Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Decoupled temperature and pressure hydrothermal synthesis of carbon sub-micron spheres from cellulose
Decoupled temperature and pressure hydrothermal synthesis of carbon sub-micron spheres from cellulose
Temperature and pressure are typically dependent parameters in hydrothermal processes. Here, authors devise a hydrothermal system that allows independent control of these parameters and realize low-temperature fast synthesis of carbon sub-micron spheres directly from cellulose at higher pressure.
- Shijie Yu
- , Xinyue Dong
- & Hui Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Breaking the nanoparticle’s dispersible limit via rotatable surface ligands
Breaking the nanoparticle’s dispersible limit via rotatable surface ligands
Nanoparticles that can disperse in a broad range of solvents are desirable. Here, the authors report nanoparticles featuring rotatable surface ligands that enable the formation of stable dispersions in a wide range of solvents.
- Yue Liu
- , Na Peng
- & Shikuan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Bis-Schiff base linkage-triggered highly bright luminescence of gold nanoclusters in aqueous solution at the single-cluster level
Bis-Schiff base linkage-triggered highly bright luminescence of gold nanoclusters in aqueous solution at the single-cluster level
Boosting the luminescence of atomically precise metal clusters is a main goal in view of applications. Here, the authors describe a strategy to increase the photoluminescence quantum yield of water-soluble gold clusters at the single-cluster level via formation of bis-Schiff base linkages, providing detailed insight into the mechanism.
- Haohua Deng
- , Kaiyuan Huang
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancement of electrocatalytic oxygen evolution by chiral molecular functionalization of hybrid 2D electrodes
Enhancement of electrocatalytic oxygen evolution by chiral molecular functionalization of hybrid 2D electrodes
While solar-to-fuel catalysis requires the careful transfer of electrons, there are still challenges understanding how electron spin contributes to reactivity. Here, authors employ chiral fused thiadiazole-helicenes to control spin polarization in oxygen evolution electrocatalysts.
- Yunchang Liang
- , Karla Banjac
- & Magalí Lingenfelder
-
Article
| Open Access Epitaxial growth of inch-scale single-crystal transition metal dichalcogenides through the patching of unidirectionally orientated ribbons
Epitaxial growth of inch-scale single-crystal transition metal dichalcogenides through the patching of unidirectionally orientated ribbons
Here, the authors report the direct growth of periodic arrays of 2D semiconductor ribbons by exploiting the step edges of high-miller-index Au facets, showing potential for 2D electronic devices. The synthesized ribbons could also be merged to obtain wafer-scale single-crystal monolayers.
- Pengfei Yang
- , Dashuai Wang
- & Yanfeng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic non-classical crystallization drives hierarchical structuring of efficient circularly polarized phosphors
Biomimetic non-classical crystallization drives hierarchical structuring of efficient circularly polarized phosphors
Chiral emitters with high photoluminescence quantum yield are desirable for use in circularly polarized LEDs. The authors demonstrate the transfer of chirality from nanoscale copper iodide clusters to microscale chiral luminescent polycrystals by non-classical crystallization.
- Li-Zhe Feng
- , Jing-Jing Wang
- & Hong-Bin Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast self-heating synthesis of robust heterogeneous nanocarbides for high current density hydrogen evolution reaction
Ultrafast self-heating synthesis of robust heterogeneous nanocarbides for high current density hydrogen evolution reaction
Industry-level water splitting requires highly active and stable hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) catalysts. Herein, an ultrafast self-heating synthesis delivers robust Mo2C/MoC/CNT HER catalysts that can work at 1000 mA cm−2 for 14 days.
- Chenyu Li
- , Zhijie Wang
- & Kai Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Assembling covalent organic framework membranes via phase switching for ultrafast molecular transport
Assembling covalent organic framework membranes via phase switching for ultrafast molecular transport
Covalent organic framework (COF) membranes are important in low energy and cost-effective molecular separations but most COF membranes are assembled via a one-step procedure by concurrent polymerization and crystallization which compromises the ordered structure. Here, the authors propose a two-step phase switching strategy for assembling compact and highly crystalline COF membranes decoupling the polymerization and the crystallization process.
