Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Clustering and halogen effects enabled red/near-infrared room temperature phosphorescence from aliphatic cyclic imides
Clustering and halogen effects enabled red/near-infrared room temperature phosphorescence from aliphatic cyclic imides
Pure organic room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) materials become increasingly important but achieving red and near-infrared (NIR) RTP remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate that succinimide derived cyclic imides can emit RTP in the red and NIR spectral range with outstanding efficiencies of up to 9.2%.
- Tianwen Zhu
- , Tianjia Yang
- & Wang Zhang Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid meniscus-guided printing of stable semi-solid-state liquid metal microgranular-particle for soft electronics
Rapid meniscus-guided printing of stable semi-solid-state liquid metal microgranular-particle for soft electronics
In this article, meniscus-guided printing of polyelectrolyte-attached liquid metal particles to simultaneously achieve mechanical stability and initial electrical conductivity at high resolution is introduced.
- Gun-Hee Lee
- , Ye Rim Lee
- & Steve Park
-
Article
| Open Access Medial packing and elastic asymmetry stabilize the double-gyroid in block copolymers
Medial packing and elastic asymmetry stabilize the double-gyroid in block copolymers
Double-gyroid networks assemble in diverse soft materials, yet the molecular packing that underlies their complex structure remains obscure. Here, authors advance a theory that resolves a long-standing puzzle about their formation in block copolymers.
- Abhiram Reddy
- , Michael S. Dimitriyev
- & Gregory M. Grason
-
Article
| Open Access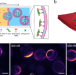 Activity-induced polar patterns of filaments gliding on a sphere
Activity-induced polar patterns of filaments gliding on a sphere
Active matter exhibits a range of collective behaviors offering insights into how complex patterns can emerge at different length scales. Here, Hsu et al. confine active filaments on the spherical surface of a lipid vesicle and observe the formation of off-equator polar vortices and jammed patterns.
- Chiao-Peng Hsu
- , Alfredo Sciortino
- & Andreas R. Bausch
-
Article
| Open Access Cascade reaction networks within audible sound induced transient domains in a solution
Cascade reaction networks within audible sound induced transient domains in a solution
It is difficult to achieve spatiotemporal control over chemical cascade reactions. Here, the authors report on the generation of transient domains in an aqueous medium using sound induced liquid vibrations allowing for control of chemical gradients and patterns and use this to pattern nanoparticles in hydrogels.
- Prabhu Dhasaiyan
- , Tanwistha Ghosh
- & Kimoon Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Switchable bifunctional molecular recognition in water using a pH-responsive Endo-functionalized cavity
Switchable bifunctional molecular recognition in water using a pH-responsive Endo-functionalized cavity
The development of synthetic host-guest systems for stimuli-responsive molecular recognition in water is challenging. Here, the authors report a pair of water-soluble naphthotubes with a pH-responsive cavity for which switchable bifunctional recognition in water is achieved.
- Xiaoping Wang
- , Mao Quan
- & Wei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Coacervation in polyzwitterion-polyelectrolyte systems and their potential applications for gastrointestinal drug delivery platforms
Coacervation in polyzwitterion-polyelectrolyte systems and their potential applications for gastrointestinal drug delivery platforms
Coacervation is widely studied as potential drug delivery platform, but formation of coacervates at lower pH ranges, such as found in the gastrointestinal tract, remains challenging. Here, using theory and experimental methods, the authors demonstrate the formation of a polyzwitterionic complex, formed by coacervation of a polyzwitterion and a polyelectrolyte, exhibiting orthogonal phase behavior under physiological low pH conditions.
- Khatcher O. Margossian
- , Marcel U. Brown
- & Murugappan Muthukumar
-
Article
| Open Access Lateral growth of cylinders
Lateral growth of cylinders
Precise control of the microstructure of nanomaterials is of interest but living lateral growth of cylinders is still very challenging. Here, the authors propose a crystallization-driven fusion-induced particle assembly strategy to prepare cylinders with growing diameters by controlled fusion of spherical micelles self-assembled from an amphiphilic homopolymer.
- Hui Sun
- , Shuai Chen
- & Jianzhong Du
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular communications in complex systems of dynamic supramolecular polymers
Molecular communications in complex systems of dynamic supramolecular polymers
The dynamic structure of supramolecular polymers is challenging to determine both in experiments and in simulations. Here the authors use coarse-grained molecular models to provide a comprehensive analysis of the molecular communication in these complex molecular systems.
