Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access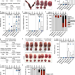 Iron-dependent apoptosis causes embryotoxicity in inflamed and obese pregnancy
Iron-dependent apoptosis causes embryotoxicity in inflamed and obese pregnancy
Iron is essential during pregnancy for embryo and placental development and maternal health. However, in this study using mouse models, the authors demonstrate that excess maternal iron causes adverse embryo outcomes in pregnancies with underlying systemic inflammation.
- Allison L. Fisher
- , Veena Sangkhae
- & Elizabeta Nemeth
-
Article
| Open Access TCF21+ mesenchymal cells contribute to testis somatic cell development, homeostasis, and regeneration in mice
TCF21+ mesenchymal cells contribute to testis somatic cell development, homeostasis, and regeneration in mice
Whether the adult testis harbours a somatic progenitor population is unknown. Here, the authors provide evidence that the testis interstitial cells expressing the transcription factor Tcf21 maintain adult testis homeostasis during aging, and act as potential reserve somatic progenitors following injury.
- Yu-chi Shen
- , Adrienne Niederriter Shami
- & Saher Sue Hammoud
-
Article
| Open Access Direct activation of the proton channel by albumin leads to human sperm capacitation and sustained release of inflammatory mediators by neutrophils
Direct activation of the proton channel by albumin leads to human sperm capacitation and sustained release of inflammatory mediators by neutrophils
The human voltage-gated proton channel (hHv1) maintains intracellular pH and membrane potential in sperm and neutrophils. Here, the authors show that albumin activates hHv1, by binding to the channel voltage sensor domains to enhance open probability and increases proton current, and that activation is required to trigger sperm to allow oocyte fertilization and to sustain production and release of immune inflammatory mediators during the neutrophil respiratory burst.
- Ruiming Zhao
- , Hui Dai
- & Steve A. N. Goldstein
-
Article
| Open Access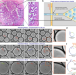 Curvature in the reproductive tract alters sperm–surface interactions
Curvature in the reproductive tract alters sperm–surface interactions
The effect of fallopian tube’s curvature on sperm motion has not been studied in detail. Here, the authors use droplet microfluidics to create soft curved interfaces, revealing a dynamic switch in sperm motility from a progressive surface-aligned mode at low curvatures, to an aggressive surface-attacking mode at high curvatures.
- Mohammad Reza Raveshi
- , Melati S. Abdul Halim
- & Reza Nosrati
-
Article
| Open Access Oocyte-derived microvilli control female fertility by optimizing ovarian follicle selection in mice
Oocyte-derived microvilli control female fertility by optimizing ovarian follicle selection in mice
How structural features on oocytes regulate mammalian female reproduction is unclear. Here, the authors provide imaging and physiological evidence (for example on Radixin knockout) to identify oocyte-derived mushroom-like microvilli that control the female reproductive lifespan by governing the fate of follicles.
- Yan Zhang
- , Ye Wang
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Control of oviductal fluid flow by the G-protein coupled receptor Adgrd1 is essential for murine embryo transit
Control of oviductal fluid flow by the G-protein coupled receptor Adgrd1 is essential for murine embryo transit
Lack of correct embryo transport can cause ectopic pregnancy. Here, the authors show that female mice lacking the adhesion G-protein coupled receptor Adgrd1 are infertile, due to embryos being trapped in the ampulla as the result of dysregulated oviductal fluid flow.
- Enrica Bianchi
- , Yi Sun
- & Gavin J. Wright
-
Article
| Open Access Triptonide is a reversible non-hormonal male contraceptive agent in mice and non-human primates
Triptonide is a reversible non-hormonal male contraceptive agent in mice and non-human primates
No male contraceptive pills are currently available. Here, the authors use triptonide, a compound derived from a Chinese plant, to deform sperm so that they cannot move properly, thereby causing reversible infertility in male mice and monkeys.
- Zongliang Chang
- , Weibing Qin
- & Wei Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell transcriptome profiling of the vaginal wall in women with severe anterior vaginal prolapse
Single-cell transcriptome profiling of the vaginal wall in women with severe anterior vaginal prolapse
Anterior vaginal prolapse (AVP), the most common form of pelvic organ prolapse, has deleterious effects on women’s health. Here the authors employ single-cell RNA-seq to construct a transcriptomic atlas of vaginal wall cells from AVP patients, and find that extracellular matrix dysregulation and immune reaction are associated with AVP.