- Niaz Ali Khan
- , Runnan Zhang
- & Zhongyi Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid crystals of neat boron nitride nanotubes and their assembly into ordered macroscopic materials
Liquid crystals of neat boron nitride nanotubes and their assembly into ordered macroscopic materials
Boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTS) have only been shown to dissolve in chlorosulfonic acid (CSA) at low concentrations. Here the authors successfully demonstrate the formation of liquid crystals of BNNTs in CSA that can be used to produce macroscopically aligned neat fibers of BNNTs.
- Cedric J. Simonsen Ginestra
- , Cecilia Martínez-Jiménez
- & Matteo Pasquali
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene nanoribbons initiated from molecularly derived seeds
Graphene nanoribbons initiated from molecularly derived seeds
The authors report on harnessing sp2-organic molecules as a basis for uniformly initiating the homoepitaxial-like, size-controlled, synthesis of sub-5 nm semiconducting graphene nanoribbons for electronics via chemical vapor deposition.
- Austin J. Way
- , Robert M. Jacobberger
- & Michael S. Arnold
-
Article
| Open Access Homogeneous solution assembled Turing structures with near zero strain semi-coherence interface
Homogeneous solution assembled Turing structures with near zero strain semi-coherence interface
Turing structures emerge in reaction-diffusion processes far from thermodynamic equilibrium involving chemicals with different diffusion coefficients in classic Turing systems. Here, authors show that a Turing structure with near zero strain semi-coherence interfaces can be constructed in homogeneous solutions.
- Yuanming Zhang
- , Ningsi Zhang
- & Zhigang Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Topological control of liquid-metal-dealloyed structures
Topological control of liquid-metal-dealloyed structures
Liquid metal dealloying is a method to fabricate bicontinuous composite structures with ultra-high interfacial area for diverse applications. This paper demonstrates how the topology of those structures can be controlled by the choice of melt composition.
- Longhai Lai
- , Bernard Gaskey
- & Alain Karma
-
Article
| Open Access Direct synthesis of highly stretchable ceramic nanofibrous aerogels via 3D reaction electrospinning
Direct synthesis of highly stretchable ceramic nanofibrous aerogels via 3D reaction electrospinning
Ceramic aerogels are generally brittle and often tend to structurally collapse under large external tensile strain. Here the authors synthesize large-scale stretchable ceramic aerogels with interwoven crimped nanofibers by combining electrohydrodynamic method and 3D reaction electrospinning.
- Xiaota Cheng
- , Yi-Tao Liu
- & Bin Ding
-
Comment
| Open Access Large-scale synthesis of graphene and other 2D materials towards industrialization
Large-scale synthesis of graphene and other 2D materials towards industrialization
The industrial application of two-dimensional (2D) materials strongly depends on the large-scale manufacturing of high-quality 2D films and powders. Here, the authors analyze three state-of-the art mass production techniques, discussing the recent progress and remaining challenges for future improvements.
- Soo Ho Choi
- , Seok Joon Yun
- & Young Hee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Hygroscopic holey graphene aerogel fibers enable highly efficient moisture capture, heat allocation and microwave absorption
Hygroscopic holey graphene aerogel fibers enable highly efficient moisture capture, heat allocation and microwave absorption
Functionalization of aerogel fibers, characterized by high porosity and low thermal conductivity, to obtain multifunctional materials is highly desirable. Here the authors report hygroscopic holey graphene aerogel fibers hosting LiCl salt, enabling moisture capture, heat allocation, and microwave absorption performance.
- Yinglai Hou
- , Zhizhi Sheng
- & Xuetong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Inter-element miscibility driven stabilization of ordered pseudo-binary alloy
Inter-element miscibility driven stabilization of ordered pseudo-binary alloy
Synthetic routes of stabilizing crystal structures can discover atomic pickings with desired properties. Here the authors demonstrate inter-element miscibility of In can act as a stabilizer to create Z3-based ordered alloy without significantly changing the original density of state of Z3-FePd3.