- Martina Crippa
- , Claudio Perego
- & Giovanni M. Pavan
-
Article
| Open Access Construction of emissive ruthenium(II) metallacycle over 1000 nm wavelength for in vivo biomedical applications
Construction of emissive ruthenium(II) metallacycle over 1000 nm wavelength for in vivo biomedical applications
Ruthenium (Ru(II)) compounds are of interest as platinum drug replacements but have suffered from suboptimal therapeutic efficiency. Here, the authors design a Ru(II) metallacycle with NIR excitation and emission wavelengths and demonstrate application for deep tumour imaging and chemo-photo therapy.
- Yuling Xu
- , Chonglu Li
- & Yao Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Freestanding non-covalent thin films of the propeller-shaped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon decacyclene
Freestanding non-covalent thin films of the propeller-shaped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon decacyclene
Molecularly thin films are important in material sciences but their use in a wide range of applications requires control over their chemical functionalities, which is difficult to achieve. Here, the authors use decacyclene to form such freestanding and mechanically stable molecular films held together by supramolecular interactions without requiring covalent crosslinking of any kind
- Alex van der Ham
- , Xue Liu
- & Grégory F. Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple yet switchable hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks with white-light emission
Multiple yet switchable hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks with white-light emission
Switchable hydrogen-bonded frameworks have potential applications in the development of smart materials. Herein, the authors report eleven hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks and two non-porous structures that can undergo reversible structural and fluorescence switching; white-light emission is enabled.
- Yadong Shi
- , Shuodong Wang
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Activity-induced interactions and cooperation of artificial microswimmers in one-dimensional environments
Activity-induced interactions and cooperation of artificial microswimmers in one-dimensional environments
Biological microswimmers such as bacteria show collective motion that is made possible by an intricate interplay of sensing and signaling. Ketzetzi et al. reproduce this phenomenon in a catalytic system undergoing, for instance, cooperative speed-ups and dynamic reconfiguration of microswimmer chains.
- Stefania Ketzetzi
- , Melissa Rinaldin
- & Daniela J. Kraft
-
Article
| Open Access Double helical π-aggregate nanoarchitectonics for amplified circularly polarized luminescence
Double helical π-aggregate nanoarchitectonics for amplified circularly polarized luminescence
Synthesized or self-assembled helical architectures advance the development of chiral functional materials. Here the authors report a selective-recognized and chirality-matched co-assembly strategy for the fabrication of fluorescent π-amino acids into double helical π-aggregates with exceptional strong circularly polarized luminescence
- Yuan Wang
- , Dian Niu
- & Minghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Hyper-CEST NMR of metal organic polyhedral cages reveals hidden diastereomers with diverse guest exchange kinetics
Hyper-CEST NMR of metal organic polyhedral cages reveals hidden diastereomers with diverse guest exchange kinetics
Self-assembling nanostructures that trap guest molecules find applications in materials research and the life sciences. Here, authors describe how ultra-sensitive NMR reveals sub-types with broken symmetry that significantly impacts guest exchange.
- Jabadurai Jayapaul
- , Sanna Komulainen
- & Leif Schröder
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding self-assembly at molecular level enables controlled design of DNA G-wires of different properties
Understanding self-assembly at molecular level enables controlled design of DNA G-wires of different properties
G-wire structures have potential applications in bio-nanotechnology, however, this is limited by a lack of understanding about the assembly process and structures formed. Here, the authors use nuclear magnetic resonance and molecular dynamic simulations to understand the guiding principles of G-wire assembly.
- Daša Pavc
- , Nerea Sebastian
- & Primož Šket
-
Article
| Open Access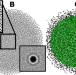 Hyperuniformity and phase enrichment in vortex and rotor assemblies
Hyperuniformity and phase enrichment in vortex and rotor assemblies
Rotor-like dynamics is observed in many natural systems, from the rotor proteins in cellular membranes to atmospheric models. Here, the authors uncover geometrical conservation laws that limit distribution of driven rotors in a membrane or a soap film and allow to predict their structural states.
