Abstract
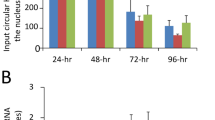
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) core has a pleiotropic effect on various promoters. In this study, we found that the expression of nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 was enhanced in HCV core-expressing cells and, moreover, HCV core interacts directly with the C-terminal end of B23. Using sucrose gradient centrifugation analysis and immunoprecipitation assays, HCV core was found in a large complex containing B23 and its interacting partner transcription factor YY1. Both B23 and HCV core associated with YY1 in the central GA/GK-rich and C-terminal zinc finger domain. These physical interactions between core, B23, and YY1 led to ternary complex formation that was bound to the YY1 response element. In a transient cotransfection experiment, relief of the trans-suppression activity of YY1 on the YY1-response element-driven reporter by core and B23 was found. This is also true when examining the effects of these three constructs on the B23 promoter-driven reporter. Additionally, chromatin immunoprecipitation assays indicated that a transcriptional activation complex consisting of core, together with B23, p300, and YY1, was recruited to the YY1 response element of B23 promoter, and this probably occurred through complex formation between core and these three cellular transcription regulators. This is different from the situation in the absence of core, where YY1 and histone deacetylase 1, but not B23 and p300, were associated on the YY1 element as the transcription repression complex. Together, our results indicate that HCV core can recruit B23 and p300 to relieve the repression effect of YY1 on B23 promoter activity, a property that requires the intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity of p300. Thus, because these three core-associated cellular transcription regulators have a multitude of cellular interacting proteins and are involved in a versatility of cellular processes, the complex formation described here may partially account for the pleiotropic effects of core protein on gene expression and cellular function in HCV-infected cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barba G, Harper F, Harada T, Kohara M, Goulinet S, Matsuura Y et al. (1997). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 1200–1205.
Borer RA, Lehner CF, Eppenberger HM, Nigg EA . (1989). Cell 56: 379–390.
Brockmann D, Lehmkuhler O, Schmucker U, Esche H . (2001). Gene 277: 111–120.
Bruix J, Barrera JM, Calvet X, Ercilla G, Costa J, Sanchez-Tapias JM et al. (1989). Lancet 2: 1004–1006.
Chan HM, La Thangue NB . (2001). J Cell Sci 114: 2363–2373.
Chan PK, Chan FY, Morris SW, Xie Z . (1997). Nucleic Acids Res 25: 1225–1232.
Chang J, Yang SH, Hwang SB, Hahn YS, Sung YC . (1998). J Virol 72: 3060–3065.
Chen CM, You LR, Hwang LH, Lee YHW . (1997). J Virol 71: 9417–9426.
Chen SY, Kao CF, Chen CM, Shih CM, Hsu MJ, Chao CH et al. (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 591–607.
Cheng PL, Chang MH, Chao CH, Lee YHW . (2004). Oncogene 23: 7821–7838.
Choo QL, Kuo G, Weiner AJ, Overby LR, Bradley DW, Houghton M . (1989). Science 244: 359–362.
Colombo E, Marine JC, Danovi D, Falini B, Pelicci PG . (2002). Nat Cell Biol 4: 529–533.
Dhar SK, Lynn BC, Daosukho C, St Clair DK . (2004). J Biol Chem 279: 28209–28219.
Donohoe ME, Zhang X, McGinnis L, Biggers J, Li E, Shi Y . (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: 7237–7244.
Gomez-Gonzalo M, Benedicto I, Carretero M, Lara-Pezzi E, Maldonado-Rodriguez A, Moreno-Otero R et al. (2004). Virology 328: 120–130.
Goodman RH, Smolik S . (2000). Genes Dev 14: 1553–1577.
Gronroos E, Terentiev AA, Punga T, Ericsson J . (2004). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 12165–12170.
Hingorani K, Szebeni A, Olson MO . (2000). J Biol Chem 275: 24451–24457.
Hsieh CL, Chen BF, Wang CC, Liu HH, Chen DS, Hwang LH . (1995). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 214: 910–917.
Huang WH, Yung BY, Syu WJ, Lee YHW . (2001). J Biol Chem 276: 25166–25175.
Hyde-DeRuyscher RP, Jennings E, Shenk T . (1995). Nucleic Acids Res 23: 4457–4465.
Inouye CJ, Seto E . (1994). J Biol Chem 269: 6506–6510.
Ito A, Lai CH, Zhao X, Saito S, Hamilton MH, Appella E et al. (2001). EMBO J 20: 1331–1340.
Kalkhoven E . (2004). Biochem Pharmacol 68: 1145–1155.
Kao CF, Chen SY, Lee YHW . (2004a). J Biomed Sci 11: 72–94.
Kao CF, Chen SY, Chen JY, Lee YHW . (2004b). Oncogene 23: 2472–2483.
Kondo T, Minamino N, Nagamura-Inoue T, Matsumoto M, Taniguchi T, Tanaka N . (1997). Oncogene 15: 1275–1281.
Krippner-Heidenreich A, Walsemann G, Beyrouthy MJ, Speckgens S, Kraft R, Thole H et al. (2005). Mol Cell Biol 25: 3704–3714.
Kuo G, Choo QL, Alter HJ, Gitnick GL, Redeker AG, Purcell RH et al. (1989). Science 244: 362–364.
Kurki S, Peltonen K, Latonen L, Kiviharju TM, Ojala PM, Meek D et al. (2004). Cancer Cell 5: 465–475.
Lai MM, Ware CF . (2000). Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 242: 117–134.