- Kenshi Matsumoto
- , Ryota Sato
- & Toshiharu Teranishi
-
Article
| Open Access Ammonia pools in zeolites for direct fabrication of catalytic centers
Ammonia pools in zeolites for direct fabrication of catalytic centers
Reduction process is a key step to fabricate metal zeolite catalysts, but existing reduction technologies are always energy intensive and inevitably cause the agglomeration of metallic particles or destroy zeolite structure. Here the authors find that zeolites after ion exchange of ammonium display an interesting and unexpected self-reducing feature.
- Jie Yao
- , Yingluo He
- & Noritatsu Tsubaki
-
Article
| Open Access Data-informed discovery of hydrolytic nanozymes
Data-informed discovery of hydrolytic nanozymes
Developing hydrolytic nanozymes remains challenging. Here the authors present a rational methodology to design hydrolytic nanozyme by developing a data-informed strategy to screen and identify potential scaffold and active sites of hydrolase-like nanozyme.
- Sirong Li
- , Zijun Zhou
- & Hui Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Solvent-free bottom-up patterning of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks
Solvent-free bottom-up patterning of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks
There is a long-standing interest in the development of patterning process for porous materials. Here, the authors report a solvent-free bottom-up approach for the patterning of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks; well-resolved patterns with features down to the scale of 100 nm can be achieved.
- Yurun Miao
- , Dennis T. Lee
- & Michael Tsapatsis
-
Article
| Open Access Coordination modulation of iridium single-atom catalyst maximizing water oxidation activity
Coordination modulation of iridium single-atom catalyst maximizing water oxidation activity
Single-atom catalysts represent a promising materials class for efficient catalytic transformations. Here, authors prepare a high surface distribution density of iridium atoms on nickel-iron sulfide nanosheet arrays to deliver high water oxidation activity and stability.
- Zhanwu Lei
- , Wenbin Cai
- & Ruiguo Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Domain-selective thermal decomposition within supramolecular nanoribbons
Domain-selective thermal decomposition within supramolecular nanoribbons
Molecular self-assembly in water is conventionally limited to amphiphilic molecules. This study harnesses sacrificial surface groups and a post-assembly chemical reaction to form nanostructures unachievable by spontaneous self-assembly alone.
- Yukio Cho
- , Ty Christoff-Tempesta
- & Julia H. Ortony
-
Article
| Open Access Strong metal-support interactions induced by an ultrafast laser
Strong metal-support interactions induced by an ultrafast laser
Constructing strong metal-support interactions (SMSI) is an effective means of regulating the interfacial properties of noble metal-based supported catalysts. Here, the authors propose a strategy of ultrafast laser-induced SMSI that can be constructed on a CeO2-supported Pt system by confining electric field in localized interface.
- Jian Zhang
- , Dezhi Zhu
- & Chang-An Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A reasonable approach for the generation of hollow icosahedral kernels in metal nanoclusters
A reasonable approach for the generation of hollow icosahedral kernels in metal nanoclusters
The origin of the hollow icosahedral M12 kernel in metal nanoclusters is under debate. Here the authors demonstrate the Au alloying-induced kernel collapse from small-sized nano-building blocks as a viable approach for the generation of hollow icosahedral M12 kernel in metal nanoclusters.
- Xi Kang
- , Xiao Wei
- & Manzhou Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-selective formation of ordered 1D and 2D GaBi structures on wurtzite GaAs nanowire surfaces
Self-selective formation of ordered 1D and 2D GaBi structures on wurtzite GaAs nanowire surfaces
Site-selected crystal material synthesis at the atomic scale has been a long-standing challenge. Here the authors use nanowire crystal phase heterostructures as templates for self-selective growth of one- and two-dimensional GaBi nanostructures, which allows versatile design with atomic-scale precision.
- Yi Liu
- , Johan V. Knutsson
- & Rainer Timm
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing designer quantum states in stable macrocycle quantum corrals
Visualizing designer quantum states in stable macrocycle quantum corrals
Creating atomically-precise quantum architectures with high digital fidelity and desired quantum states is an important goal for quantum technology applications. Here the authors devise an on-surface synthetic protocol to construct atomically-precise covalently linked organic quantum corrals with the formation of a series of new quantum resonance states.