- Naomi Oppenheimer
- , David B. Stein
- & Michael J. Shelley
-
Article
| Open Access Boosting the electronic and catalytic properties of 2D semiconductors with supramolecular 2D hydrogen-bonded superlattices
Boosting the electronic and catalytic properties of 2D semiconductors with supramolecular 2D hydrogen-bonded superlattices
Here, the authors report the functionalization of monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides with hydrogen-bonded 2D supramolecular networks of cyanuric acid and melamine, leading to a pronounced n-doping effect and enhancement of MoS2 catalytic activity for hydrogen evolution reactions.
- Can Wang
- , Rafael Furlan de Oliveira
- & Paolo Samorì
-
Article
| Open Access Selective photoinduced charge separation in perylenediimide-pillar[5]arene rotaxanes
Selective photoinduced charge separation in perylenediimide-pillar[5]arene rotaxanes
The development of complex molecular machinery requires a detailed appreciation of the factors that control energy pathways through the nanoscale scaffold. Here, the authors demonstrate that hetero-rotaxanes can be employed to create assemblies of different redox and photo-active components that enable selective tuning of energy transfer pathways.
- Nicholas Pearce
- , Katherine E. A. Reynolds
- & Neil R. Champness
-
Article
| Open Access A case of antiferrochirality in a liquid crystal phase of counter-rotating staircases
A case of antiferrochirality in a liquid crystal phase of counter-rotating staircases
A 3D‐ordered liquid crystal phase of regular right and left helically twisted columns self‐assembles from straight‐ and bent‐rod molecules. Here calculations indicate that, among four alternative models, the observed complex Fddd structure provides the lowest packing energy for twisted ribbons.
- Ya-xin Li
- , Hong-fei Gao
- & Goran Ungar
-
Article
| Open Access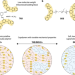 Mechanically robust supramolecular polymer co-assemblies
Mechanically robust supramolecular polymer co-assemblies
Reversible assembly of supramolecular polymers renders these materials with healing and recycling properties but mechanical properties are often inferior to those of conventional plastics. Here, the authors demonstrate that strong and tough but healable materials can be accessed through the combination of metallosupramolecular polymers with complementary mechanical properties that feature the same metal-ligand complex as binding motif
- Julien Sautaux
- , Franziska Marx
- & Stephen Schrettl
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the length of porphyrin supramolecular polymers via coupled equilibria and dilution-induced supramolecular polymerization
Controlling the length of porphyrin supramolecular polymers via coupled equilibria and dilution-induced supramolecular polymerization
Controlling multicomponent systems is difficult due to convoluted behavior, pathway complexity, and coupled equilibria. Here the authors showed modulation of aggregate morphology in a zinc porphyrin-based supramolecular system via judicious capping with a manganese porphyrin monomer, in which the monomer’s chirality can influence the supramolecular behavior.
- Elisabeth Weyandt
- , Luigi Leanza
- & E. W. Meijer
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperation in a fluid swarm of fuel-free micro-swimmers
Cooperation in a fluid swarm of fuel-free micro-swimmers
The authors introduce a light powered artificial micro-swimmers performing biological-like dynamics relevant for swarm robotics. The experimental dense swarms are shown to form artificial active clusters with internal fluid-like and turbulent dynamics, similar to real swarming bacteria.
- Matan Yah Ben Zion
- , Yaelin Caba
- & Paul M. Chaikin
-
Article
| Open Access Size compatibility and concentration dependent supramolecular host–guest interactions at interfaces
Size compatibility and concentration dependent supramolecular host–guest interactions at interfaces
Quantification of supramolecular host–guest interactions is important for modulating supramolecular systems but accurately evaluating the adhesion energies of host–guest pairs remains challenging. Here, the authors directly quantify the interaction energies between cyclodextrin modified surfaces and ditopic adamantane using a surface force apparatus.
- Jintae Park
- , Jinwoo Park
- & Dong Woog Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Parallel-stacked aromatic molecules in hydrogen-bonded inorganic frameworks
Parallel-stacked aromatic molecules in hydrogen-bonded inorganic frameworks
Hydrogen-bonded inorganic frameworks are porous structures that may lead to novel materials with unprecedented properties and functionalities. Here the authors report the solid-state structures of orthosilicic acid-based hydrogen-bonded inorganic frameworks that can encapsulate small unsaturated cyclic molecules such as benzene, which are found stacked in parallel.
