–258.
Lakso M, Steeg PS, Westphal H . (1992). Cell Growth Differ 3: 873–879.
Madlener M, Mauch C, Conca W, Brauchle M, Parks WC, Werner S . (1996). Biochem J 320: 659–664.
Narayanan R, Ramaswami M . (2003). J Bioenerg Biomembr 35: 49–55.
Ornitz DM, Itoh N . (2001). Genome Biol 2, reviews3005.1–3005.12.
Postel EH . (2003). J Bioenerg Biomembr 35: 31–40.
Rheinwald JG, Green H . (1975). Cell 6: 331–343.
Rubin JS, Osada H, Finch PW, Taylor WG, Rudikoff S, Aaronson SA . (1989). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 802–806.
Sager R . (1997). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 952–955.
Sato Y, Tsuchiya B, Urao T, Baba H, Shiku H, Kodama T et al. (2000). Pathol Int 50: 200–205.
Schoop V, Mirancea N, Fusenig NE . (1999). J Invest Dermatol 112: 343–353.
Schultz G, Rotatori DS, Clark W . (1991). J Cell Biochem 45: 346–352.
Stahl JA, Leone A, Rosengard AM, Porter L, King CR, Steeg PS . (1991). Cancer Res 51: 445–449.
Stark HJ, Szabowski A, Fusenig NE, Maas-Szabowski N . (2004). Biol Proced Online 6: 55–60.
Steeg PS . (1989). Invasion Metastasis 9: 351–359.
Steeg PS, de la Rosa A, Flatow U, MacDonald NJ, Benedict M, Leone A . (1993). Breast Cancer Res Treat 25: 175–187.
Wei SJ, Trempus CS, Ali RC, Hansen LA, Tennant RW . (2004). J Biol Chem 279: 5993–6004.
Weinstein GD, McCullough JL, Ross PA . (1985). J Invest Dermatol 85: 579–583.
Werner S . (1998). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 9: 153–165.
Werner S, Peters KG, Longaker MT, Fuller-Pace F, Banda MJ, Williams LT . (1992). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 6896–6900.
Werner S, Smola H, Liao X, Longaker MT, Krieg T, Hofschneider PH et al. (1994). Science 266: 819–822.
Werner S, Weinberg W, Liao X, Peters KG, Blessing M, Yuspa SH et al. (1993). EMBO J 12: 2635–2643.
Wilkinson DG, Bailes JA, Champion JE, McMahon AP . (1987). Development 99: 493–500.
Zhang L, Zhou W, Velculescu VE, Kern SE, Hruban RH, Hamilton SR et al. (1997). Science 276: 1268–1272.
Acknowledgements
We thank Christiane Born-Berclaz, Michelle Meyer and Iris Nord for excellent technical assistance, Dr Marcus Gassmann for the generation of the subtractive cDNA library, AMGEN Inc, Thousand Oaks, CA for kindly providing recombinant human KGF, and Dr Daniel Hohl, University of Lausanne for the kind gift of the loricrin antibody. This work was supported by a grant from the EC/Swiss Ministry for Education and Research (LSHG-CT-2003-503447, WOUND) to SW and PB and by grants from the Swiss National Science Foundation (31-61358.00 and 3100A0-109340/1) to SW.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braun, S., Mauch, C., Boukamp, P. et al. Novel roles of NM23 proteins in skin homeostasis, repair and disease. Oncogene 26, 532–542 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209822
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209822
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Proteomic identification of cryostress in epididymal spermatozoa
Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology (2016)
-
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK, NM23, AWD): recent regulatory advances in endocytosis, metastasis, psoriasis, insulin release, fetal erythroid lineage and heart failure; translational medicine exemplified
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2009)
-
The NM23 family in development
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2009)
-
The cystic fibrosis transmembrane recruiter the alter ego of CFTR as a multi-kinase anchor
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2007)