- Xinnan Peng
- , Harshitra Mahalingam
- & Jiong Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Approaching disorder-tolerant semiconducting polymers
Approaching disorder-tolerant semiconducting polymers
In conjugated polymers, n-doping is often limited by the tradeoff between doping efficiency and charge carrier mobilities, since dopants often randomly distribute within polymers, leading to significant structural and energetic disorder. Here, the authors screen a large number of polymer building block combinations and explore the possibility of designing n-type conjugated polymers with good tolerance to dopant-induced disorder.
- Xinwen Yan
- , Miao Xiong
- & Ting Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Surface lattice engineering for fine-tuned spatial configuration of nanocrystals
Surface lattice engineering for fine-tuned spatial configuration of nanocrystals
The spatial configuration of heterostructured nanocrystals has important roles in their applications, but it is difficult to fine tune. Here the authors report a surface lattice engineering approach that can be used to achieve precise control of geometrical symmetry, spatial composition, and dimension of metal heterostructured nanocrystals.
- Bo Jiang
- , Yifei Yuan
- & Jun Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Topological phase transition in chiral graphene nanoribbons: from edge bands to end states
Topological phase transition in chiral graphene nanoribbons: from edge bands to end states
Graphene nanoribbons are potential systems for engineering topological phases of matter, but the pre-required gapped phases are difficult to find. Here, the authors show that chiral graphene nanoribbons undergo a transition from metallic to topological insulators, and then to trivial band insulators as they are narrowed down to nanometer widths.
- Jingcheng Li
- , Sofia Sanz
- & Jose Ignacio Pascual
-
Article
| Open Access Flat epitaxial quasi-1D phosphorene chains
Flat epitaxial quasi-1D phosphorene chains
Similarly to graphene, attempts to fabricate phosphorene by epitaxy or starting from a few layers of bulk black phosphorus have failed so far. Here, the authors present a controllable bottom-up approach to grow atomically thin, crystalline 1D flat phosphorus chains on a Ag(111) substrate.
- Wei Zhang
- , Hanna Enriquez
- & Hamid Oughaddou
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-fast single-crystal polymerization of large-sized covalent organic frameworks
Ultra-fast single-crystal polymerization of large-sized covalent organic frameworks
Rapid growth of highly crystalline Covalent organic framework (COF) materials remains challenging. Here, the authors accelerate single-crystal polymerization using supercritical CO2 and realize the fabrication of two-dimensional COF single crystals within several minutes.
- Lan Peng
- , Qianying Guo
- & Dacheng Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Anion-exchange-mediated internal electric field for boosting photogenerated carrier separation and utilization
Anion-exchange-mediated internal electric field for boosting photogenerated carrier separation and utilization
Research on the bulk internal electric field (IEF) regulation is significant for designing high-efficiency photocatalysts. Here, the authors report distinctive bismuth oxyhydroxide nanorods photocatalyst and increase the bulk IEF intensity by halogen ions exchange.
- Tong Han
- , Xing Cao
- & Yadong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of pyrrole derivatives with aggregation-induced phosphorescence characteristics for time-resolved and two-photon luminescence imaging
Rational design of pyrrole derivatives with aggregation-induced phosphorescence characteristics for time-resolved and two-photon luminescence imaging
Aggregation-induced emission (AIE) fluorescence probes are indispensable for biomedical imaging, however, interference with tissue autofluorescence results in low signal-to-noise ratio limiting the development of bioimaging with AIE materials. Here the authors develop AIEgen room-temperature phosphors with long emission lifetimes efficiently eliminating intereference with the background signal in imaging.
- Jianhui Yang
- , Yahui Zhang
- & Xin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring atomic diffusion for in situ fabrication of different heterostructures
Tailoring atomic diffusion for in situ fabrication of different heterostructures
Atomic diffusion is a powerful tool for the synthesis of heterostructures, even though controlled atomic diffusion is difficult to achieve. Here, the authors control solid-solid atomic diffusion between an Ag nanowire and a Te nanowire, producing 1D heterostructures by applying an electrical bias inside a TEM.
