Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of a deltacoronavirus spike protein bound to porcine and human receptors
Structures of a deltacoronavirus spike protein bound to porcine and human receptors
As a potential zoonotic pathogen, porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) has been shown to cause febrile illness in humans. Here, Ji et al. report the structures of PDCoV spike protein bound to porcine and human aminopeptidase receptors, pointing to the likely underlying mechanism of PDCoV zoonotic transmission.
- Weiwei Ji
- , Qi Peng
- & Shuijun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of protein unfolding by fast cross-linking mass spectrometry using di-ortho-phthalaldehyde cross-linkers
Characterization of protein unfolding by fast cross-linking mass spectrometry using di-ortho-phthalaldehyde cross-linkers
Conformations sampled by a protein while it unfolds are difficult to visualize. Here, the authors develop di-ortho-phthalaldehyde cross-linkers for rapid chemical cross-linking mass spectrometry analysis and demonstrate that this method captures the conformations of protein unfolding intermediates.
- Jian-Hua Wang
- , Yu-Liang Tang
- & Xiaoguang Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism and biomass association of glucuronoyl esterase: an α/β hydrolase with potential in biomass conversion
Mechanism and biomass association of glucuronoyl esterase: an α/β hydrolase with potential in biomass conversion
Zong and coworkers combine computational and experimental methods to decipher in detail the mechanism of action of glucuronoyl esterases, enzymes with significant biotechnological potential for decoupling lignin from polysaccharides in biomass.
- Zhiyou Zong
- , Scott Mazurkewich
- & Leila Lo Leggio
-
Article
| Open Access Flagellin outer domain dimerization modulates motility in pathogenic and soil bacteria from viscous environments
Flagellin outer domain dimerization modulates motility in pathogenic and soil bacteria from viscous environments
It has been suggested that the outer domains of bacterial flagellins are not needed for motility. Here, the authors show that flagellar filament outer domains from some bacteria have unique structures which can alter the motility of the bacteria.
- Mark A. B. Kreutzberger
- , Richard C. Sobe
- & Edward H. Egelman
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-guided unlocking of NaX reveals a non-selective tetrodotoxin-sensitive cation channel
Structure-guided unlocking of NaX reveals a non-selective tetrodotoxin-sensitive cation channel
NaX is an atypical member of the voltage-gated sodium channel family that may contribute to Na+ homeostasis. Here, the authors describe the structural and functional attributes of the human NaX channel to reveal new insights into its physiology.
- Cameron L. Noland
- , Han Chow Chua
- & Jian Payandeh
-
Article
| Open Access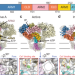 Structural basis for activation and gating of IP3 receptors
Structural basis for activation and gating of IP3 receptors
IP3 receptors are intracellular calcium channels involved in numerous signaling pathways. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of type-3 IP3 receptors in multiple gating conformations, including the active state revealing the molecular mechanism of the receptor activation.
- Emily A. Schmitz
- , Hirohide Takahashi
- & Erkan Karakas
-
Article
| Open Access Global profiling of regulatory elements in the histone benzoylation pathway
Global profiling of regulatory elements in the histone benzoylation pathway
Lysine benzoylation (Kbz) is a recently discovered histone modification. Here, the authors characterize writers, erasers and readers of histone Kbz in S. cerevisiae and identify non-histone proteins bearing Kbz, laying foundations to dissect the roles of Kbz in diverse cellular processes.
- Duo Wang
- , Fuxiang Yan
- & Yong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access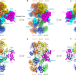 Structural Insight into the MCM double hexamer activation by Dbf4-Cdc7 kinase
Structural Insight into the MCM double hexamer activation by Dbf4-Cdc7 kinase
The Dbf4-dependent kinase Cdc7 (DDK) is essential for eukaryotic DNA replication. Here, the authors present a series of cryo-EM structures elucidating the versatility of this kinase in exerting an ordered phosphorylation of its essential target to promote replication initiation.