- Masayasu Igarashi
- , Takeshi Nozawa
- & Kazuhiko Sato
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle-assembled bioadhesive coacervate coating with prolonged gastrointestinal retention for inflammatory bowel disease therapy
Nanoparticle-assembled bioadhesive coacervate coating with prolonged gastrointestinal retention for inflammatory bowel disease therapy
The development of a drug delivery system capable of prolonged retention in the gastrointestinal tract remains a clinical challenge. Here the authors present a bio-adhesive liquid coacervate coating on the intestinal tract that acts as a flowable drug carrier, mediates the sustained release of diverse drugs, and potentially enhances therapeutic efficacy against gastrointestinal diseases.
- Pengchao Zhao
- , Xianfeng Xia
- & Liming Bian
-
Article
| Open Access Self assembling cluster crystals from DNA based dendritic nanostructures
Self assembling cluster crystals from DNA based dendritic nanostructures
Experimental realization of cluster crystals- periodic structures with lattice sites occupied by several, overlapping building blocks, has been elusive. Here, the authors show the existence of well-controlled soft matter cluster crystals composed of a thermosensitive water-soluble polymer and nanometer-scale all-DNA dendrons.
- Emmanuel Stiakakis
- , Niklas Jung
- & Christos N. Likos
-
Article
| Open Access A H2O2-activatable nanoprobe for diagnosing interstitial cystitis and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury via multispectral optoacoustic tomography and NIR-II fluorescent imaging
A H2O2-activatable nanoprobe for diagnosing interstitial cystitis and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury via multispectral optoacoustic tomography and NIR-II fluorescent imaging
Fluorescent imaging in the second biological window has advantages for in vivo applications. Here, the authors synthesise a molecular nanoprobe which activates upon binding H2O2, generating both strong fluorescent NIR-II emission and ultrasound signal for multi-mode imaging of inflammatory diseases.
- Junjie Chen
- , Longqi Chen
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient protein incorporation and release by a jigsaw-shaped self-assembling peptide hydrogel for injured brain regeneration
Efficient protein incorporation and release by a jigsaw-shaped self-assembling peptide hydrogel for injured brain regeneration
The extracellular matrix contributes to tissue regeneration by binding and releasing growth factors. Here the authors present the jigsaw-shaped self-assembling peptide JigSAP as an artificial ECM and show that VEGF-JigSAP has therapeutic effects on the subacute-chronic phase of brain stroke.
- Atsuya Yaguchi
- , Mio Oshikawa
- & Itsuki Ajioka
-
Article
| Open Access Propagating wave in a fluid by coherent motion of 2D colloids
Propagating wave in a fluid by coherent motion of 2D colloids
Tiny movable components could generate macroscopic mechanical motion if precise coherent operation can be exerted simultaneously. Here, the authors demonstrate this by using 10^10 pieces of colloidally dispersed nanosheets to generate wave under non-equilibrium state.
- Koki Sano
- , Xiang Wang
- & Takuzo Aida
-
Article
| Open Access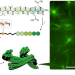 Supramolecular fibrillation of peptide amphiphiles induces environmental responses in aqueous droplets
Supramolecular fibrillation of peptide amphiphiles induces environmental responses in aqueous droplets
One-dimensional (1D) supramolecular polymers are commonly found in natural and synthetic systems but very little is currently known about the physico-chemical consequences and functional role of 1D supramolecular polymerisation confined in aqueous compartments. Here, the authors describe the different phenomena that resulted from the chemically triggered supramolecular fibrillation of synthetic peptide amphiphiles inside water microdroplets.
- Richard Booth
- , Ignacio Insua
- & Javier Montenegro
-
Article
| Open Access Metamachines of pluripotent colloids
Metamachines of pluripotent colloids
Mobile micromachines have the potential to probe and manipulate matter at small scales emulating the biological machinery of living organisms. Here, the authors take advantage of the anisotropy of self-propelled colloidal heterodimers to control anisotropic and reprogrammable interactions between particles.
- Antoine Aubret
- , Quentin Martinet
- & Jeremie Palacci
-
Article
| Open Access A chemosensor-based chiral coassembly with switchable circularly polarized luminescence
A chemosensor-based chiral coassembly with switchable circularly polarized luminescence
‘Fluorescent chemisensors with fast response time and pronounced luminescence variation are important but have not been well investigated for self-assembled chiral systems. Here, the authors present a coassembled multiple component system that responds to SO2 derivatives, giving rise to dynamic aggregation behaviors and switchable luminescence as well as circularly polarized luminescence.