- Hui Zhang
- , Tao Xu
- & Litao Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Imparting multi-functionality to covalent organic framework nanoparticles by the dual-ligand assistant encapsulation strategy
Imparting multi-functionality to covalent organic framework nanoparticles by the dual-ligand assistant encapsulation strategy
Despite many reports on nanoparticle-covalent organic frameworks (COF) composites, a universal strategy for the synthesis of monodisperse core-shell structured COF nanocomposites remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a strategy for interfacial growth of highly crystalline COFs on functional nanoparticles with abundant optical, electrical and magnetic properties.
- Liang Chen
- , Wenxing Wang
- & Xiaomin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Tailored growth of single-crystalline InP tetrapods
Tailored growth of single-crystalline InP tetrapods
It is challenging to control the growth of colloidal III-V quantum dots, due to complex reaction pathways. Here, the authors isolate a single-crystalline tetrapod species as a late-stage intermediate and use it as a tailored-growth platform in colloidal synthesis.
- Youngsik Kim
- , Hyekyoung Choi
- & Sohee Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale cooperative adsorption for materials control
Nanoscale cooperative adsorption for materials control
Adsorption is a fundamentally important process but challenging to quantify, especially at the nanoscale. Here, the authors map the adsorption affinity and cooperativity of various ligands on single gold nanoparticles and discover adsorption crossover behaviors between different facets, leading to a strategy to control particle shape.
- Rong Ye
- , Ming Zhao
- & Peng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Phase management in single-crystalline vanadium dioxide beams
Phase management in single-crystalline vanadium dioxide beams
Control of the phases associated with the metal-insulator transition in VO2 underpins its applications as a phase change material. Here, the authors report phase management by means of oxide inhibitor-assisted growth and present high-performance VO2 actuators based on asymmetric phase transition routes.
- Run Shi
- , Yong Chen
- & Chun Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access A mechanochromic donor-acceptor torsional spring
A mechanochromic donor-acceptor torsional spring
Force sensing using mechanochromic polymers is currently limited to two state systems and does not allow directly correlating the force with the absorption or emission wavelength. Here, the authors present a mechanochromic donor-acceptor torsional spring that undergoes force-induced planarization during uniaxial elongation leading to force dependent red-shifted absorption and emission spectra.
- Maximilian Raisch
- , Wafa Maftuhin
- & Michael Sommer
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoengineering of cathode layers for solid oxide fuel cells to achieve superior power densities
Nanoengineering of cathode layers for solid oxide fuel cells to achieve superior power densities
High-performance cathode materials are crucial for the development of solid oxide fuel cells. Here, the authors present a nanoengineering approach to boost cathode performance in conventional anode-supported cells, demonstrating a viable route to attaining higher power output.
- Katherine Develos-Bagarinao
- , Tomohiro Ishiyama
- & Katsuhiko Yamaji
-
Article
| Open Access Diversity-oriented synthesis of nanographenes enabled by dearomative annulative π-extension
Diversity-oriented synthesis of nanographenes enabled by dearomative annulative π-extension
Nanographenes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are important classes of compounds with numerous applications, but challenging to access due to a lack of programmable and diversity-oriented methods. Here, the authors report a diversity-oriented, growth-from-template synthesis of nanographenes enabled by iterative annulative π-extension reactions from small PAH starting materials.
- Wataru Matsuoka
- , Hideto Ito
- & Kenichiro Itami
-
Article
| Open Access Atomistic insights into the nucleation and growth of platinum on palladium nanocrystals
Atomistic insights into the nucleation and growth of platinum on palladium nanocrystals
Creating predictable, controllable nanoparticles relies on a mechanistic understanding of their synthesis. Here, through integrated in situ liquid microscopy and first-principles calculations, the authors elucidate the atomistic details involved in the formation of colloidal core-shell nanoparticles.
