Abstract
Objective:
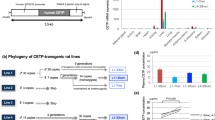
To investigate the mechanism by which fat-specific transgenic expression of resistin affects fatty acid metabolism in the spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR).
Design:
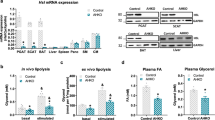
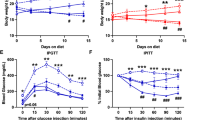
Basal- and adrenaline-stimulated lipolysis, basal- and insulin-stimulated lipogenesis as well as the site (glycerol versus acyl moiety) of glucose incorporated into triglycerides were determined in adipose tissue isolated from SHR-Resistin transgenic and SHR control rats.
Results:
A moderate expression of transgenic resistin in adipose tissue was associated with significant increase in the FFA/glycerol ratio during adrenaline-stimulated lipolysis in the SHR-Resistin transgenic rats (3.27±0.26) compared to SHR controls (2.11±0.10, P=0.0005). Transgenic SHR also exhibited a significant decrease in FFA re-esterification in adipose tissue (approximately by 23%).
Conclusion:
These findings raise the possibility that the prodiabetic effects of transgenic resistin may be partly mediated by increased FFA release from adipose tissue due to impaired FFA re-esterification in adipocytes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM et al. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001; 409: 307–312.
Pravenec M, Kazdová L, Landa V, Zidek V, Mlejnek P, Jansa P et al. Transgenic and recombinant resistin impair skeletal muscle glucose metabolism in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 45209–45215.
Vrána A, Kazdová L . Increased adipose tissue lipolysis in a hypertriglyceridemic rat line. Ann NY Acad Sci 1997; 827: 510–513.
Folch J, Lees M, Stanley GHS . A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 1957; 226: 497–509.
Vrána A, Fábry P, Kazdová L . Effect of dietary fructose on fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissue and on triglyceride concentration in blood in the rat. Nutr Metab 1973; 15: 305–313.
Sreenan S, Keck S, Fuller T, Cockburn B, Burant CF . Effects of troglitazone on substrate storage and utilization in insulin-resistant rats. Am J Physiol 1999; 276: E1119–E1129.
Rajala MW, Obici S, Scherer PE, Rossetti L . Adipose-derived resistin and gut-derived resistin-like molecule-beta selectively impair insulin action on glucose production. J Clin Invest 2003; 111: 225–230.
Banerjee RR, Rangwala SM, Shapiro JS, Rich AS, Rhoades B, Qi Y et al. Regulation of fasted blood glucose by resistin. Science 2004; 303: 1195–1198.
Satoh H, Nguyen MT, Miles PD, Imamura T, Usui I, Olefsky JM . Adenovirus-mediated chronic ‘hyper-resistinemia‘ leads to in vivo insulin resistance in normal rats. J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 224–231.
Muse ED, Obici S, Bhanot S, Monia BP, McKay RA, Rajala MW et al. Role of resistin in diet-induced hepatic insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 232–239.
Rangwala SM, Rich AS, Rhoades B, Shapiro JS, Obici S, Rossetti L et al. Abnormal glucose homeostasis due to chronic hyperresistinemia. Diabetes 2004; 53: 1937–1941.
Shrago E, Spenneta T, Shahidsaless FM, Elson C . Glyceroneogenesis in rat and guinea pig adipose tissue during the fed and fasted states. Metabolism 1978; 27: 563–569.
Reshef L, Olswang Y, Cassuto H, Blum B, Croniger CM, Kalhan SC et al. Glyceroneogenesis and the triglyceride/fatty acid cycle. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 30413–30416.
Tordjman J, Chauvet G, Quette J . Thiazolidinediones block fatty acid release by inducing glyceroneogenesis in fat cells. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 18785–18790.
Beale EG, Hammer RE, Antoine B, Forest C . Disregulated glyceroneogenesis: PCK1 as a candidate diabetes and obesity gene. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2004; 15: 129–135.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grant 301/03/0751 from the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic to MP, by grant 1M6837805002 from the Ministry of Education of the Czech Republic to MP, grant 7403–3 from Internal Grant Agency of the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic to LK and grants TWO1236 and HL63709 from the National Institutes of Health to TK. MP is an International Research Scholar of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pravenec, M., Kazdová, L., Cahová, M. et al. Fat-specific transgenic expression of resistin in the spontaneously hypertensive rat impairs fatty acid re-esterification. Int J Obes 30, 1157–1159 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803237
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803237