Abstract
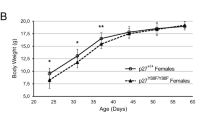
Cyclin E and p27Kip1 are key regulators for cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) acting at the G1-/S-phase transition of the cell cycle. Whereas cyclin E is required for the activation of Cdk2, p27Kip1 is a specific Cdk inhibitor and can block cell division. High levels of cyclin E and low levels of p27Kip1 expression have been associated with malignant lymphomas in humans; the level of p27Kip1 is even considered of prognostic significance. However, mice that lack p27Kip1 do not develop any malignant lymphomas despite a pronounced lymphoid hyperplasia in thymus and spleen. We have previously described transgenic mice that carry a construct in which the cyclin E cDNA is under the control of the CD2 promoter/enhancer region and thus express high levels of cyclin E in the T-cell compartment (CD2-cyclin E). These animals are not predisposed for T-cell lymphomas in the absence of other cooperating events. Here we show that T-cells from CD2-cyclin E mice that at the same time are deficient for p27Kip1 show a significantly higher Cdk2 activity than cells from wilde-type or single mutant animals. Accordingly, a higher percentage of T cells in S/G2/M phase is found in CD2-cyclin E/p27Kip1−/− mice. After a long latency period of over 200 days, these animals develop spontaneous monoclonal T cell lymphoma whereas none of the single CD2-cyclin E transgenics or the p27Kip1-deficient mice showed any sign of lymphoid malignancies. Our findings demonstrate that a deregulation of control mechanisms at the G1/S transition by the combination of high cyclin E levels in the absence of p27Kip1 is sufficient to predispose mice to develop lymphoid malignancies and further support a role of p27Kip1 as a tumor suppressor and of cyclin E as a dominant oncogene.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartek J, Bartkova J and Lukas J . (1996). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 8, 805–914.
Bodrug SE, Warner BJ, Bath ML, Lindeman GJ, Harris AW and Adams JM . (1994) EMBO J., 13, 2124–2130.
Bortner DM and Rosenberg MP . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 453–459.
Deng C, Zhang P, Harper JW, Elledge SJ and Leder P . (1995). Cell, 82, 675–684.
Di Cristofano A, De Acetis M, Koff A, Cordon-Cardo C and Pandolfi PP . (2001). Nat. Genet., 27, 222–224.
Donnellan R and Chetty R . (1999). FASEB J., 13, 773–780.
Erlanson M and Landberg G . (2001). Leukemia Lymphoma, 40, 461–470.
Erlanson M, Portin C, Linderholm B, Lindh J, Roos G and Landberg G . (1998). Blood, 92, 770–777.
Fero ML, Randel E, Gurley KE, Roberts JM and Kemp CJ . (1998). Nature, 396, 177–180.
Fero ML, Rivkin M, Tasch M, Porter P, Carow CE, Firpo E, Polyak K, Tsai LH, Broudy V, Perlmutter RM, Kaushansky K and Roberts JM . (1996). Cell, 85, 733–744.
Galaktionov K, Lee AK, Eckstein J, Draetta G, Meckler J, Loda M and Beach D . (1995). Science, 269, 1575–1577.
Geisen C and Möröy T . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 39909–39918.
Haas K, Johannes C, Geisen C, Schmidt T, Karsunky H, Blass-Kampmann S, Obe G and Möröy T . (1997a). Oncogene, 15, 2615–2623.
Haas K, Staller P, Geisen C, Bartek J, Eilers M and Möröy T . (1997b). Oncogene, 15, 179–192.
Hall M, Bates S and Peters G . (1995). Oncogene, 11, 1581–1588.
Hall M and Peters G . (1996). Adv. Cancer Res., 68, 67–108.
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA . (2000). Cell, 100, 57–70.
Harper JW and Elledge SJ . (1996). Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 6, 56–64.
Hogan B, Beddington R, Costantini F and Lacy E . (1994). Manipulating the Mouse Embryo. CSH-Laboratory Press, New York, USA.
Hwang HC, Martins CP, Bronkhorst Y, Randel E, Berns A, Fero M and Clurman BE . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 11293–11298.
Karsunky H, Geisen C, Schmidt T, Haas K, Zevnik B, Gau E and Möröy T . (1999). Oncogene 18, 7816–8274.
Kiyokawa H, Kineman RD, Manova-Todorova KO, Soares VC, Hoffman ES, Ono M, Khanam D, Hayday AC, Frohman LA and Koff A . (1996). Cell 85, 721–732.
Lovec H, Grzeschiczek A, Kowalski MB and Möröy T . (1994a). EMBO J., 13, 3487–3495.
Lovec H, Sewing A, Lucibello FC, Müller R and Möröy T . (1994b). Oncogene, 9, 323–326.
Lüscher B . (2001). Gene, 277, 1–14.
Martins CP and Berns A . (2002). EMBO J., 21, 3739–3748.
Minella AC, Swanger J, Bryant E, Welcker M, Hwang H and Clurman BE . (2002). Curr. Biol., 12, 1817–1827.
Morgan DO . (1995). Nature, 374, 131–134.
Möröy T, Fisher P, Guidos C, Ma A, Zimmerman K, Tesfaye A, DePinho R, Weissman I and Alt FW . (1990). EMBO J., 9, 3659–3666.
Möröy T, Grzeschiczek A, Petzold S and Hartmann KU . (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 10734–10738.
Nakayama K, Ishida N, Shirane M, Inomata A, Inoue T, Shishido N, Horii I, Loh DY and Nakayama K . (1996). Cell, 85, 707–720.
Planas-Silva MD and Weinberg RA . (1997). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 9, 768–772.
Polyak K, Kato JY, Solomon MJ, Sherr CJ, Massague J, Roberts JM and Koff A . (1994). Genes Dev., 8, 9–22.
Reynisdottir I, Polyak K, Iavarone A and Massague J . (1995). Genes Dev., 9, 1831–1845.
Ruas M Peters G . (1998). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1378, F115–F177.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF and Maniatis T . (1989). Molecular Cloning – A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA.
Sherr CJ . (1996). Science, 274, 1672–1677.
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM . (1995). Genes Dev., 9, 1149–1163.
Slingerland J and Pagano M . (2000). J. Cell Physiol., 183, 10–17.
Weinberg RA . (1996). Cell, 85, 457–459.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Mo 435/11-1) and the Dr Mildred Scheel Stiftung für Krebsforschung and the Fonds der chemischen Industrie.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geisen, C., Karsunky, H., Yücel, R. et al. Loss of p27Kip1 cooperates with cyclin E in T-cell lymphomagenesis. Oncogene 22, 1724–1729 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206340
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206340
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Combined loss of p21waf1/cip1 and p27kip1 enhances tumorigenesis in mice
Laboratory Investigation (2011)
-
Deregulated cyclin E promotes p53 loss of heterozygosity and tumorigenesis in the mouse mammary gland
Oncogene (2006)
-
Cyclin E in normal and neoplastic cell cycles
Oncogene (2005)
-
Use of human cDNA arrays to analyze canine gene expression in two cases of canine lymphoma
Comparative Clinical Pathology (2005)
-
Different cooperating effect of p21 or p27 deficiency in combination with INK4a/ARF deletion in mice
Oncogene (2004)