Abstract
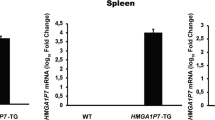
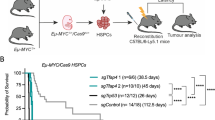
The basic helix–loop–helix factor E2A plays an important role in the development of B and T lymphocytes. In addition, E2a has been implicated as a gene with tumor suppressor activity, since mice deficient for E2a succumb to T cell lymphomas. We have performed retroviral tagging in EμMyc transgenic mice to identify genes that contribute to lymphomagenesis. The EμMyc transgenic mouse is a well-established model of a common translocation in human B cell lymphomas. Analyses of the proviral insertion sites in the MuLV-induced lymphomas revealed that a number of T cell lymphomas carried proviral insertions in the promoter region of E2a. These proviral insertions yield hybrid viral-E2a mRNAs resulting in a marked rise in E2A protein levels. The proviral insertions in E2a were predominantly of clonal origin indicating that E2a insertions are early events in these T cell lymphomas. The primary oncogenic effect of E2A is likely to be associated with enhancement of transcription of the c-Myc transgene via binding to the regulatory immunoglobulin enhancers. The results herein thus provide the first evidence that in a specific setting E2A overexpression can contribute to T-lymphomagenesis. This implies that E2a contains oncogenic features in addition to the previously described tumor suppressive properties.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, Corcoran LM, Alexander WS, Cory S, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL . 1985 Nature 318: 533–538
Adams JM, Harris AW, Strasser A, Ogilvy S, Cory S . 1999 Oncogene 18: 5268–5277
Alexander WS, Schrader JW, Adams JM . 1987 Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 1436–1444
Alkema MJ, van der Lugt NM, Bobeldijk RC, Berns A, van Lohuizen M . 1995 Nature 374: 724–727
Allen JD, Verhoeven E, Domen J, van der Valk M, Berns A . 1997 Oncogene 15: 1133–1141
Bain G, Engel I, Robanus Maandag EC, te Riele HP, Voland JR, Sharp LL, Chun J, Huey B, Pinkel D, Murre C . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 4782–4791
Bain G, Gruenwald S, Murre C . 1993 Mol. Cell. Biol. 13: 3522–3529
Bain G, Maandag EC, Izon DJ, Amsen D, Kruisbeek AM, Weintraub BC, Krop I, Schlissel MS, Feeney AJ, van Roon M . 1994 Cell 79: 885–892
Bain G, Quong MW, Soloff RS, Hedrick SM, Murre C . 1999 J. Exp. Med. 190: 1605–1616
Barndt RJ, Dai M, Zhuang Y . 2000 Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 6677–6685
Benezra R, Davis RL, Lockshon D, Turner DL, Weintraub H . 1990 Cell 61: 49–59
Berns A, van der Lugt N, Alkema M, van Lohuizen M, Domen J, Acton D, Allen J, Laird PW, Jonkers J . 1994 Symp. Quant. Biol. 59: 435–447
Domen J, van der Lugt NM, Acton D, Laird PW, Linders K, Berns A . 1993 J. Exp. Med. 178: 1665–1673
Engel I, Johns C, Bain G, Rivera RR, Murre C . 2001 J. Exp. Med. 194: 733–745
Engel I, Murre C . 1999 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 996–1001
Felsher DW, Bishop JM . 1999 Mol. Cell 4: 199–207
Fisher GH, Wellen SL, Klimstra D, Lenczowski JM, Tichelaar JW, Lizak MJ, Whitsett JA, Koretsky A, Varmus HE . 2001 Genes Dev. 15: 3249–3262
Gilks CB, Bear SE, Grimes HL, Tsichlis PN . 1993 Mol. Cell. Biol. 13: 1759–1768
Gorer PA . 1950 Br. J. Cancer 4: 372–379
Grimes HL, Gilks CB, Chan TO, Porter S, Tsichlis PN . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 14569–14573
Hsu B, Marin MC, el-Naggar AK, Stephens LC, Brisbay S, McDonnell TJ . 1995 Oncogene 11: 175–179
Inaba T, Roberts WM, Shapiro LH, Jolly KW, Raimondi SC, Smith SD, Look AT . 1992 Science 257: 531–534
Jacobs JJ, Kieboom K, Marino S, DePinho RA, van Lohuizen M . 1999a Nature 397: 164–168
Jacobs JJ, Scheijen B, Voncken JW, Kieboom K, Berns A, van Lohuizen M . 1999b Genes Dev. 13: 2678–2690
