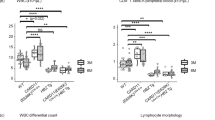
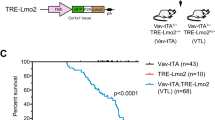
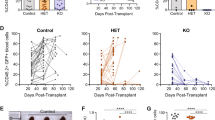
Abstract
Analysis of the INK4A/ARF locus in human T-ALL patients revealed frequent deletions in exon 2, the exon common to both p16INK4A and p14ARF. Other studies have described selective deletion of exon 1β of p14ARF or methylation of the p16INK4A promoter. Therefore, it is unclear from these studies whether loss of p16INK4A and/or p14ARF contributes to the development of T-ALL. To elucidate the relative contribution of the ink4a/arf locus to T-cell leukemogenesis, we mated our tal1 transgenic mice to ink4a/arf−/−, p16ink4a−/−, and p19arf−/− mice and generated tal1/ink4a/arf+/−, tal1/p16ink4a+/−, and tal1/p19arf+/− mice. Each of these mice developed T-cell leukemia rapidly, indicating that loss of either p16ink4a or p19arf cooperates with Tal1 to induce leukemia in mice. Preleukemic studies reveal that Tal1 expression stimulates entry into the cell cycle and thymocyte apoptosis in vivo. Interestingly, mice expressing a DNA-binding mutant of Tal1 do not exhibit increases in S phase cells. The S phase induction is accompanied by an increase in thymocyte apoptosis in tal1 transgenic mice. Whereas apoptosis is reduced to wild-type levels in tal1/ink4a/arf−/− mice, S phase induction remains unaffected. Thus, Tal1 stimulates cell cycle entry independent of the ink4a/arf locus, but its ability to induce apoptosis is Ink4a/Arf-dependent.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batova A, Diccianni MB, Yu JC, Nobori T, Link MP, Pullen J et al. (1997). Cancer Res 57: 832–836.
Baudino TA, Maclean KH, Brennan J, Parganas E, Yang C, Aslanian A et al. (2003). Mol Cell 11: 905–914.
Bellavia D, Campese AF, Alesse E, Vacca A, Felli MP, Balestri A et al. (2000). Embo J 19: 3337–3348.
Cayuela JM, Hebert J, Sigaux F . (1995). Blood 85: 854.
Cayuela JM, Madani A, Sanhes L, Stern MH, Sigaux F . (1996). Blood 87: 2180–2186.
Condorelli GL, Facchiano F, Valtieri M, Proietti E, Vitelli L, Lulli V et al. (1996). Cancer Res 56: 5113–5119.
Condorelli GL, Tocci A, Botta R, Facchiano F, Testa U, Vitelli L et al. (1997). Mol Cell Biol 17: 2954–2969.
Coppola JA, Cole MD . (1986). Nature 320: 760–763.
Drexler HG . (1998). Leukemia 12: 845–859.
Eischen CM, Weber JD, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ, Cleveland JL . (1999). Genes Dev 13: 2658–2669.
Evan GI, Wyllie AH, Gilbert CS, Littlewood TD, Land H, Brooks M et al. (1992). Cell 69: 119–128.
Ferrando AA, Herblot S, Palomero T, Hansen M, Hoang T, Fox EA et al. (2004). Blood 103: 1909–1911.
Ferrando AA, Neuberg DS, Staunton J, Loh ML, Huard C, Raimondi SC et al. (2002). Cancer Cell 1: 75–87.
Gardie B, Cayuela JM, Martini S, Sigaux F . (1998). Blood 91: 1016–1020.
Green AR, DeLuca E, Begley CG . (1991). Embo J 10: 4153–4158.
Harrison CJ . (2001). Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 14: 593–607.
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H, Zawel L, da Costa LT et al. (1998). Science 281: 1509–1512.
Hebert J, Cayuela JM, Berkeley J, Sigaux F . (1994). Blood 84: 4038–4044.
Herblot S, Steff AM, Hugo P, Aplan PD, Hoang T . (2000). Nat Immunol 1: 138–144.
Iavarone A, Garg P, Lasorella A, Hsu J, Israel MA . (1994). Genes Dev 8: 1270–1284.
Jamieson CH, Ailles LE, Dylla SJ, Muijtjens M, Jones C, Zehnder JL et al. (2004). N Engl J Med 351: 657–667.
Kamijo T, Zindy F, Roussel MF, Quelle DE, Downing JR, Ashmun RA et al. (1997). Cell 91: 649–659.
Kees UR, Burton PR, Lu C, Baker DL . (1997). Blood 89: 4161–4166.
Kelliher MA, Seldin DC, Leder P . (1996). Embo J 15: 5160–5166.
Lasorella A, Iavarone A, Israel MA . (1996). Mol Cell Biol 16: 2570–2578.
Look AT . (1997). Science 278: 1059–1064.
O'Neil J, Billa M, Oikemus S, Kelliher M . (2001). Oncogene 20: 3897–3905.
O'Neil J, Calvo J, McKenna K, Krishnamoorthy V, Aster JC, Bassing CH et al. (2005). Blood, 2005-06-2553.
O'Neil J, Shank J, Cusson N, Murre C, Kelliher M . (2004). Cancer Cell 5: 587–596.
Pagliuca A, Gallo P, De Luca P, Lania L . (2000). Cancer Res 60: 1376–1382.
Peverali FA, Ramqvist T, Saffrich R, Pepperkok R, Barone MV, Philipson L . (1994). Embo J 13: 4291–4301.
Rao L, Debbas M, Sabbatini P, Hockenbery D, Korsmeyer S, White E . (1992). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 7742–7746.
Serrano M, Lee H, Chin L, Cordon-Cardo C, Beach D, DePinho RA . (1996). Cell 85: 27–37.
Sharpless NE, Bardeesy N, Lee KH, Carrasco D, Castrillon DH, Aguirre AJ et al. (2001). Nature 413: 86–91.
Staal FJ, Clevers HC . (2005). Nat Rev Immunol 5: 21–30.
Valtieri M, Tocci A, Gabbianelli M, Luchetti L, Masella B, Vitelli L et al. (1998). Cancer Res 58: 562–569.
Weng AP, Ferrando AA, Lee W, Morris JPt, Silverman LB, Sanchez-Irizarry C et al. (2004). Science 306: 269–271.
Zhou M, Gu L, Yeager AM, Findley HW . (1997). Pediatr Hematol Oncol 14: 141–150.
Zindy F, Eischen CM, Randle DH, Kamijo T, Cleveland JL, Sherr CJ et al. (1998). Genes Dev 12: 2424–2433.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Grant from the NIH/NCI (CA096899) to MK. MK is also a scholar of the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shank-Calvo, J., Draheim, K., Bhasin, M. et al. p16Ink4a or p19Arf loss contributes to Tal1-induced leukemogenesis in mice. Oncogene 25, 3023–3031 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209326
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209326
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Stem Cell Leukemia: how a TALented actor can go awry on the hematopoietic stage
Leukemia (2016)
-
Dynamic interaction between TAL1 oncoprotein and LSD1 regulates TAL1 function in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis
Oncogene (2012)
-
Molecular pathogenesis of T-cell leukaemia and lymphoma
Nature Reviews Immunology (2008)