- Yaqian Li
- , Qing-Yang Zhang
- & Lan Zhu
-
Perspective
| Open Access Origin and function of the yolk sac in primate embryogenesis
Origin and function of the yolk sac in primate embryogenesis
Why do human embryos need a yolk sac and how does it form? This Perspective by Thorsten Boroviak and Connor Ross explores the development and function of the yolk sac in primate embryogenesis.
- Connor Ross
- & Thorsten E. Boroviak
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic analysis of male puberty timing highlights shared genetic basis with hair colour and lifespan
Genomic analysis of male puberty timing highlights shared genetic basis with hair colour and lifespan
Age at voice-breaking is used to determine puberty timing in men, recall of which is considered less accurate than age at first menarche in women. Here, the authors perform multi-trait GWAS for male puberty timing by including both age at voice breaking and age of first facial hair for improved phenotype definition and power.
- Ben Hollis
- , Felix R. Day
- & John R. B. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access Distinctive phenotypes and functions of innate lymphoid cells in human decidua during early pregnancy
Distinctive phenotypes and functions of innate lymphoid cells in human decidua during early pregnancy
As an interface between maternal and fetal tissues, decidua hosts immune cells specialized in fostering a successful pregnancy. Here the authors carry out high-dimensional characterization of function, morphology and surface markers of human decidual innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), identifying subsets with features distinct from blood ILC.
- Oisín Huhn
- , Martin A. Ivarsson
- & Francesco Colucci
-
Article
| Open Access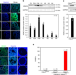 HDAC3 maintains oocyte meiosis arrest by repressing amphiregulin expression before the LH surge
HDAC3 maintains oocyte meiosis arrest by repressing amphiregulin expression before the LH surge
Before ovulation, a surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the resumption of meiosis in oocytes, which is mediated by EGF-like growth factors. Here, the authors show that HDAC3 inhibits mouse oocyte maturation by negatively regulating the expression of EGF-like factor before the LH surge.
- Huarong Wang
- , Han Cai
- & Chao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Neonatal Wnt-dependent Lgr5 positive stem cells are essential for uterine gland development
Neonatal Wnt-dependent Lgr5 positive stem cells are essential for uterine gland development
Uterine gland development is essential for successful embryo implantation, decidua formation and placental development. Here the authors demonstrate that neonatal Wnt-dependent Lgr5 expressing stem/progenitor cells at the tips of developing glands are indispensable for uterine gland development.
- Ryo Seishima
- , Carly Leung
- & Nick Barker
-
Article
| Open Access RUNX1 maintains the identity of the fetal ovary through an interplay with FOXL2
RUNX1 maintains the identity of the fetal ovary through an interplay with FOXL2
Proper ovarian differentiation requires RUNX1. Here, the authors show that double knockout of Runx1/Foxl2 results in masculinization of fetal ovaries, and that RUNX1 and FOXL2 jointly occupy common chromatin regions to maintain pre-granulosa cell identity in the fetal ovary.
- Barbara Nicol
- , Sara A. Grimm
- & Humphrey H.-C. Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association and epidemiological analyses reveal common genetic origins between uterine leiomyomata and endometriosis
Genome-wide association and epidemiological analyses reveal common genetic origins between uterine leiomyomata and endometriosis
Uterine leiomyomata (UL) or fibroids are neoplasms of the uterine smooth muscle associated with heavy menstrual bleeding and other female reproductive tract morbidity. Here, the authors identify eight previously undescribed genetic loci for UL and further look into genetic overlap with heavy menstrual bleeding and endometriosis.
- C. S. Gallagher
- , N. Mäkinen
- & C. C. Morton
-
Article
| Open Access UHRF1 suppresses retrotransposons and cooperates with PRMT5 and PIWI proteins in male germ cells
UHRF1 suppresses retrotransposons and cooperates with PRMT5 and PIWI proteins in male germ cells
Retrotransposons are silenced by an epigenetic mechanism and piRNA pathway in the mammalian germline. Here, the authors report that UHRF1 suppresses retrotransposons by interacting with PRMT5 and PIWI proteins during spermatogenesis.
- Juan Dong
- , Xiaoli Wang
- & Shuiqiao Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Rare mutations in the complement regulatory gene CSMD1 are associated with male and female infertility
Rare mutations in the complement regulatory gene CSMD1 are associated with male and female infertility
Many molecular and physiological mechanisms in the regulation of fertility are shared between female and male mammals. Here, Lee et al. report an association of CNVs in CSMD1 with early idiopathic menopause in women and show that loss of Csmd1 leads to gonadal dysfunction in both male and female mice.