- Qiuhong Cheng
- , Aiyou Hao
- & Pengyao Xing
-
Article
| Open Access A class of organic cages featuring twin cavities
A class of organic cages featuring twin cavities
The preparation of nanocages with unprecedented architectures may lead to new functions. Here the authors report the self-assembly of organic cages featuring twin cavities; the geometry and pocket size determine the molecular packing and the proton conductivity performance.
- Zhenyu Yang
- , Chunyang Yu
- & Shaodong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A three-tiered colloidosomal microreactor for continuous flow catalysis
A three-tiered colloidosomal microreactor for continuous flow catalysis
Integration of biological and inorganic components into hierarchical assembled structures to enhance catalytic reactions remains challenging. Here, the authors report a rational design of three-tiered colloidosomes via the Pickering emulsion process and demonstrate the acceleration of lipase catalyzed ester hydrolysis within a continuous flow reactor packed with the colloidosomes.
- Hua Wu
- , Xuanlin Du
- & Yan Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling complementary strategy to flexible graph neural network for quick discovery of coformer in diverse co-crystal materials
Coupling complementary strategy to flexible graph neural network for quick discovery of coformer in diverse co-crystal materials
Experimental determination of new cocrystals remains challenging due to the need of a systematic screening with a large range of coformers. Here the authors develop a flexible deep learning framework based on graph neural network demonstrated to quickly predict the formation of co-crystals.
- Yuanyuan Jiang
- , Zongwei Yang
- & Xuemei Pu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-regulated co-assembly of soft and hard nanoparticles
Self-regulated co-assembly of soft and hard nanoparticles
Colloidal self-assembly enables bottom-up manufacture of materials with designed hierarchies and functions. Here the authors develop a facile method to construct multidimensional colloidal architectures via the association of soft block copolymer micelles with simple unvarnished hard nanoparticles.
- Yan Cui
- , Hongyan Zhu
- & Huibin Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Generating circularly polarized luminescence from clusterization‐triggered emission using solid phase molecular self-assembly
Generating circularly polarized luminescence from clusterization‐triggered emission using solid phase molecular self-assembly
Organic cluster-triggered emission (CTE) displays promising application in bioimaging, chemical sensing, and multicolor luminescence but circular polarize luminescence derived from CTE remains less studied. Here, the authors demonstrate CTE based CPL emission from a supramolecular film derived from solid phase molecular self-assembly.
- Peilong Liao
- , Shihao Zang
- & Yun Yan
-
Article
| Open Access A contorted nanographene shelter
A contorted nanographene shelter
Encapsulating large and contorted nanographenes inside artificial receptors remain challenging. This work reports the synthesis, characterization and binding properties of a trigonal prismatic cage compound that can serve as a receptor for contorted nanographene derivatives.
- Huang Wu
- , Yu Wang
- & J. Fraser Stoddart
-
Article
| Open Access Light-fueled transient supramolecular assemblies in water as fluorescence modulators
Light-fueled transient supramolecular assemblies in water as fluorescence modulators
Dissipative self-assembly, which requires a continuous supply of fuel to maintain the assembled states far from equilibrium, is the foundation of biological systems but it remains a challenge to introduce light as fuel into artificial dissipative self-assemblies. Here, the authors report an artificial dissipative self-assembly system that is constructed from light-induced amphiphiles.
- Xu-Man Chen
- , Xiao-Fang Hou
- & Quan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Protein interface redesign facilitates the transformation of nanocage building blocks to 1D and 2D nanomaterials
Protein interface redesign facilitates the transformation of nanocage building blocks to 1D and 2D nanomaterials
Various strategies to assemble protein building blocks into one-, two- and three-dimensional hierarchical nanostructures were described, but controlling the transformation between those different assemblies is largely uninvestigated. Here, the authors describe a protein interface redesign strategy and use it for the self-assembly transformation of dimeric building blocks from hollow protein nanocage to filament, nanorod and nanoribbon.
