Abstract
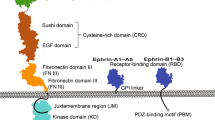
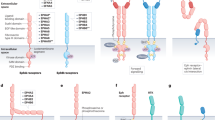
Receptor tyrosine kinases of the Eph family are upregulated in several different types of cancer. One family member in particular, the EphA2 receptor, has been linked to breast, prostate, lung and colon cancer, as well as melanoma. However, mechanisms by which EphA2 contributes to tumor progression are far from clear. In certain tumor cell lines, EphA2 receptor is underphosphorylated, raising the question of whether ligand-induced receptor phosphorylation and its kinase activity play a role in oncogenesis. To test directly the role of EphA2 receptor phosphorylation/kinase activity in tumor progression, we generated EphA2 receptor variants that were either lacking the cytoplasmic domain or carrying a point mutation that inhibits its kinase activity. Expression of these EphA2 mutants in breast cancer cells resulted in decreased tumor volume and increased tumor apoptosis in primary tumors. In addition, the numbers of lung metastases were significantly reduced in both experimental and spontaneous metastasis models. Reduced tumor volume and metastasis are not due to defects in tumor angiogenesis, as there is no significant difference in tumor vessel density between wild-type tumors and tumors expressing EphA2-signaling-defective mutants. In contrast, tumor cells expressing the EphA2 mutants are defective in RhoA GTPase activation and cell migration. Taken together, these results suggest that receptor phosphorylation and kinase activity of the EphA2 receptor, at least in part, contribute to tumor malignancy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berclaz G, Andres A, Albrecht D, Dreher E, Ziemiecki A, Gusterson B and Crompton M . (1996). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 226, 869–875.
Bergers G, Javaherian K, Lo K-M, Folkman J and Hanahan D . (1999). Science, 284, 808–812.
Birgbauer E, Cowan CA, Sretavan DW and Henkemeyer M . (2000). Development, 127, 1231–1241.
Brantley DM, Cheng N, Thompson EJ, Lin Q, Brekken RA, Thorpe PE, Muraoka RS, Cerretti DP, Pozzi A, Jackson D, Lin C and Chen J . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 7011–7026.
Brantley-Sieders D, Caughron J, Hicks D, Pozzi A, Ruiz JC and Chen J . (2004a). J. Cell Sci., 117, 2037–2049.
Brantley-Sieders D and Chen J . (2004). Angiogenesis, 7, 17–28.
Brantley-Sieders D, Schmidt S, Parker M and Chen J . (2004b). Curr Pharmaceutical Des, 10, 3431–3442.
Carles-Kinch K, Kilpatrick KE, Stewart JC and Kinch MS . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 2840–2847.
Cheng N, Brantley D, Liu H, Fanslow W, Cerretti DP, Reith AD, Jackson D and Chen J . (2003). Neoplasia, 5, 445–456.
Cheng N, Brantley DM, Liu H, Lin Q, Enriquez M, Gale NW, Yancopoulos G, Cerretti DP, Daniel TO and Chen J . (2002). Mol. Cancer Res. (formerly Cell Growth and Differentiation), 1, 2–11.
Coffman KT, Hu M, Carles-Kinch K, Tice D, Donacki N, Munyon K, Kifle G, Woods R, Langermann S, Kiener PA and Kinch MS . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 7907–7912.
Dalva MB, Takasu MA, Lin MZ, Shamah SM, Hu L, Gale NW and Greenberg ME . (2000). Cell, 103, 945–956.
Davy A, Nicholas WG, Murray EW, Klinghoffer RA, Soriano P, Feuerstein C and Robbins SM . (1999). Genes Dev, 13, 3125–3135.
Davy A and Robbins SM . (2000). EMBO J, 19, 5396–5405.
Dobrzanski P, Hunter K, Jones-Bonlin S, Chang H, Robinson C, Pritchard S, Zhao H and Ruggeri B . (2004). Cancer Res., 64, 910–919.
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW and Whang EE . (2004a). Oncogene, 23, 1448–1456.
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW and Whang EE . (2004b). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 320, 1096–1102.
Fukata M, Nakagawa M and Kaibuchi K . (2003). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 15, 590–597.
Gale NW, Holland SJ, Valenzuela DM, Flenniken A, Pan L, Ryan TE, Henkemeyer M, Strebhardt K, Hirai H and Wilkinson DG . (1996). Neuron, 17, 9–19.
Grunwald IC, Korte M, Wolfer D, Wilkinson GA, Unsicker K, Lipp HP, Bonhoeffer T and Klein R . (2001). Neuron, 32, 1027–1040.
Gu C and Park S . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 4579–4597.
Gurniak CB and Berg LJ . (1996). Oncogene, 13, 777–786.
Holder N and Klein R . (1999). Development, 126, 2033–2044.
Huai J and Drescher U . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 6689–6694.