- Arthur S. Lee
- , Jannette Rusch
- & Donald F. Conrad
-
Article
| Open Access Ambient black carbon particles reach the fetal side of human placenta
Ambient black carbon particles reach the fetal side of human placenta
Exposure to air pollution during pregnancy has been associated with impaired birth outcomes. Here, Bové et al. report evidence of black carbon particle deposition on the fetal side of human placentae, including at early stages of pregnancy, suggesting air pollution could affect birth outcome through direct effects on the fetus.
- Hannelore Bové
- , Eva Bongaerts
- & Tim S. Nawrot
-
Article
| Open Access Variants in the fetal genome near pro-inflammatory cytokine genes on 2q13 associate with gestational duration
Variants in the fetal genome near pro-inflammatory cytokine genes on 2q13 associate with gestational duration
Gestational duration depends on both maternal and fetal genetic influences. Here, the authors perform a fetal genome-wide association meta-analysis and find that a locus on 2q13 is associated with pregnancy duration and further show that the lead SNP rs7594852 changes the binding properties of transcriptional repressor HIC1.
- Xueping Liu
- , Dorte Helenius
- & Bjarke Feenstra
-
Article
| Open Access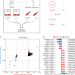 Assisted reproductive technologies are associated with limited epigenetic variation at birth that largely resolves by adulthood
Assisted reproductive technologies are associated with limited epigenetic variation at birth that largely resolves by adulthood
Use of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) is increasing globally but their impact on long term health remains unclear. Here the authors show that ART-conceived individuals show variation in epigenetic profile at birth that largely resolves by adulthood, with no evidence of an impact on long term outcomes.
- Boris Novakovic
- , Sharon Lewis
- & Richard Saffery
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of egg coat cross-linking sheds light on ZP1-associated female infertility
Molecular basis of egg coat cross-linking sheds light on ZP1-associated female infertility
Glycoprotein ZP1 is a component of the oocyte’s zona pellucida (ZP), and mutations in human ZP1 are linked to female infertility. Here, using structure-function analysis, the authors suggest that filament cross-linking by ZP1 is required to form a stable ZP in human, and infertility mutations interfere with cross-linking.
- Kaoru Nishimura
- , Elisa Dioguardi
- & Luca Jovine
-
Article
| Open Access Developmental kinetics and transcriptome dynamics of stem cell specification in the spermatogenic lineage
Developmental kinetics and transcriptome dynamics of stem cell specification in the spermatogenic lineage
In neonatal testes, prospermatogonia generate both spermatogonia for the first wave of spermatogenesis and spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs) for maintenance of spermatogenesis in males. Here the authors characterize the development of mouse SSCs from prospermatogonia using single-cell RNA-seq and transplantation assays.
- Nathan C. Law
- , Melissa J. Oatley
- & Jon M. Oatley
-
Article
| Open Access DDX5 plays essential transcriptional and post-transcriptional roles in the maintenance and function of spermatogonia
DDX5 plays essential transcriptional and post-transcriptional roles in the maintenance and function of spermatogonia
Sustained sperm production is dependent on activity of undifferentiated spermatogonia. Here, the authors demonstrate an essential role for RNA helicase DDX5 in maintenance of spermatogonia in adults through control of gene transcription plus RNA processing and export.
- Julien M. D. Legrand
- , Ai-Leen Chan
- & Robin M. Hobbs
-
Article
| Open Access SIRT1 mediates obesity- and nutrient-dependent perturbation of pubertal timing by epigenetically controlling Kiss1 expression
SIRT1 mediates obesity- and nutrient-dependent perturbation of pubertal timing by epigenetically controlling Kiss1 expression
The onset of mammalian puberty is sensitive to metabolic changes and nutritional status, but the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon are poorly understood. Here the authors show that the epigenetic regulator of transcription, SIRT1, mediates the effects of under and overnutrition on pubertal timing by controlling the expression of Kiss1 in hypothalamic neurons.
- M. J. Vazquez
- , C. A. Toro
- & M. Tena-Sempere
-
Article
| Open Access Uterine glands coordinate on-time embryo implantation and impact endometrial decidualization for pregnancy success
Uterine glands coordinate on-time embryo implantation and impact endometrial decidualization for pregnancy success
The transcription factor FOXA2 is specifically expressed in uterine glands. Here, using two conditional FOXA2 knockout mouse models, the authors show that glandular epithelia of the endometrium are required for timely embryo implantation and subsequent endometrial decidualization during successful pregnancy establishment.
