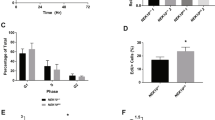
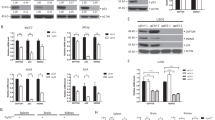
Abstract
The p53 tumour suppressor functions as a transcriptional activator, and several p53-inducible genes that play a critical proapoptotic role have been described. Moreover, p53 regulates the expression of various proteins participating in autoregulatory feedback loops, including proteins that negatively control p53 stability (Mdm2 and Pirh2) or modulate stress-induced phosphorylation of p53 on Ser-46 (p53DINP1 or Wip1), a key event for p53-induced apoptosis. Here, we describe a new systematic analysis of p53 targets using oligonucleotide chips, and report the identification of dapk1 as a novel p53 target. We demonstrate that dapk1 mRNA levels increase in a p53-dependent manner in various cellular settings. Both human and mouse dapk1 genomic loci contain DNA sequences that bind p53 in vitro and in vivo. Since dapk1 encodes a serine/threonine kinase previously shown to suppress oncogene-induced transformation by activating a p19ARF/p53-dependent apoptotic checkpoint, our results suggest that Dapk1 participates in a new positive feedback loop controlling p53 activation and apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcalay M, Meani N, Gelmetti V, Fantozzi A, Fagioli M, Orleth A, Riganelli D, Sebastiani C, Cappelli E, Casciari C, Sciurpi MT, Mariano AR, Minardi SP, Luzi L, Muller H, Di Fiore PP, Frosina G and Pelicci PG . (2003). J. Clin. Invest., 112, 1751–1762.
Barak Y, Juven T, Haffner R and Oren M . (1993). EMBO J., 12, 461–468.
El-Deiry WS . (1998). Semin. Cancer Biol., 8, 345–357.
Esteller M, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Rosell R, Sidransky D, Baylin SB and Herman JG . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 67–70 (Erratum in: Cancer Res., 59, 3853).
Fiscella M, Zhang H, Fan S, Sakaguchi K, Shen S, Mercer WE, Vande Woude GF, O’Connor PM and Appella E . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 6048–6053.
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M . (1997). Nature, 387, 296–299.
Hoh J, Jin S, Parrado T, Edington J, Levine AJ and Ott J . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 8467–8472.
Jeffers JR, Parganas E, Lee Y, Yang C, Wang J, Brennan J, MacLean KH, Han J, Chittenden T, Ihle JN, McKinnon PJ, Cleveland JL and Zambetti GP . (2003). Cancer Cell, 4, 321–328.
Katzenellenbogen RA, Baylin SB and Herman JG . (1999). Blood, 93, 4347–4353.
Kissil JL, Feinstein E, Cohen O, Jones PA, Tsai YC, Knowles MA, Eydmann ME and Kimchi A . (1997). Oncogene, 15, 403–407.
Kuo ML, Duncavage EJ, Mathew R, den Besten W, Pei D, Naeve D, Yamamoto T, Cheng C, Sherr CJ and Roussel MF . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 1046–1053.
Lane DP . (1992). Nature, 358, 15–16.
Leng RP, Lin Y, Ma W, Wu H, Lemmers B, Chung S, Parant JM, Lozano G, Hakem R and Benchimol S . (2003). Cell, 112, 779–791.
Levine AJ . (1997). Cell, 88, 323–331.
Marine JC and Jochemsen A . (2004). Cell Cycle, 3, 900–904.
Migliorini D, Denchi EL, Danovi D, Jochemsen A, Capillo M, Gobbi A, Helin K, Pelicci PG and Marine JC . (2002). Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 5527–5538.
Nakano K and Vousden KH . (2001). Mol. Cell, 7, 683–694.
Okamura S, Arakawa H, Tanaka T, Nakanishi H, Ng CC, Taya Y, Monden M and Nakamura Y . (2001). Mol. Cell, 8, 85–94.
Raveh T, Droguett G, Horwitz MS, DePinho RA and Kimchi A . (2001). Nat. Cell Biol., 3, 1–7.
Sanchez-Cespedes M, Esteller M, Wu L, Nawroz-Danish H, Yoo GH, Koch WM, Jen J, Herman JG and Sidransky D . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 892–895.
Schmitt CA, Fridman JS, Yang M, Baranov E, Hoffman RM and Lowe SW . (2002). Cancer Cell, 1, 289–298.
Takekawa M, Adachi M, Nakahata A, Nakayama I, Itoh F, Tsukuda H, Taya Y and Imai K . (2000). EMBO J., 19, 6517–6526.
Villunger A, Michalak EM, Coultas L, Mullauer F, Bock G, Ausserlechner MJ, Adams JM and Strasser A . (2003). Science, 302, 1036–1038.
Vousden KH and Lu X . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 594–604.
Zindy F, Eischen CM, Randle DH, Kamijo T, Cleveland JL, Sherr CJ and Roussel MF . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 2424–2433.
Acknowledgements
We thank Alberto Gobbi and Manuella Capillo for help with mice, Simone Minardi, Loris Bernard and Laura Tizzoni for technical help with the Affymetrix and Q-PCR technologies. We also thank M Rouselle and C Sherr (St Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, TN, USA) for the pMTArf cell line, R Jaenisch (Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research, Cambridge, USA) for the p53-deficient ES cells and K Vousden for the SAOS-2-p53 cell line. A Martoriati and G Doumont were supported by grants from the FNRS, FRIA and Télévie, respectively. This work was supported in part by grants from FB Insurance, AICR and ‘Fédération Belge contre le Cancer’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary information accompanies the paper on http://www.dmbr.ugent.be/lmcb/contents/p53targets/.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martoriati, A., Doumont, G., Alcalay, M. et al. dapk1, encoding an activator of a p19ARF-p53-mediated apoptotic checkpoint, is a transcription target of p53. Oncogene 24, 1461–1466 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208256
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208256
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Death-associated protein kinase 1 as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease
Translational Neurodegeneration (2024)
-
Death-associated protein kinase 1 phosphorylates MDM2 and inhibits its protein stability and function
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2023)
-
STAT3 regulates miR93-mediated apoptosis through inhibiting DAPK1 in renal cell carcinoma
Cancer Gene Therapy (2021)
-
Comparison of Selected Protein Levels in Tumour and Surgical Margin in a Group of Patients with Oral Cavity Cancer
Biochemical Genetics (2017)
-
Transcription control of DAPK
Apoptosis (2014)