Abstract
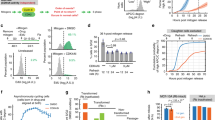
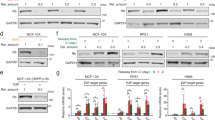
The role of the transcriptional coactivator p300 in cell cycle control has not been analysed in detail due to the lack of appropriate experimental systems. We have now examined cell cycle progression of p300-deficient cancer cell lines, where p300 was disrupted either by gene targeting (p300− cells) or knocked down using RNAi. Despite significant proliferation defects under normal growth conditions, p300-deficient cells progressed rapidly through G1 with premature S-phase entry. Accelerated G1/S transition was associated with early retinoblastoma (RB) hyperphosphorylation and activation of E2F targets. The p300-acetylase activity was dispensable since expression of a HAT-deficient p300 mutant reversed these changes. Co-immunoprecipitation showed p300/RB interaction occurs in vivo during G1, and this interaction has two peaks: in early G1 with unphosphorylated RB and in late G1 with phosphorylated RB. In vitro kinase assays showed that p300 directly inhibits cdk6-mediated RB phosphorylation, suggesting p300 acts in early G1 to prevent RB hyperphosphorylation and delay premature S-phase entry. Paradoxically, continued cycling of p300− cells despite prolonged serum depletion was observed, and this occurred in association with persistent RB hyperphosphorylation. Altogether, these results suggest that p300 has an important role in G1/S control, possibly by modulating RB phosphorylation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait-Si-Ali S, Polesskaya A, Filleur S, Ferreira R, Duquet A, Robin P et al. (2000). Oncogene 19: 2430–2437.
Baluchamy S, Rajabi HN, Thimmapaya R, Navaraj A, Thimmapaya B . (2003). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 9524–9529.
Chan HM, Krstic-Demonacos M, Smith L, Demonacos C, La Thangue NB . (2001). Nat Cell Biol 3: 667–674.
Chan TA, Hermeking H, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . (1999). Nature 401: 616–620.
Chrivia JC, Kwok RP, Lamb N, Hagiwara M, Montminy MR, Goodman RH . (1993). Nature 365: 855–859.
Dimitrova DS, Todorov IT, Melendy T, Gilbert DM . (1999). J Cell Biol 146: 709–722.
Dolbeare F, Kuo WL, Beisker W, Vanderlaan M, Gray JW . (1990). Methods Cell Biol 33: 207–216.
Eckner R, Ewen ME, Newsome D, Gerdes M, DeCaprio JA, Lawrence JB et al. (1994). Genes Dev 8: 869–884.
Gayther SA, Batley SJ, Linger L, Bannister A, Thorpe K, Chin SF et al. (2000). Nat Genet 24: 300–303.
Giordano A, Avantaggiati ML . (1999). J Cell Physiol 181: 218–230.
Goodman RH, Smolik S . (2000). Genes Dev 14: 1553–1577.
Grossman SR . (2001). Eur J Biochem 268: 2773–2778.
Gu W, Roeder RG . (1997). Cell 90: 595–606.
Hagemeier C, Cook A, Kouzarides T . (1993). Nucleic Acids Res 21: 4998–5004.
Iyer NG, Chin SF, Ozdag H, Daigo Y, Hu DE, Cariati M et al. (2004a). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 7386–7391.
Iyer NG, Ozdag H, Caldas C . (2004b). Oncogene 23: 4225–4231.
Kolli S, Buchmann AM, Williams J, Weitzman S, Thimmapaya B . (2001). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 4646–4651.
Kraus WL, Kadonaga JT . (1998). Genes Dev 12: 331–342.
Liu L, Scolnick DM, Trievel RC, Zhang HB, Marmorstein R, Halazonetis TD et al. (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: 1202–1209.
Martinez-Balbas MA, Bauer UM, Nielsen SJ, Brehm A, Kouzarides T . (2000). EMBO J 19: 662–671.
Nguyen DX, Baglia LA, Huang SM, Baker CM, McCance DJ . (2004). EMBO J 23: 1609–1618.
Ozdag H, Batley SJ, Forsti A, Iyer NG, Daigo Y, Boutell J et al. (2002). Br J Cancer 87: 1162–1165.
Rajabi HN, Baluchamy S, Kolli S, Nag A, Srinivas R, Raychaudhuri P et al. (2005). J Biol Chem 280: 361–374.
Sage J, Miller AL, Perez-Mancera PA, Wysocki JM, Jacks T . (2003). Nature 424: 223–228.
Sakaguchi K, Herrera JE, Saito S, Miki T, Bustin M, Vassilev A et al. (1998). Genes Dev 12: 2831–2841.
Sherr CJ, McCormick F . (2002). Cancer Cell 2: 103–112.
Suganuma T, Kawabata M, Ohshima T, Ikeda MA . (2002). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 13073–13078.
Sun Y, Kolligs FT, Hottiger MO, Mosavin R, Fearon ER, Nabel GJ . (2000). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97: 12613–12618.
Waldman T, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . (1995). Cancer Res 55: 5187–5190.
Ward R, Johnson M, Shridhar V, van Deursen J, Couch FJ . (2005). J Med Genet 42: 514–518.
Yang XJ, Ogryzko VV, Nishikawa J, Howard BH, Nakatani Y . (1996). Nature 382: 319–324.
Yao TP, Oh SP, Fuchs M, Zhou ND, Ch'ng LE, Newsome D et al. (1998). Cell 93: 361–372.
Yuan ZM, Huang Y, Ishiko T, Nakada S, Utsugisawa T, Shioya H et al. (1999). Oncogene 18: 5714–5717.
Acknowledgements
We are particularly grateful to Dr S Mittnacht for reagents and technical advice in performing RB kinase assays. We thank Drs MA Ikeda, TP Yao, WL Kraus and J Kadonaga for kindly providing reagents. NGI was recipient of an NMRC (Singapore) Medical Research Fellowship. This work was funded by Cancer Research UK and NMRC (Singapore).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iyer, N., Xian, J., Chin, SF. et al. p300 is required for orderly G1/S transition in human cancer cells. Oncogene 26, 21–29 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209771
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209771
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Opposing roles of the aldo-keto reductases AKR1B1 and AKR1B10 in colorectal cancer
Cellular Oncology (2017)
-
Inhibition of bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) proteins increases NKG2D ligand MICA expression and sensitivity to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma cells: role of cMYC-IRF4-miR-125b interplay
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016)
-
Negative regulation of the p300-p53 interplay by DDX24
Oncogene (2016)
-
Histone acetyltransferase inhibitor II induces apoptosis in glioma cell lines via the p53 signaling pathway
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2014)
-
Selective Inhibition of p300 HAT Blocks Cell Cycle Progression, Induces Cellular Senescence, and Inhibits the DNA Damage Response in Melanoma Cells
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2013)