Abstract
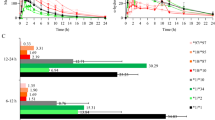
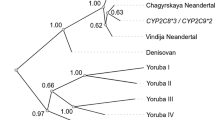
In 97 unselected volunteers and two additional homozygous carriers of CYP2C9*3, we investigated the oral clearance of torsemide in relation to 37 polymorphisms at the CYP2C gene locus. Torsemide total oral clearance was linearly associated with the number of CYP2C9*3 alleles (geometric mean: 59, 40 and 20 ml/min in carriers of no, one and two alleles) and so were the methyl- and ring-hydroxylation but not the carboxylation clearance. Haplotypes including the CYP2C9*3 allele were similarly associated with the clearances but no other variant and no haplotype not including the CYP2C9*3 variant. The extended haplotype length (EHL) of the CYP2C9 haplotypes was positively associated with higher activity of the gene product. Torsemide total oral clearance was predictable with r2=82.1% using plasma concentrations at 0.5, 1, 2 and 24 h. In conclusion, torsemide's biotransformation strongly depended on the CYP2C9*3 variant but no other. Higher clearance CYP2C9 haplotypes appear to be evolutionarily selected.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miners JO, Birkett DJ . Cytochrome P4502C9: an enzyme of major importance in human drug metabolism. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1998; 45: 525–538.
Kirchheiner J, Tsahuridu MWJ, Roots I, Brockmöller J . The CYP2C9 polymorphism: from enzyme kinetics to clinical dose recommendations. Personalized Med 2004; 1: 63–84.
Wilkinson GR . Drug metabolism and variability among patients in drug response. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 2211–2221.
Kirchheiner J, Brockmöller J . Clinical consequences of cytochrome P450 2C9 polymorphisms. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005; 77: 1–16.
Totah RA, Rettie AE . Cytochrome P450 2C8: substrates, inhibitors, pharmacogenetics, and clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005; 77: 341–352.
Rendic S . Summary of information on human CYP enzymes: human P450 metabolism data. Drug Metab Rev 2002; 34: 83–448.
Klotz U, Schwab M, Treiber G . CYP2C19 polymorphism and proton pump inhibitors. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2004; 95: 2–8.
Kirchheiner J, Nickchen K, Bauer M, Wong ML, Licinio J, Roots I et al. Pharmacogenetics of antidepressants and antipsychotics: the contribution of allelic variations to the phenotype of drug response. Mol Psychiatry 2004; 9: 442–473.
Kinobe RT, Parkinson OT, Mitchell DJ, Gillam EM . P450 2C18 catalyzes the metabolic bioactivation of phenytoin. Chem Res Toxicol 2005; 18: 1868–1875.
de Morais SM, Wilkinson GR, Blaisdell J, Nakamura K, Meyer UA, Goldstein JA . The major genetic defect responsible for the polymorphism of S-mephenytoin metabolism in humans. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 15419–15422.
DeLozier TC, Lee SC, Coulter SJ, Goh BC, Goldstein JA . Functional characterization of novel allelic variants of CYP2C9 recently discovered in southeast Asians. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005; 315: 1085–1090.
DeLozier TC, Tsao CC, Coulter SJ, Foley J, Bradbury JA, Zeldin DC et al. CYP2C44, a new murine CYP2C that metabolizes arachidonic acid to unique stereospecific products. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004; 310: 845–854.
Veenstra DL, Blough DK, Higashi MK, Farin FM, Srinouanprachan S, Rieder MJ et al. CYP2C9 haplotype structure in European American warfarin patients and association with clinical outcomes. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005; 77: 353–364.
Takahashi H, Ieiri I, Wilkinson GR, Mayo G, Kashima T, Kimura S et al. 5′-Flanking region polymorphisms of CYP2C9 and their relationship to S-warfarin metabolism in white and Japanese patients. Blood 2004; 103: 3055–3057.
Shintani M, Ieiri I, Inoue K, Mamiya K, Ninomiya H, Tashiro N et al. Genetic polymorphisms and functional characterization of the 5′-flanking region of the human CYP2C9 gene: in vitro and in vivo studies. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2001; 70: 175–182.