- Jiaxuan Cheng
- , Ningning Li
- & Yuanliang Zhai
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the sequence specificity of heterotypic amyloid interactions enables the identification of aggregation modifiers
Mapping the sequence specificity of heterotypic amyloid interactions enables the identification of aggregation modifiers
In this work, Louros et al. uncover a rule book for interactions of amyloids with other proteins. This grammar was shown to promote cellular spreading of tau aggregates in cells, but can also be harvested to develop structure-based aggregation blockers.
- Nikolaos Louros
- , Meine Ramakers
- & Joost Schymkowitz
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for allosteric agonism and G protein subtype selectivity of galanin receptors
Molecular basis for allosteric agonism and G protein subtype selectivity of galanin receptors
The basis for the diverse peptide-binding modes and the G protein selectivity of peptide GPCRs remains elusive. Here, the authors offer a structural basis for allosteric-like agonism and G protein selectivity of a neuropeptide GPCR, galanin receptor.
- Jia Duan
- , Dan-Dan Shen
- & Yi Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based design of prefusion-stabilized human metapneumovirus fusion proteins
Structure-based design of prefusion-stabilized human metapneumovirus fusion proteins
The degree to which the conformation of the human metapneumovirus fusion (F) protein affects immunogenicity has been debated. Here, Hsieh et al. engineer prefusion-stabilized F variants with enhanced thermostability that elicit higher neutralizing antibody titers in mice than postfusion F.
- Ching-Lin Hsieh
- , Scott A. Rush
- & Jason S. McLellan
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying and comparing radiation damage in the Protein Data Bank
Quantifying and comparing radiation damage in the Protein Data Bank
Radiation damage hampers protein structure determination by X-ray crystallography. Here, the AUs introduce the Bnet metric, a single value summarising the extent of radiation damage of a protein crystal structure, and use Bnet to detect radiation damage in structures deposited in the Protein Data Bank.
- Kathryn L. Shelley
- & Elspeth F. Garman
-
Article
| Open Access The structural basis for regulation of the glutathione transporter Ycf1 by regulatory domain phosphorylation
The structural basis for regulation of the glutathione transporter Ycf1 by regulatory domain phosphorylation
Ycf1, a C-family member ATP Binding Cassette (ABC) transporter, transports glutathione and glutathione-metal complexes in yeast. Here the authors use cryo-EM and biochemical analysis to show how an intrinsically-disordered regulatory domain (R-domain) controls activity upon phosphorylation by engaging with a Nucleotide Binding Domain.
- Nitesh Kumar Khandelwal
- , Cinthia R. Millan
- & Thomas M. Tomasiak
-
Article
| Open Access Secondary structure prediction for RNA sequences including N6-methyladenosine
Secondary structure prediction for RNA sequences including N6-methyladenosine
RNA folding free energy nearest neighbor parameters were determined for sequences with the nucleotide m6A. The RNAstructure software package can accommodate modified nucleotides, enabling secondary structure prediction of sequences with m6A.
- Elzbieta Kierzek
- , Xiaoju Zhang
- & David H. Mathews
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for modulation of human NaV1.3 by clinical drug and selective antagonist
Structural basis for modulation of human NaV1.3 by clinical drug and selective antagonist
NaV1.3 is involved in neuronal development, hormone secretion and pain perception. Here, the authors elucidate the molecular mechanism for modulation of NaV1.3 by a site-2 neurotoxin bulleyaconitine A and a subtype selective antagonist ICA121431.
- Xiaojing Li
- , Feng Xu
- & Daohua Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access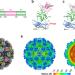 Atomic structure of the predominant GII.4 human norovirus capsid reveals novel stability and plasticity
Atomic structure of the predominant GII.4 human norovirus capsid reveals novel stability and plasticity
GII.4 variants of human noroviruses cause pandemic viral gastroenteritis. The atomic structure of GII.4 virus-like particles reveal novel insights into capsid stability, dynamics and antigenic presentation potentially useful for ongoing vaccine development.
- Liya Hu
- , Wilhelm Salmen
- & B. V. Venkataram Prasad
-
Article
| Open Access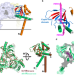 An open-like conformation of the sigma-1 receptor reveals its ligand entry pathway
An open-like conformation of the sigma-1 receptor reveals its ligand entry pathway
The nonopioid sigma-1 receptor (σ1R) is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), interacts with multiple effector proteins and various synthetic ligands, and is implicated in many diseases. Here, authors provide structural and functional evidence to reveal the likely ligand entry pathway for σ1R.