- Xiaorong Zhang
- , Yu Liu
- & Guanghua Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable artificial microswimmers with internal feedback
Reconfigurable artificial microswimmers with internal feedback
Changing the propulsion of simple artificial colloidal microswimmers usually proceeds by globally tuning the strength of the driving mechanism. Alvarez et al. implement an independent reconfiguration scheme, bringing small active particles one step closer to adaptive, autonomous behaviour.
- L. Alvarez
- , M. A. Fernandez-Rodriguez
- & Lucio Isa
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid discovery of self-assembling peptides with one-bead one-compound peptide library
Rapid discovery of self-assembling peptides with one-bead one-compound peptide library
Self-assembling peptides have a range of potential applications but developing self-assembling sequences can be challenging. Here, the authors report on a one-bead one-compound combinatorial library where fluorescence is used to detect the potential for self-assembly and identified candidates are evaluated.
- Pei-Pei Yang
- , Yi-Jing Li
- & Kit S. Lam
-
Article
| Open Access Astral hydrogels mimic tissue mechanics by aster-aster interpenetration
Astral hydrogels mimic tissue mechanics by aster-aster interpenetration
The development of tissue-like materials which replicate the mechanical properties of tissue is of interest for a range of applications. Here, the authors report on the development of radial asters that form a gel network to stiffen in compression and soften in extension, resembling tissue mechanics.
- Qingqiao Xie
- , Yuandi Zhuang
- & Lingxiang Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly using a retro Diels-Alder reaction
Self-assembly using a retro Diels-Alder reaction
Despite their great utility in synthetic and materials chemistry, Diels-Alder and retro Diels-Alder reactions have been vastly unexplored in promoting self-assembly processes. Here the authors show the release of steric bulkiness associated with a bridged bicyclic Diels Alder adduct by the retro Diels-Alder reaction that allowed generation of two building blocks that spontaneously self-assembled to form a supramolecular polymer.
- Jaeyoung Park
- , Jung-Moo Heo
- & Jong-Man Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of photocatalytic and dark-operating catalytic biomimetic transformations through DNA-based constitutional dynamic networks
Integration of photocatalytic and dark-operating catalytic biomimetic transformations through DNA-based constitutional dynamic networks
Nucleic acid-based constitutional dynamic networks (CDNs) enable control of various catalytic processes, but it is challenging to achieve intercommunication between different CDNs and by that mimic complex cell biology networks. Here, the authors report two CDNs that control the integration of photochemical and dark-operating processes, and show their intercommunication afforded by environmental components.
- Chen Wang
- , Michael P. O’Hagan
- & Itamar Willner
-
Article
| Open Access A curved host and second guest cooperatively inhibit the dynamic motion of corannulene
A curved host and second guest cooperatively inhibit the dynamic motion of corannulene
The preparation of artificial host–guest systems that display dynamic adaptation during guest binding is challenging. Here the authors report a chiral self-assembled tetrahedral cage featuring curved walls that reconfigures stereochemically to fit fullerene guests, regulates corannulene inversion, and enables the determination of co-guest enantiomeric excess by NMR spectroscopy.
- Yang Yang
- , Tanya K. Ronson
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular insertion regulates the donor-acceptor interactions in cocrystals for the design of piezochromic luminescent materials
Molecular insertion regulates the donor-acceptor interactions in cocrystals for the design of piezochromic luminescent materials
The design of piezochromic luminescent materials with desirable stimuliresponsive properties remains challenging. Here, the authors report the insertion of a non-emissive molecule into a donor and acceptor binary cocrystal and realize desirable piezochromic luminescent properties by manipulation of intermolecular interactions between the donor and acceptor molecules.
- Chunguang Zhai
- , Xiu Yin
- & Bingbing Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative 3D real-space analysis of Laves phase supraparticles
Quantitative 3D real-space analysis of Laves phase supraparticles
3D real-space analysis of thick nanoparticle crystals is non-trivial. Here, the authors demonstrate the structural analysis of a bulk-like Laves phase by imaging an off-stoichiometric binary mixture of hard-sphere-like nanoparticles in spherical confinement by electron tomography, enabling defect analysis on the single-particle level.
- Da Wang
- , Ernest B. van der Wee
- & Alfons van Blaaderen

 Chiral self-assembly of cellulose nanocrystals is driven by crystallite bundles
Chiral self-assembly of cellulose nanocrystals is driven by crystallite bundles