- Andrew M. Kelleher
- , Jessica Milano-Foster
- & Thomas E. Spencer
-
Article
| Open Access Tridimensional visualization reveals direct communication between the embryo and glands critical for implantation
Tridimensional visualization reveals direct communication between the embryo and glands critical for implantation
Embryo implantation initiates the interaction of the blastocyst with the uterus and occurs within a specialised crypt formed by uterine epithelial cells. Here, using 3D imaging techniques of wild type and mutant uteri, the authors show that crypt formation occurs with preexisting glands of the uterus, opening communication between glands and the implanting embryo.
- Jia Yuan
- , Wenbo Deng
- & Sudhansu. K. Dey
-
Article
| Open Access Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor-1α are required for normal endometrial repair during menstruation
Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor-1α are required for normal endometrial repair during menstruation
About a quarter of pre-menopausal women will suffer from heavy menstrual bleeding in their lives. Here, Maybin and colleagues show hypoxia and subsequent activation of HIF-1α during menses are required for normal endometrial repair, and identify pharmacological stabilisation of HIF-1α as a potential therapeutic strategy for this debilitating condition.
- Jacqueline A. Maybin
- , Alison A. Murray
- & Hilary O. D. Critchley
-
Article
| Open Access Tbx3-dependent amplifying stem cell progeny drives interfollicular epidermal expansion during pregnancy and regeneration
Tbx3-dependent amplifying stem cell progeny drives interfollicular epidermal expansion during pregnancy and regeneration
The abdominal skin expands rapidly during pregnancy. Here the authors show that a population of highly proliferative stem cell progenies expressing the transcription factor Tbx3 is required for abdominal skin expansion in pregnant mice.
- Ryo Ichijo
- , Hiroki Kobayashi
- & Fumiko Toyoshima
-
Article
| Open Access Decidualisation and placentation defects are a major cause of age-related reproductive decline
Decidualisation and placentation defects are a major cause of age-related reproductive decline
Advanced maternal age has been associated with lower reproductive success and higher risk of pregnancy complications. Here the authors show that maternal ageing-related embryonic abnormalities in mouse are caused by decidualisation and placentation defects that can be rescued by transferring the embryo from an old to a young uterus.
- Laura Woods
- , Vicente Perez-Garcia
- & Myriam Hemberger
-
Article
| Open Access A microfluidic culture model of the human reproductive tract and 28-day menstrual cycle
A microfluidic culture model of the human reproductive tract and 28-day menstrual cycle
The female reproductive tract constitutes the ovary, fallopian tubes, uterus, and cervix, but it is challenging to engineer this systemin vitro. Here, the authors develop a microfluidic device (EVATAR) with reproductive tract and peripheral tissues to replicate hormone release of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
- Shuo Xiao
- , Jonathan R. Coppeta
- & Teresa K. Woodruff
-
Article
| Open Access BCAS2 is involved in alternative mRNA splicing in spermatogonia and the transition to meiosis
BCAS2 is involved in alternative mRNA splicing in spermatogonia and the transition to meiosis
Breast cancer amplified sequence 2 (BCAS2) is involved in pre-mRNA splicing but its physiological role is unclear. Here, the authors find BCAS2 enriched in mice spermatogonia in the testes, and BCAS2 deletion in germ cells alters alternative splicing of spermatogenesis-related genes, causing male infertility.
- Wenbo Liu
- , Fengchao Wang
- & Lei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Two pathways regulate cortical granule translocation to prevent polyspermy in mouse oocytes
Two pathways regulate cortical granule translocation to prevent polyspermy in mouse oocytes
Mammalian eggs release cortical granules to avoid being fertilized by more than a single sperm as polyspermy results in nonviable embryos. Here, the authors describe the mechanism driving translocation of the granules to the cortex in the mouse egg and show this process is essential to prevent polyspermy.
- Liam P. Cheeseman
- , Jérôme Boulanger
- & Melina Schuh
-
Article
| Open Access Neofunctionalization of zona pellucida proteins enhances freeze-prevention in the eggs of Antarctic notothenioids
Neofunctionalization of zona pellucida proteins enhances freeze-prevention in the eggs of Antarctic notothenioids
Despite subzero temperature of their surroundings, eggs of Antarctic notothenioid fishes do not freeze. This study shows the expansion of genes related to freezing temperature in notothenioid which also acquired of ice melting-promoting zona pellucida proteins with specific structural properties.