Ireton RC and Chen J . (2005). Curr. Cancer Drug Targets, 5, 149–157.
Kinch MS, Moore MB and Harpole DHJ . (2003). Clin. Cancer Res., 9, 613–618.
Koolpe M, Dail M and Pasquale EB . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 46974–46979.
Kullander K and Klein R . (2002). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 3, 475.
Kullander K, Mather NK, Diella F, Dottori M, Boyd AW and Klein R . (2001). Neuron, 29, 73–84.
Lozano E, Bretson M and Braga VMM . (2003). BioEssays, 25, 452–463.
Madhusudan S and Ganesan TS . (2004). Clin. Biochem., 37, 618–635.
Malliri A and Collard JG . (2003). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 15, 583–589.
Manning G, Plowman GD, Hunter T and Sudarsanam S . (2002). Trends Biochem Sci., 27, 514–520.
Miao H, Strebhardt K, Pasquale EB, Shen TL, Guan JL and Wang B . (2004). J. Biol. Chem., 280, 923–932.
Miyazaki T, Kato H, Fukuchi M, Nakajima M and Kuwano H . (2003). Int. J. Cancer, 103, 657–663.
Munarini N, Jager R, Abderhalden S, Zuercher G, Rohrbach V, Loercher S, Pfanner-Meyer B, Andres AC and Ziemiecki A . (2002). J. Cell Sci., 115, 25–37.
Nakamoto M and Bergmann A . (2002). Microsc Res Tech., 59, 58–67.
Noren NK, Lu M, Freeman AL, Koolpe M and Pasquale EB . (2004). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 5583–5588.
Noren NK and Pasquale EB . (2004). Cell Signal., 16, 655–666.
Ogawa K, Pasqualini R, Lindberg RA, Kain R, Freeman AL and Pasquale EB . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 6043–6052.
Pasquale EB . (2005). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 6, 462–475.
Reith AD, Ellis C, Lyman SD, Anderson DM, Williams DE, Bernstein A and Pawson T . (1991). EMBO J., 10, 2451–2459.
Reith AD, Ellis C, Maroc N, Pawson T, Bernsten A and Dubreuil P . (1993). Oncogene, 8, 45–53.
Reith AD, Rottapel R, Giddens E, Brady C, Forrester L and Bernstein A . (1990). Genes Dev., 4, 390–400.
Ridley AJ . (2001). J. Cell Sci., 114, 2713–2722.
Saito T, Masuda N, Miyazaki T, Kanoh K, Suzuki H, Shimura T, Asao T and Kuwano H . (2004). Oncol Rep., 11, 605–611.
Segatto O, King CR, Pierce JH, Di Fiore PP and Aaronson SA . (1988). Mol. Biol. Cell, 8, 5570–5574.
Walker-Daniels J, Hess AR, Hendrix MJC and Kinch MS . (2003). Am. J. Pathol., 162, 1037.
Walker-Daniels J, Riese DJ and Kinch MS . (2002). Mol. Cancer Res., 1, 79–87.
Wicki A and Niggli V . (2001). Int. J. Cancer, 91, 763–771.
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S, Itzykson RA, Come C, Savagner P, Gitelman I, Richardson A and Weinberg RA . (2004). Cell, 117, 927–939.
Zantek ND, Azimi M, Fedor-Chaiken M, Wang B, Brackenbury R and Kinch MS . (1999). Cell Growth Diff, 10, 629–638.
Zelinski DP, Zantek ND, Stewart JC, Irizarry AR and Kinch MS . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 2301–2306.
Zisch AH and Pasquale EB . (1997). Cell Tissue Res., 290, 217–226.
Acknowledgements
We thank Donna Hicks and Yoonha Hwang for expert administrative and technical help, and Rut Porta for early technical assistance. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants CA95004, CA114301, and Department of Defense grant DAMD17-02-1-0604 to J Chen; an NCI breast cancer training Grant 2T32 CA78136 and an DOD predoctoral fellowship BC043255 to WB Fang; Department of Defense postdoctoral fellowship DAMD17-03-1-0379 to D Brantley-Sieders; and an NIH postdoctoral fellowship 5F32 HL074517 to M Parker.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, W., Brantley-Sieders, D., Parker, M. et al. A kinase-dependent role for EphA2 receptor in promoting tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene 24, 7859–7868 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208937
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208937
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Oncogenic functions and therapeutic targeting of EphA2 in cancer
Oncogene (2021)
-
Effect of EphA2 knockdown on melanoma metastasis depends on intrinsic ephrinA1 level
Cellular Oncology (2020)
-
Eph receptor signalling: from catalytic to non-catalytic functions
Oncogene (2019)
-
Dying to communicate: apoptotic functions of Eph/Ephrin proteins
Apoptosis (2018)
-
Overexpression of Ephrin A2 receptors in cancer stromal cells is a prognostic factor for the relapse of gastric cancer
Gastric Cancer (2015)