- Fuhui Meng
- , Yang Xiao
- & Xiaoming Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2
Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2
Predicting the structure of protein complexes is extremely difficult. Here, authors apply AlphaFold2 with optimized multiple sequence alignments to model complexes of interacting proteins, enabling prediction of both if and how proteins interact with state-of-art accuracy.
- Patrick Bryant
- , Gabriele Pozzati
- & Arne Elofsson
-
Article
| Open Access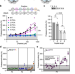 The YΦ motif defines the structure-activity relationships of human 20S proteasome activators
The YΦ motif defines the structure-activity relationships of human 20S proteasome activators
The proteasome complexes, composed of 20S core particles and one or two regulatory particles (proteasome activators), degrade most eukaryotic proteins. Here, the authors identify a sequence motif and resolve its interactions mediating the activation of the human 20S proteasome.
- Kwadwo A. Opoku-Nsiah
- , Andres H. de la Pena
- & Jason E. Gestwicki
-
Article
| Open Access Structural snapshots of V/A-ATPase reveal the rotary catalytic mechanism of rotary ATPases
Structural snapshots of V/A-ATPase reveal the rotary catalytic mechanism of rotary ATPases
The rotary ATPases use a rotary catalytic mechanism to drive transmembrane proton movement powered by ATP hydrolysis. Here, the authors report a collection of V/A-ATPase V1 domain structures, providing insights into rotary mechanism of the enzyme and potentially other rotary motor proteins driven by ATP hydrolysis.
- J. Kishikawa
- , A. Nakanishi
- & K. Yokoyama
-
Article
| Open Access Differential recognition of canonical NF-κB dimers by Importin α3
Differential recognition of canonical NF-κB dimers by Importin α3
Nuclear translocation of the p50/p65 heterodimer is essential for NF-κB signaling. Here, the authors identify a bipartite Nuclear Localization Signal in the NF-κB p50/p65 heterodimer that is recognized with high affinity by importin α3.
- Tyler J. Florio
- , Ravi K. Lokareddy
- & Gino Cingolani
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the human host
Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the human host
The SARS-CoV-2 spike has been evolving in the human population. The variants of concern alpha and beta evolved to optimise spike openness and so ability to bind its receptor ACE2, the affinity towards the receptor, and stability upon receptor binding.
- Antoni G. Wrobel
- , Donald J. Benton
- & Steven J. Gamblin
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular basis of FimT-mediated DNA uptake during bacterial natural transformation
The molecular basis of FimT-mediated DNA uptake during bacterial natural transformation
Many bacteria can take up exogenous DNA, in a process that often requires surface appendages composed of thousands of protein subunits called pilins. Here, Braus et al. show that a minor pilin binds directly to DNA and is important for DNA uptake in the pathogen Legionella pneumophila.
- Sebastian A. G. Braus
- , Francesca L. Short
- & Manuela K. Hospenthal
-
Article
| Open Access Ubiquitin and a charged loop regulate the ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of Ark2C
Ubiquitin and a charged loop regulate the ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of Ark2C
Attachment of ubiquitin to proteins is tightly regulated and controls many signalling pathways. Here, the authors show that addition of ubiquitin by the RING E3 ligases Arkadia and Ark2C is enhanced by ubiquitin and a charged loop that precedes the RING domain.
- Andrej Paluda
- , Adam J. Middleton
- & Catherine L. Day
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of a SARS-CoV-2 omicron spike protein ectodomain
Cryo-EM structure of a SARS-CoV-2 omicron spike protein ectodomain
This study determined the structure of the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant, revealing a predominantly open conformation of the molecule that may help omicron infect cells more efficiently than do previous variants.