Sabeti PC, Reich DE, Higgins JM, Levine HZ, Richter DJ, Schaffner SF et al. Detecting recent positive selection in the human genome from haplotype structure. Nature 2002; 419: 832–837.
Walsh EC, Sabeti P, Hutcheson HB, Fry B, Schaffner SF, de Bakker PI et al. Searching for signals of evolutionary selection in 168 genes related to immune function. Hum Genet 2006; 119: 92–102.
Schirmer M, Toliat MR, Haberl M, Suk A, Kamdem LK, Klein K et al. Genetic signature consistent with selection against the CYP3A4*1B allele in non-African populations. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2006; 16: 59–71.
Miners JO, Coulter S, Birkett DJ, Goldstein JA . Torsemide metabolism by CYP2C9 variants and other human CYP2C subfamily enzymes. Pharmacogenetics 2000; 10: 267–270.
Miners JO, Rees DL, Valente L, Veronese ME, Birkett DJ . Human hepatic cytochrome P450 2C9 catalyzes the rate-limiting pathway of torsemide metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1995; 272: 1076–1081.
Vormfelde SV, Engelhardt S, Zirk A, Meineke I, Tuchen F, Kirchheiner J et al. CYP2C9 polymorphisms and the interindividual variability in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the loop diuretic drug torsemide. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2004; 76: 557–566.
Kerdpin O, Elliot DJ, Boye SL, Birkett DJ, Yoovathaworn K, Miners JO . Differential contribution of active site residues in substrate recognition sites 1 and 5 to cytochrome P450 2C8 substrate selectivity and regioselectivity. Biochemistry 2004; 43: 7834–7842.
Kirchheiner J, Bauer S, Meineke I, Rohde W, Prang V, Meisel C et al. Impact of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 polymorphisms on tolbutamide kinetics and the insulin and glucose response in healthy volunteers. Pharmacogenetics 2002; 12: 101–109.
Rieder MJ, Reiner AP, Gage BF, Nickerson DA, Eby CS, McLeod HL et al. Effect of VKORC1 haplotypes on transcriptional regulation and warfarin dose. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 2285–2293.
Kaminsky LS, de Morais SM, Faletto MB, Dunbar DA, Goldstein JA . Correlation of human cytochrome P4502C substrate specificities with primary structure: warfarin as a probe. Mol Pharmacol 1993; 43: 234–239.
Kim JS, Nafziger AN, Gaedigk A, Dickmann LJ, Rettie AE, Bertino Jr JS . Effects of oral vitamin K on S- and R-warfarin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: enhanced safety of warfarin as a CYP2C9 probe. J Clin Pharmacol 2001; 41: 715–722.
Yasar U, Dahl ML, Christensen M, Eliasson E . Intra-individual variability in urinary losartan oxidation ratio, an in vivo marker of CYP2C9 activity. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2002; 54: 183–185.
Wedlund PJ, Aslanian WS, McAllister CB, Wilkinson GR, Branch RA . Mephenytoin hydroxylation deficiency in Caucasians: frequency of a new oxidative drug metabolism polymorphism. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1984; 36: 773–780.
Cascorbi I, Drakoulis N, Brockmöller J, Maurer A, Sperling K, Roots I . Arylamine N-acetyltransferase (NAT2) mutations and their allelic linkage in unrelated Caucasian individuals: correlation with phenotypic activity. Am J Hum Genet 1995; 57: 581–592.
Ahmadi KR, Weale ME, Xue ZY, Soranzo N, Yarnall DP, Briley JD et al. A single-nucleotide polymorphism tagging set for human drug metabolism and transport. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 84–89.
Walton R, Kimber M, Rockett K, Trafford C, Kwiatkowski D, Sirugo G . Haplotype block structure of the cytochrome P450 CYP2C gene cluster on chromosome 10. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 915–916; author reply 916.
Anonymous. The International HapMap Project. Nature 2003; 426: 789–796.
Crespi CL, Miller VP . The R144C change in the CYP2C9*2 allele alters interaction of the cytochrome P450 with NADPH:cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase. Pharmacogenetics 1997; 7: 203–210.