- Wenpei Gao
- , Ahmed O. Elnabawy
- & Miaofang Chi
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the etching process of water-soluble Au25 nanoclusters at the molecular level
Revealing the etching process of water-soluble Au25 nanoclusters at the molecular level
Etching is one of the key considerations in the synthesis, storage, and application of metal nanoparticles. Here, the authors study the etching of water-soluble thiolate-protected gold nanoclusters at a molecular level and reveal an unusual recombination process in the oxidative reaction environment.
- Yitao Cao
- , Tongyu Liu
- & Jianping Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid fabrication of complex nanostructures using room-temperature ultrasonic nanoimprinting
Rapid fabrication of complex nanostructures using room-temperature ultrasonic nanoimprinting
Nanoimprinting faces challenges with imprinting hard materials at low or room temperature, and with fabricating complex nanostructures rapidly. Here, the authors overcome these challenges by a room-temperature ultrasonic nanoimprinting technique that capitalizes on the concentration of ultrasonic energy flow at nanoscale.
- Junyu Ge
- , Bin Ding
- & Hong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusion dynamics controlled colloidal synthesis of highly monodisperse InAs nanocrystals
Diffusion dynamics controlled colloidal synthesis of highly monodisperse InAs nanocrystals
Monodisperse colloidal InAs quantum dots have been envisioned as Pb-free materials for various infrared applications. Here, the authors provide a growth model based on monomer diffusion dynamics, enabling extended spectral coverage of InAs quantum dots beyond 1Smax of 1600 nm.
- Taewan Kim
- , Seongmin Park
- & Sohee Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Shape control of size-selected naked platinum nanocrystals
Shape control of size-selected naked platinum nanocrystals
Tetrahedral nanocrystals are out-of-equilibrium structures whose growth mechanism is a long-standing open problem. Here, the authors show that pure Pt tetrahedral nanocrystals grow in the gas phase and single out the defect-mediated mechanism leading to the symmetry-breaking for tetrahedral growth.
- Yu Xia
- , Diana Nelli
- & Z. Y. Li
-
Article
| Open Access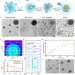 Crystallization of nanoparticles induced by precipitation of trace polymeric additives
Crystallization of nanoparticles induced by precipitation of trace polymeric additives
Growing nanoparticle crystals typically requires strict control over interparticle interactions and assembly. Here, the authors show that a trace amount of polymeric impurities induces reproducible, rapid growth of high quality 3D nanoparticle crystals in solution and on patterned substrates.
- Yiwen Qian
- , Alessandra da Silva
- & Ting Xu
-
Article
| Open Access A seamlessly integrated device of micro-supercapacitor and wireless charging with ultrahigh energy density and capacitance
A seamlessly integrated device of micro-supercapacitor and wireless charging with ultrahigh energy density and capacitance
Miniaturized energy storage devices integrated with wireless charging bring opportunities for next generation electronics. Here, authors report seamlessly integrated wireless charging micro-supercapacitors with high energy density capable of driving a model electrical car.
- Chang Gao
- , Jiancheng Huang
- & Liangti Qu
-
Article
| Open Access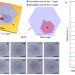 Hetero-site nucleation for growing twisted bilayer graphene with a wide range of twist angles
Hetero-site nucleation for growing twisted bilayer graphene with a wide range of twist angles
The synthesis of twisted bilayer graphene with controllable angles is challenging. Here, the authors devise a chemical vapor deposition approach using a hetero-site nucleation strategy that affords twist angles ranging from 0° to 30°.
- Luzhao Sun
- , Zihao Wang
- & Zhongfan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected organic hydrate luminogens in the solid state
Unexpected organic hydrate luminogens in the solid state
Developing organic photoluminescent materials with high emission efficiencies in the solid state under a water atmosphere is important for practical applications. Here, the authors report the formation of intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds in a tautomerizable Schiff base and intercalation of water in the crystal lattice leading to a luminescent organic hydrate.
- Feng Zhou
- , Peiyang Gu
- & Jianmei Lu

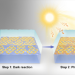 Photo-tailored heterocrystalline covalent organic framework membranes for organics separation
Photo-tailored heterocrystalline covalent organic framework membranes for organics separation