Jonkers J, Berns A . 1996 Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1287: 29–57
Jonkers J, Korswagen HC, Acton D, Breuer M, Berns A . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 441–450
Kamps MP, Murre C, Sun XH, Baltimore D . 1990 Cell 60: 547–555
Kee BL, Murre C . 1998 J. Exp. Med. 188: 699–713
Kochetov AV, Ischenko IV, Vorobiev DG, Kel AE, Babenko VN, Kisselev LL, Kolchanov NA . 1998 FEBS Lett. 440: 351–355
Kuppers R, Dalla-Favera R . 2001 Oncogene 20: 5580–5594
Langdon WY, Harris AW, Cory S, Adams JM . 1986 Cell 47: 11–18
Mikkers H, Allen J, Knipscheer P, Romeyn L, Hart A, Vink E, Berns A . 2002 Nature Genet. (in press)
Murre C, McCaw PS, Vaessin H, Caudy M, Jan LY, Jan YN, Cabrera CV, Buskin JN, Hauschka SD, Lassar AB . 1989 Cell 58: 537–544
Nourse J, Mellentin JD, Galili N, Wilkinson J, Stanbridge E, Smith SD, Cleary ML . 1990 Cell 60: 535–545
Park ST, Nolan GP, Sun XH . 1999 J. Exp. Med. 189: 501–508
Peverali FA, Ramqvist T, Saffrich R, Pepperkok R, Barone MV, Philipson L . 1994 EMBO J. 13: 4291–4301
Rivera RR, Johns CP, Quan J, Johnson RS, Murre C . 2000 Immunity 12: 17–26
Sakamuro D, Eviner V, Elliott KJ, Showe L, White E, Prendergast GC . 1995 Oncogene 11: 2411–2418
Scheijen B, Jonkers J, Acton D, Berns A . 1997 J. Virol. 71: 9–16
Schlissel M, Voronova A, Baltimore D . 1991 Genes Dev. 5: 1367–1376
Shen CP, Kadesch T . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 4518–4524
van 't Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He YD, Hart AA, Mao M, Peterse HL, van der Kooy K, Marton MJ, Witteveen AT, Schreiber GJ, Kerkhoven RM, Roberts C, Linsley PS, Bernards R, Friend SH . 2002 Nature 415: 530–536
van der Lugt NM, Domen J, Verhoeven E, Linders K, van der Gulden H, Allen J, Berns A . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 2536–2544
van der Putten H, Terwindt E, Berns A, Jaenisch R . 1979 Cell 18: 109–116
van Lohuizen M, Verbeek S, Krimpenfort P, Domen J, Saris C, Radaszkiewicz T, Berns A . 1989 Cell 56: 673–682
van Lohuizen M, Verbeek S, Scheijen B, Wientjens E, van der Gulden H, Berns A . 1991 Cell 65: 737–752
Voronova AF, Adler HT, Sefton BM . 1987 Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 4407–4413
Yan W, Young AZ, Soares VC, Kelley R, Benezra R, Zhuang Y . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 7317–7327
Zhao F, Vilardi A, Neely RJ, Choi JK . 2001 Mol. Cell. Biol. 21: 6346–6357
Zhuang Y, Soriano P, Weintraub H . 1994 Cell 79: 875–884
Zweidler-Mckay PA, Grimes HL, Flubacher MM, Tsichlis PN . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 4024–4034
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank C Murre for providing reagents, N Bosnie, L Rijswijk, A Zwerver, T Maidment, C Spaans and F van der Ahé for animal care, and M Nawijn for critically reading the manuscript. This work was supported by the Dutch Cancer Society (H Mikkers) and the Leukemia Society of America (J Allen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikkers, H., Allen, J. & Berns, A. Proviral activation of the tumor suppressor E2a contributes to T cell lymphomagenesis in EμMyc transgenic mice. Oncogene 21, 6559–6566 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205930
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205930
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of novel Bach2 transcripts and protein isoforms through tagging analysis of retroviral integrations in B-cell lymphomas
BMC Molecular Biology (2009)
-
Retroviral insertional mutagenesis: past, present and future
Oncogene (2005)
-
Fgf10 is an oncogene activated by MMTV insertional mutagenesis in mouse mammary tumors and overexpressed in a subset of human breast carcinomas
Oncogene (2004)