Lee JS, Galvin KM, See RH, Eckner R, Livingston D, Moran E et al. (1995). Genes Dev 9: 1188–1198.
Lewis BA, Tullis G, Seto E, Horikoshi N, Weinmann R, Shenk T . (1995). J Virol 69: 1628–1636.
Liang P, Pardee AB . (1992). Science 257: 967–971.
Machida K, Cheng KT, Sung VM, Lee KJ, Levine AM, Lai MM . (2004a). J Virol 78: 8835–8843.
Machida K, Cheng KT, Sung VM, Shimodaira S, Lindsay KL, Levine AM et al. (2004b). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 4262–4267.
Maiguel DA, Jones L, Chakravarty D, Yang C, Carrier F . (2004). Mol Cell Biol 24: 3703–3711.
McLauchlan J . (2000). J Viral Hepat 7: 2–14.
Moriya K, Fujie H, Shintani Y, Yotsuyanagi H, Tsutsumi T, Ishibashi K et al. (1998). Nat Med 4: 1065–1067.
Moss T, Stefanovsky VY . (2002). Cell 109: 545–548.
Okuda M . (2002). Oncogene 21: 6170–6174.
Palko L, Bass HW, Beyrouthy MJ, Hurt MM . (2004). J Cell Sci 117: 465–476.
Petkova V, Romanowski MJ, Sulijoadikusumo I, Rohne D, Kang P, Shenk T et al. (2001). J Biol Chem 276: 7932–7936.
Ray RB, Ray R . (2001). FEMS Microbiol Lett 202: 149–156.
Ray S, Sherman CT, Lu M, Brasier AR . (2002). Mol Endocrinol 16: 824–836.
Reed KE, Rice CM . (2000). Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 242: 55–84.
Saito I, Miyamura T, Ohbayashi A, Harada H, Katayama T, Kikuchi S et al. (1990). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 6547–6549.
Shi Y, Lee JS, Galvin KM . (1997). Biochim Biophys Acta 1332: F49–66.
Shi Y, Seto E, Chang LS, Shenk T . (1991). Cell 67: 377–388.
Shih CM, Chen CM, Chen SY, Lee YHW . (1995). J Virol 69: 1160–1171.
Shih CM, Lo SJ, Miyamura T, Chen SY, Lee YHW . (1993). J Virol 67: 5823–5832.
Song CZ, Keller K, Murata K, Asano H, Stamatoyannopoulos G . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 7029–7036.
Sui G, Affar el B, Shi Y, Brignone C, Wall NR, Yin P et al. (2004). Cell 117: 859–872.
Sun H, Lu J, Wei L, Wang X, Xu X, Dong M et al. (2004). Mol Immunol 41: 1241–1246.
Takebe Y, Seiki M, Fujisawa J, Hoy P, Yokota K, Arai K et al. (1988). Mol Cell Biol 8: 466–472.
Takemura M, Ohoka F, Perpelescu M, Ogawa M, Matsushita H, Takaba T et al. (2002). Exp Cell Res 276: 233–241.
Tellinghuisen TL, Rice CM . (2002). Curr Opin Microbiol 5: 419–427.
Thomas MJ, Seto E . (1999). Gene 236: 197–208.
van Pelt JF, Severi T, Crabbe T, Eetveldt AV, Verslype C, Roskams T et al. (2004). Cancer Lett 209: 197–205.
Vanden Berghe W, De Bosscher K, Boone E, Plaisance S, Haegeman G . (1999). J Biol Chem 274: 32091–32098.
Watashi K, Shimotohno K . (2003). Cancer Sci 94: 937–943.
Weinmann AS, Bartley SM, Zhang T, Zhang MQ, Farnham PJ . (2001). Mol Cell Biol 21: 6820–6832.
Wu MH, Yung BY . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 48234–48240.
Wu MH, Chang JH, Yung BY . (2002). Carcinogenesis 23: 93–100.
You LR, Chen CM, Yeh TS, Tsai TY, Mai RT, Lin CH et al. (1999). J Virol 73: 2841–2853.
Yuan ZM, Huang Y, Ishiko T, Nakada S, Utsugisawa T, Shioya H et al. (1999). Oncogene 18: 5714–5717.
Yung BY, Chan PK . (1987). Biochim Biophys Acta 925: 74–82.
Acknowledgements
We thank LH Hwang for generously providing HuH-7 cells that constitutively express HCV core protein. We also thank YM Lee, SJ Lo, FF Chen, BY Yung, TP Yao, and JL Juan for providing the plasmids used in this study. We are grateful to R Kirby for critical reading and comments on this manuscript. This work was supported by the following grants to YHW Lee: NHRI-GT-EX89B502L, NHRI-GT-EX89B502Ls, NHRI-EX90-9002BL, NHRI-EX91-9002BL, NHRI-EX92-9002BL, NHRI-EX93-9002BL, and NHRI-EX94-9002BL from the National Health Research Institute, and in part by grant NSC93-2320-010-049 and NSC93-2320-B-010-050 from the National Science Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mai, RT., Yeh, TS., Kao, CF. et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein recruits nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 and coactivator p300 to relieve the repression effect of transcriptional factor YY1 on B23 gene expression. Oncogene 25, 448–462 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209052
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209052
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
YB-1 disrupts mismatch repair complex formation, interferes with MutSα recruitment on mismatch and inhibits mismatch repair through interacting with PCNA
Oncogene (2014)
-
Granzyme M: behind enemy lines
Cell Death & Differentiation (2014)
-
Hepatitis B virus core interacts with the host cell nucleolar protein, nucleophosmin 1
The Journal of Microbiology (2009)