Johnson DL, Lewis BC, Elliot DJ, Miners JO, Martin LL . Electrochemical characterisation of the human cytochrome P450 CYP2C9. Biochem Pharmacol 2005; 69: 1533–1541.
Yasar U, Lundgren S, Eliasson E, Bennet A, Wiman B, de Faire U et al. Linkage between the CYP2C8 and CYP2C9 genetic polymorphisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 299: 25–28.
Depre M, Van Hecken A, Oeyen M, De Lepeleire I, Laethem T, Rothenberg P et al. Effect of aprepitant on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of warfarin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2005; 61: 341–346.
Miners JO, Birkett DJ . Use of tolbutamide as a substrate probe for human hepatic cytochrome P450 2C9. Methods Enzymol 1996; 272: 139–145.
Tomalik-Scharte D, Jetter A, Kinzig-Schippers M, Skott A, Sorgel F, Klaassen T et al. Effect of propiverine on cytochrome P450 enzymes: a cocktail interaction study in healthy volunteers. Drug Metab Dispos 2005; 33: 1859–1866.
Scordo MG, Pengo V, Spina E, Dahl ML, Gusella M, Padrini R . Influence of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on warfarin maintenance dose and metabolic clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2002; 72: 702–710.
Chaobal HN, Kharasch ED . Single-point sampling for assessment of constitutive, induced, and inhibited cytochrome P450 3A activity with alfentanil or midazolam. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005; 78: 529–539.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–265.
Lewontin RC . The interaction of selection and linkage. Ii. Optimum models. Genetics 1964; 50: 757–782.
Zeggini E, Barton A, Eyre S, Ward D, Ollier W, Worthington J et al. Characterisation of the genomic architecture of human chromosome 17q and evaluation of different methods for haplotype block definition. BMC Genet 2005; 6: 21.
Ding K, Zhou K, Zhang J, Knight J, Zhang X, Shen Y . The effect of haplotype-block definitions on inference of haplotype-block structure and htSNPs selection. Mol Biol Evol 2005; 22: 148–159.
Zhu X, Zhang S, Kan D, Cooper R . Haplotype block definition and its application. Pac Symp Biocomput 2004; 9: 152–163.
Stephens M, Donnelly P . A comparison of bayesian methods for haplotype reconstruction from population genotype data. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 1162–1169.
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P . A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 68: 978–989.
Sabeti PC, Walsh E, Schaffner SF, Varilly P, Fry B, Hutcheson HB et al. The case for selection at CCR5-Delta32. PLoS Biol 2005; 3: e378.
Engelhardt S, Meineke I, Brockmöller J . Improved solid-phase extraction and HPLC measurement of torasemide and its important metabolites. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2006; 831: 31–35.
Sheiner LB, Beal SL . Some suggestions for measuring predictive performance. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 1981; 9: 503–512.
Acknowledgements
The study was in part supported by the national genome research network Grants 01 GS 0107 and 01 GR 0416. The skilful contributions of Franziska Tuchen, Michaela Torn and Jan Westermann to the clinical study part and that of Sabine Engelhardt to the drug concentration analyses are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Duality of Interest
The authors are unaware of any further duality of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vormfelde, S., Schirmer, M., Toliat, M. et al. Genetic variation at the CYP2C locus and its association with torsemide biotransformation. Pharmacogenomics J 7, 200–211 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500410
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500410
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A pharmacogenetic investigation of intravenous furosemide in decompensated heart failure: a meta-analysis of three clinical trials
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2017)
-
Relative Impact of Genotype and Enzyme Induction on the Metabolic Capacity of CYP2C9 in Healthy Volunteers
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2009)
-
Interindividual Variation in the Pharmacokinetics of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol as Related to Genetic Polymorphisms in CYP2C9
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2009)
-
Prediction of the Effects of Genetic Polymorphism on the Pharmacokinetics of CYP2C9 Substrates from In Vitro Data
Pharmaceutical Research (2009)
-
The Polymorphisms Asn130Asp and Val174Ala in OATP1B1 and the CYP2C9 Allele *3 Independently Affect Torsemide Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2008)