- Gang Ye
- , Bin Liu
- & Fang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of leukotriene B4 receptor 1 activation
Structural basis of leukotriene B4 receptor 1 activation
In the paper, Dr. Wang et al reported a cryo-EM structure of the human leukotriene B4 receptor 1 (BLT1) in complex with its native ligand leukotriene B4 (LTB4) in an active conformation complexed with Gi protein. The structure reveals the molecule determinant of LTB4 binding and the mechanism of receptor activation. These structural information will boost the understanding of LTB4-BLT1 signaling and provide a rational basis for designing novel anti-leukotriene drugs.
- Na Wang
- , Xinheng He
- & Yuanzheng He
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of cooperative N-glycan processing by the multi-modular endoglycosidase EndoE
Mechanism of cooperative N-glycan processing by the multi-modular endoglycosidase EndoE
EndoE is a multi-domain glycoside hydrolase of the human pathogen Enterococcus faecalis. Here, the authors present crystal structures of EndoE and provide biochemical insights into the molecular basis of EndoE’s substrate specificity and catalytic mechanism.
- Mikel García-Alija
- , Jonathan J. Du
- & Marcelo E. Guerin
-
Article
| Open Access A multi-factor trafficking site on the spliceosome remodeling enzyme BRR2 recruits C9ORF78 to regulate alternative splicing
A multi-factor trafficking site on the spliceosome remodeling enzyme BRR2 recruits C9ORF78 to regulate alternative splicing
Bergfort et al. use biochemistry, cryoEM, structure-guided mutagenesis, transcriptomics and proteomics to reveal how the intrinsically unstructured C9ORF78 protein binds BRR2 and PRPF8, regulating cassette exons and alternative 3’-splice sites.
- Alexandra Bergfort
- , Marco Preußner
- & Markus C. Wahl
-
Article
| Open Access Leveraging the multivalent p53 peptide-MdmX interaction to guide the improvement of small molecule inhibitors
Leveraging the multivalent p53 peptide-MdmX interaction to guide the improvement of small molecule inhibitors
Peptide fragments derived from the interfaces of protein-protein interactions (PPIs) provide useful templates for designing small molecule PPI inhibitors. Here, the authors utilize the multivalency of an MdmX-binding p53 peptide to develop a weak inhibitor of MdmX into potent Mdm2/MdmX inhibitors.
- Xiyao Cheng
- , Rong Chen
- & Zhengding Su
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and assembly of the S-layer in C. difficile
Structure and assembly of the S-layer in C. difficile
The S-layer is a two-dimensional protein array that covers the cell surface of many bacteria and archaea. Here, the authors use high-resolution X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy to provide detailed insights into S-layer organisation and assembly for the bacterial pathogen Clostridioides difficile.
- Paola Lanzoni-Mangutchi
- , Oishik Banerji
- & Paula S. Salgado
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding self-assembly at molecular level enables controlled design of DNA G-wires of different properties
Understanding self-assembly at molecular level enables controlled design of DNA G-wires of different properties
G-wire structures have potential applications in bio-nanotechnology, however, this is limited by a lack of understanding about the assembly process and structures formed. Here, the authors use nuclear magnetic resonance and molecular dynamic simulations to understand the guiding principles of G-wire assembly.
- Daša Pavc
- , Nerea Sebastian
- & Primož Šket
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of translesion DNA synthesis polymerase ζ with a base pair mismatch
Cryo-EM structure of translesion DNA synthesis polymerase ζ with a base pair mismatch
The structure of mismatched DNA-Polζ ternary complex provides a basis for understanding what makes Polζ adept at extending DNA synthesis past mismatched base pairs.
- Radhika Malik
- , Robert E. Johnson
- & Aneel K. Aggarwal
-
Article
| Open Access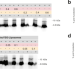 Inhibition of SRP-dependent protein secretion by the bacterial alarmone (p)ppGpp
Inhibition of SRP-dependent protein secretion by the bacterial alarmone (p)ppGpp
Bacterial responses to nutrient limitation and other stress conditions are often modulated by the nucleotide-based second messenger (p)ppGpp. Here, the authors show that (p)ppGpp inhibits the SRP membrane-protein insertion and secretion pathway by binding to GTPases Ffh and FtsY.
