Abstract
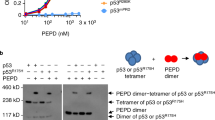
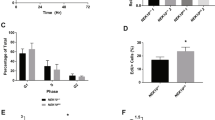
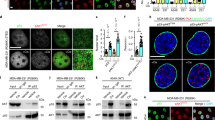
p53 is a pivotal regulator of apoptosis but its mechanism of action is obscure. We report that the polyproline (PP) region located between p53's transactivation and DNA binding domains is necessary to induce apoptosis but not cell growth arrest. The PP region was dispensable for DNA binding, inhibition of SAOS-2 tumor cell growth, suppression of E1A+RAS cell transformation, and cell cycle inhibition. A temperature-sensitive dominant inhibitory p53 mutant lacking PP (p53tsΔPP) retained its ability to cooperate with adenovirus E1A in transformation of primary BRK cells. However, while activation of wt p53 induced apoptosis in E1A+p53ts-transformed cells, activation of p53ΔPP induced cell cycle arrest but not apoptosis in E1A+p53tsΔPP-transformed cells. Similarly, PP deletion abolished apoptosis in LoVo colon carcinoma cells, which are killed by wt p53 overexpression. Transactivation was largely unaffected by PP deletion. Significantly, BAX induction was intact, indicating that additional events are required for p53 to induce apoptosis. As a recently described site for familial mutation in at least one breast cancer family, the PP region represents a domain that may be altered in human tumors. We concluded that p53's ability to induce apoptosis is dispensable for inhibiting cell growth and transformation and that the PP region plays a crucial role in apoptotic signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakamuro, D., Sabbatini, P., White, E. et al. The polyproline region of p53 is required to activate apoptosis but not growth arrest. Oncogene 15, 887–898 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201263
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201263
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
TP53 and p21 (CDKN1A) polymorphisms and the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus
Advances in Rheumatology (2023)
-
The proline rich domain of p53 is dispensable for MGMT-dependent DNA repair and cell survival following alkylation damage
Cell Death & Differentiation (2017)
-
Does p53 codon 72 polymorphism have a prognostic value in carcinoma of the vulva and vagina?
Medical Oncology (2017)
-
Association study between the TP53 Rs1042522G/C polymorphism and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in a Chinese Han population
Rheumatology International (2017)
-
Association between p53 polymorphism at codon 72 and recurrent spontaneous abortion
Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology [Medical Sciences] (2016)