Abstract
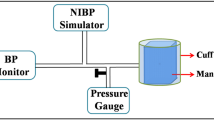
The performance of five units of the A&D UA-767 NIBP monitor and five units of the Welch Allyn Spot Vital Signs noninvasive blood pressure monitor was evaluated with the Biotek BP Pump blood pressure simulator under a variety of conditions. Using the simulator to provide a normal blood pressure waveform at 80 bpm over a range of pressures, it was found that the mean bias for the combined results from the A&D monitors was 1.9±2.8 mmHg and from the Welch Allyn monitors was 0.7±2.4 mmHg. No individual measurement showed a bias greater than 10 mmHg. A bias of greater than 5 mmHg was present in 28 out of 150 measurements for the A&D monitor and 10 out of 150 measurements for the Welch Allyn monitor. These results are comparable with ratings achieved by the instruments when tested previously according to the British Hypertension Society protocol, but testing with a simulator allowed assessment of aspects of performance which were not included in the British Hypertension Society protocol.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langford NJ, Ferner RE . Toxicity of mercury. J Hum Hypertens 1999; 13: 651–656.
O'Brien E et al. Working group on blood pressure monitoring of the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol for validation of blood pressure measuring devices in adults. Blood Pressure Monit 2002; 7: 3–17.
O'Brien E et al on behalf of the European Society of Hypertension Working Group on Blood Pressure Monitoring. Blood pressure measuring devices: validated instruments. BMJ 2001; 322: 531–536.
Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation. The National Standard of Electronic or Automated Sphygmomanometers. AAMI: Arlington, VA, 1987.
O'Brien E et al. The British Hypertension Society protocol for the evaluation of automated and semiautomated blood pressure measuring devices with special reference to ambulatory systems. J Hypertens 1990; 8: 607–619.
O'Brien E et al. The British Hypertension Society protocol for the evaluation of blood pressure measuring devices. J Hypertens 1993; 11(Suppl 2): S43–S63.
Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation. American National Standard. Electronic or Automated Sphygmomanometers. AAMI: Arlington, VA, 1993.
O'Brien E, Atkins N . A comparison of the BHS and AAMI protocols for validating blood pressure measuring devices: can the two be reconciled? J Hypertens 1994; 12: 1089–1094.
Amoore JN, Geake WB . Evaluation of the Critikon 8100 and Spacelabs 90207 non-invasive blood pressure monitors using a test simulator. J Hum Hypertens 1997; 11: 163–169.
Rogoza AN, Pavlova TS, Sergeeva MV . Validation of A&D UA-767 device for the self easurement of blood pressure. Blood Pressure Monit 2000; 5: 227–231.
Jones CR, Taylor K, Poston L, Shennan AH . Validation of the Welch Allyn ‘Vital Signs’ oscillometric blood pressure monitor. J Hum Hypertens 2001; 15: 191–195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, P., Dennis, J. & Railton, R. Evaluation of the A&D UA-767 and Welch Allyn Spot Vital Signs noninvasive blood pressure monitors using a blood pressure simulator. J Hum Hypertens 19, 197–203 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001804
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001804