- Laura Czech
- , Christopher-Nils Mais
- & Gert Bange
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular recognition of formylpeptides and diverse agonists by the formylpeptide receptors FPR1 and FPR2
Molecular recognition of formylpeptides and diverse agonists by the formylpeptide receptors FPR1 and FPR2
Zhuang et al. report four cryo-EM structures of formylpeptide receptors FPR1 and FPR2 coupled with Gi protein and diverse agonists, revealing how FPRs as pattern recognition receptors recognize formylpeptides and synthetic agonists and a distinctive receptor activation mechanism.
- Youwen Zhuang
- , Lei Wang
- & Cheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into multiplexed pharmacological actions of tirzepatide and peptide 20 at the GIP, GLP-1 or glucagon receptors
Structural insights into multiplexed pharmacological actions of tirzepatide and peptide 20 at the GIP, GLP-1 or glucagon receptors
Multi-targeting agonists at GIPR, GLP-1R or GCGR are pursued vigorously. Here, the authors report cryo-EM structures of tirzepatide-bound GIPR and GLP-1R, peptide 20-bound GIPR, GLP-1R and GCGR, revealing the molecular basis of their multiplexed pharmacological actions.
- Fenghui Zhao
- , Qingtong Zhou
- & Ming-Wei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access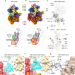 A mechanism of origin licensing control through autoinhibition of S. cerevisiae ORC·DNA·Cdc6
A mechanism of origin licensing control through autoinhibition of S. cerevisiae ORC·DNA·Cdc6
Cryo-EM structures of S. cerevisiae ORC bound to DNA and Cdc6 reveal an autoinhibited conformation and suggest a mechanism of origin licensing control in response to CDK phosphorylation.
- Jan Marten Schmidt
- , Ran Yang
- & Franziska Bleichert
-
Article
| Open Access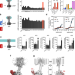 Structural basis of adenylyl cyclase 9 activation
Structural basis of adenylyl cyclase 9 activation
Adenylyl cyclases (ACs) generate the second messenger cAMP and play an important role in cellular signaling. Here, the authors use cryo-EM to trace the conformational changes resulting from binding to partial and full activators to one of these enzymes, AC9.
- Chao Qi
- , Pia Lavriha
- & Volodymyr M. Korkhov
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for a trap-and-flip mechanism in a proton-dependent lipid transporter
Evidence for a trap-and-flip mechanism in a proton-dependent lipid transporter
LtaA catalyzes glycolipid translocation by a ‘trap-and-flip’ mechanism, pointing to a shared mechanistic model among MFS lipid transporters. Asymmetric lateral openings allow access of the entire lipid substrate to the amphipathic central cavity.
- Elisabeth Lambert
- , Ahmad Reza Mehdipour
- & Camilo Perez
-
Article
| Open Access High-pH structure of EmrE reveals the mechanism of proton-coupled substrate transport
High-pH structure of EmrE reveals the mechanism of proton-coupled substrate transport
EmrE transporter effluxes cationic substrates across lipid membranes in a pH-coupled manner. Here, the authors solve the structure of ligand-bound EmrE at high pH by NMR, with insights into the transport mechanism.
- Alexander A. Shcherbakov
- , Peyton J. Spreacker
- & Mei Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Development and characterization of functional antibodies targeting NMDA receptors
Development and characterization of functional antibodies targeting NMDA receptors
Selective targeting individual subtypes of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) is a desirable therapeutic strategy for neurological disorders. Here, the authors report identification of a functional antibody that specifically targets and allosterically down-regulates ion channel activity of the GluN1—GluN2B NMDAR subtype.
- Nami Tajima
- , Noriko Simorowski
- & Hiro Furukawa
-
Article
| Open Access A late-stage assembly checkpoint of the human mitochondrial ribosome large subunit
A late-stage assembly checkpoint of the human mitochondrial ribosome large subunit
Rebelo-Guiomar et al. unveil late stage assembly intermediates of the human mitochondrial ribosome by inactivating the methyltransferase MRM2 in cells. Absence of MRM2 impairs organismal homeostasis, while its catalytic activity is dispensable for mitoribosomal biogenesis.
