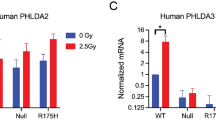
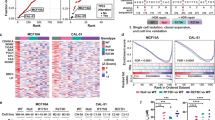
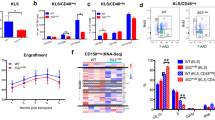
Abstract
Genetic analysis of radiation-induced lymphomas from p53 heterozygous or null mice has revealed a high frequency of genetic alterations on mouse chromosome 19. Detailed microsatellite analysis of chromosome 19 deletions identified three independent regions of loss of heterozygosity, one of which was refined to a 0.3 Mb interval that contained the Pten tumor suppressor gene. More than 50% of radiation-induced tumors from p53+/− and p53−/− mice showed heterozygous loss of one Pten allele. In most cases, the remaining allele was wild type and expressed, suggesting that Pten is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor gene for mouse lymphoma development. This conclusion was supported by the detection of specific intragenic deletions in Pten in tumors that retained one wild-type allele. Pten heterozygous mice were just as sensitive as p53+/− mice to induction of tumors by radiation, and surprisingly, the double p53+/−Pten+/−mice were equivalent to p53 null mice in radiation sensitivity. Despite the fact that Pten appears to be a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor gene, most tumors from both the single and double heterozygous mice had lost the remaining wild-type allele. The mechanism of loss in all cases involved the complete chromosome, suggesting that it is driven by other tumor suppressor genes on this chromosome. This sensitized screen therefore identified complementary roles for Pten and p53 pathways in suppression of tumor development induced by radiation exposure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal ML, Taylor WR, Chernov MV, Chernova OB and Stark GR . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 1–4.
Ali IU, Schriml L M and Dean M . (1999). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 9, 1922–1932.
Butler MP, Wang SI, Chaganti RS, Parsons R and Dalla-Favera R . (1999). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 24, 322–327.
Cai WW, Mao JH, Chow CW, Damani S, Balmain A and Bradley A . (2002). Nat. Biotechnol., 20, 393–396.
Caspari T . (2000). Curr. Biol., 10, R315–R317.
Dahia PL, Aguiar RC, Alberta J, Kum JB, Caron S, Sill H, Marsh DJ, Ritz J, Freedman A, Stiles C and Eng C . (1999). Hum. Mol. Genet., 8, 185–193.
Di Cristofano A, Pesce B, Cordon-Cardo C and Pandolfi PP . (1998). Nat. Genet., 19, 348–355.
el-Deiry WS . (1998). Semin. Cancer Biol., 8, 345–357.
Fero ML, Randel E, Gurley KE, Roberts JM and Kemp CJ . (1998). Nature, 396, 177–180.
Freeman DJ, Li AG, Wei G, Li HH, Kertesz N, Lesche R, Whale AD, Martinez-Diaz H, Rozengurt N, Cardiff RD, Liu X and Wu H . (2003). Cancer Cell, 3, 117–130.
Frisk T, Foukakis T, Dwight T, Lundberg J, Hoog A, Wallin G, Eng C, Zedenius J and Larsson C . (2002). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 35, 74–80.
Gronbaek K, Zeuthen J, Guldberg P, Ralfkiaer E and Hou-Jensen K . (1998). Blood, 91, 4388–4390.
Herranz M, Urioste M, Santos J, Martinez-Delgado JB, Rivas C, Benitez J and Fernandez-Piqueras J . (2000). Leukemia, 14, 1325–1327.
Izumoto S, Ohnishi T, Kanemura H, Arita N, Maruno M, Moriuchi T, Suzuki S and Yoshimine T . (2001). J. Neurooncol., 53, 21–26.
Kemp CJ, Wheldon T and Balmain A . (1994). Nat. Genet., 8, 66–69.
Kurose K, Gilley K, Matsumoto S, Watson PH, Zhou XP and Eng C . (2002). Nat. Genet., 32, 355–357.
Kwabi-Addo B, Giri D, Schmidt K, Podsypanina K, Parsons R, Greenberg N and Ittmann M . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 11563–11568.
Lakin ND and Jackson SP . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 7644–7655.
Leslie NR and Downes CP . (2002). Cell Signal., 14, 285–295.
Mayo LD and Donner DB . (2002). Trends Biochem. Sci., 27, 462–467.
Mayo LD, Dixon JE, Durden DL, Tonks NK and Donner DB . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 5484–5489.
Oren M, Damalas A, Gottlieb T, Michael D, Taplick J, Leal JF, Maya R, Moas M, Seger R, Taya Y and Ben-Ze'ev A . (2002). Biochem. Pharmacol., 64, 865–871.
Santos J, Herranz M, Fernandez M, Vaquero C, Lopez P and Fernandez-Piqueras J . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 2186–2189.
Santos J, Montagutelli X, Acevedo A, Lopez P, Vaquero C, Fernandez M, Arnau MR, Szatanik M, Salido E, Guenet JL and Fernandez-Piqueras J . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 6680–6683.
Shin KH, Kim JM, Rho KS, Park KH, Oh JE and Min BM . (2002). Int. J. Oncol., 21, 997–1001.
Sjoling A, Samuelson E, Adamovic T, Behboudi A, Rohme D and Levan G . (2003). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 36, 70–79.
Stambolic V, MacPherson D, Sas D, Lin Y, Snow B, Jang Y, Benchimol S and Mak TW . (2001). Mol. Cell, 8, 317–325.
Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL, Stambolic V, Elia AJ, Sasaki T, del Barco Barrantes I, Ho A, Wakeham A, Itie A, Khoo W, Fukumoto M and Mak TW . (1998). Curr. Biol., 8, 1169–1178.
Tang B, Bottinger EP, Jakowlew SB, Bagnall KM, Mariano J, Anver MR, Letterio JJ and Wakefield LM . (1998). Nat. Med., 4, 802–807.
Virolle T, Adamson ED, Baron V, Birle D, Mercola D, Mustelin T and de Belle I . (2001). Nat. Cell Biol., 3, 1124–1128.
Waite KA and Eng C . (2002). Am. J. Hum. Genet., 70, 829–884.
Wick W, Furnari FB, Naumann U, Cavenee WK and Weller M . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 3936–3943.
Acknowledgements
These studies were initially supported by the Commission of the European Communities and the Cancer Research Campaign (UK), and subsequently by NCI Grant U01 CA84244 to AB. The UCSF Cancer Center Genome Core was essential for the sequencing. Special thanks go to the CRC Beatson Institute animal house staff, and to Dr PP Pandolfi for kindly providing us Pten KO mice. Dr Jian-Hua Mao is the recipient of a Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Fellowship. Dr Jesus Perez-Losada has a Fellowship from the ‘Ministerio de Educacion y Ciencia of Spain’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, JH., Wu, D., Perez-Losada, J. et al. Genetic interactions between Pten and p53 in radiation-induced lymphoma development. Oncogene 22, 8379–8385 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207083
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207083
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
PTEN loss in the continuum of common cancers, rare syndromes and mouse models
Nature Reviews Cancer (2011)
-
PTEN regulation by Akt–EGR1–ARF–PTEN axis
The EMBO Journal (2009)
-
Multi-step lymphomagenesis deduced from DNA changes in thymic lymphomas and atrophic thymuses at various times after γ-irradiation
Oncogene (2007)
-
Beyond PTEN mutations: the PI3K pathway as an integrator of multiple inputs during tumorigenesis
Nature Reviews Cancer (2006)
-
Genomic instability in radiation-induced mouse lymphoma from p53 heterozygous mice
Oncogene (2005)