- Pedro Rebelo-Guiomar
- , Simone Pellegrino
- & Michal Minczuk
-
Article
| Open Access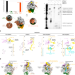 Structural snapshots of La Crosse virus polymerase reveal the mechanisms underlying Peribunyaviridae replication and transcription
Structural snapshots of La Crosse virus polymerase reveal the mechanisms underlying Peribunyaviridae replication and transcription
La Crosse is a human life threatening virus belonging to the Bunyavirales order. The structure of its polymerase solved in seven key active states by cryo-electron microscopy reveals the molecular mechanisms of viral RNA replication and transcription.
- Benoît Arragain
- , Quentin Durieux Trouilleton
- & Hélène Malet
-
Article
| Open Access HSL1 and BAM1/2 impact epidermal cell development by sensing distinct signaling peptides
HSL1 and BAM1/2 impact epidermal cell development by sensing distinct signaling peptides
HAESA and HSL2 are receptors for IDA/IDL-family signaling peptides in plants. Here the authors show that HSL1, previously shown to recognize CLE9, preferentially binds IDA/IDL peptides and regulates leaf epidermal patterning independently of CLE peptides.
- Andra-Octavia Roman
- , Pedro Jimenez-Sandoval
- & Julia Santiago
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant recognition of ACE2 receptor and broadly neutralizing antibodies
Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant recognition of ACE2 receptor and broadly neutralizing antibodies
Here the authors reveal conformational dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Delta spike and its complex with ACE2 receptor or broadly neutralizing Mab 8D3 by cryo-EM, shedding new insights into mechanisms of receptor recognition and antibody neutralization for the Delta variant.
- Yifan Wang
- , Caixuan Liu
- & Yao Cong
-
Article
| Open Access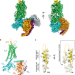 Structural basis of neuropeptide Y signaling through Y1 receptor
Structural basis of neuropeptide Y signaling through Y1 receptor
The human neuropeptide Y (NPY) acts through G-protein coupled receptors and is involved in food intake, stress response, anxiety, and memory retention. Here, the authors show that, unlike in other neuropeptides, both the N-terminal and the C-terminal regions of NPY interact with the NPY receptor 1.
- Chaehee Park
- , Jinuk Kim
- & Hee-Jung Choi
-
Article
| Open Access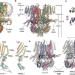 Structural insights into the Venus flytrap mechanosensitive ion channel Flycatcher1
Structural insights into the Venus flytrap mechanosensitive ion channel Flycatcher1
Flycatcher1 (FLYC1) is a candidate mechanosensitive channel involved in Venus flytrap touch-induced prey capture. Here, the authors report structural and functional details of FLYC1, with insights into gating conformational transitions.
- Sebastian Jojoa-Cruz
- , Kei Saotome
- & Andrew B. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Allosteric control of Ubp6 and the proteasome via a bidirectional switch
Allosteric control of Ubp6 and the proteasome via a bidirectional switch
The interplay of the proteasome and deubiquitinase Ubp6 is crucial for the degradation of ubiquitylated substrates. Here, the authors provide structural insights into the allosteric mechanism by which the activities of both Ubp6 and the proteasome are regulated.
- Ka Ying Sharon Hung
- , Sven Klumpe
- & Daniel Finley
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of highly flexible intracellular domain of human α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Structures of highly flexible intracellular domain of human α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
The intracellular domain (ICD) of Cys-loop receptors mediates many of their functions, but no complete structure of a Cys-loop receptor ICD is available to date. Here, the authors combine NMR and ESR spectroscopy to determine the full-length ICD structures of the human α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR).
- Vasyl Bondarenko
- , Marta M. Wells
- & Pei Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Defining molecular glues with a dual-nanobody cannabidiol sensor
Defining molecular glues with a dual-nanobody cannabidiol sensor
Molecular glue has been used as a broad term describing a class of protein interaction-promoting compounds. Here, the authors outline two unifying thermodynamic features to formally define molecular glues and guide their prospective discovery.
- Shiyun Cao
- , Shoukai Kang
- & Ning Zheng

 Inorganic phosphate in growing calcium carbonate abalone shell suggests a shared mineral ancestral precursor
Inorganic phosphate in growing calcium carbonate abalone shell suggests a shared mineral ancestral precursor