- Lixue Cao
- , Qiao Huang
- & Liangbiao Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and functional insights into IZUMO1 recognition by JUNO in mammalian fertilization
Structural and functional insights into IZUMO1 recognition by JUNO in mammalian fertilization
Sperm-egg fusion requires the interaction between IZUMO1 on the sperm and JUNO on the egg. Here, the authors report the crystal structure of mouse JUNO, and use it to explain its lack of binding to folate, along with in vivofunctional analyses.
- Kazuki Kato
- , Yuhkoh Satouh
- & Osamu Nureki
-
Article
| Open Access Male care and life history traits in mammals
Male care and life history traits in mammals
Males help care for offspring in about 10% of mammal species. Here, West and Capellini perform phylogenetic comparative analyses on a sample of 529 mammal species and find that male care is associated with shorter lactation periods by females, larger litters of offspring, and more frequent breeding events.
- Hannah E. R. West
- & Isabella Capellini
-
Article
| Open Access Fitness consequences of artificial selection on relative male genital size
Fitness consequences of artificial selection on relative male genital size
Within species, there tends to be a tight relationship between genital size and body size, suggesting strong stabilizing selection. Here, Booksmythe et al.artificially select relative genital size in mosquitofish and find that novel genital size-body size combinations do not lead to expected fitness reductions.
- Isobel Booksmythe
- , Megan L. Head
- & Michael D. Jennions
-
Article
| Open Access Rotational manipulation of single cells and organisms using acoustic waves
Rotational manipulation of single cells and organisms using acoustic waves
The precise rotational manipulation of single cells is technically challenging and relies on the optical, magnetic and electrical properties of the biospecimen. Here the authors develop an acoustic-based, on-chip manipulation method that can rotate single microparticles, cells and organisms.
- Daniel Ahmed
- , Adem Ozcelik
- & Tony Jun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Human oocyte developmental potential is predicted by mechanical properties within hours after fertilization
Human oocyte developmental potential is predicted by mechanical properties within hours after fertilization
Reliable assessments of oocyte developmental potential are lacking, making it difficult to select the best quality embryos for transfer after in vitrofertilization. Here, the authors show that a non-invasive measurement of viscoelastic properties predicts developmental potential in both humans and mice.
- Livia Z. Yanez
- , Jinnuo Han
- & David B. Camarillo
-
Article
| Open Access The Notch and Wnt pathways regulate stemness and differentiation in human fallopian tube organoids
The Notch and Wnt pathways regulate stemness and differentiation in human fallopian tube organoids
The mechanisms underlying fallopian tube epithelial renewal are unclear. Here, Kessler et al. isolate adult stem cells from the human fallopian tube epithelium and generate 3D organoids from these cells in vitrothat have a similar architecture to that of the fallopian tube.
- Mirjana Kessler
- , Karen Hoffmann
- & Thomas F. Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access A redox signalling globin is essential for reproduction in Caenorhabditis elegans
A redox signalling globin is essential for reproduction in Caenorhabditis elegans
Globins are best known for their role in respiration, but recent studies suggest they might contribute to redox signalling as well. Here, the authors present biochemical, structural and in vivoevidence that the roundworm globin Glb-12 acts as a superoxide generator necessary for germline development.
- Sasha De Henau
- , Lesley Tilleman
- & Bart P. Braeckman
-
Article
| Open Access Oocyte-triggered dimerization of sperm IZUMO1 promotes sperm–egg fusion in mice
Oocyte-triggered dimerization of sperm IZUMO1 promotes sperm–egg fusion in mice
Sperm-egg fusion is facilitated by the sperm-specific receptor IZUMO1 and the egg-specific counter-receptor JUNO. Here Inoue et al.show that JUNO first binds to monomeric IZUMO1; IZUMO1 then dimerizes and excludes JUNO from the sperm-egg interface, suggesting the existence of a IZUMO1 dimer receptor.
- Naokazu Inoue
- , Yoshihisa Hagihara
- & Ikuo Wada
-
Article
| Open Access Rare coding variants and X-linked loci associated with age at menarche
Rare coding variants and X-linked loci associated with age at menarche
Previous studies have linked over 100 genomic loci to age-at-menarche but that work was restricted to common autosomal variation. Here, Lunetta et al. identify associations with rare protein-coding and X-linked variants, implicating new mechanisms that regulate puberty timing.
- Kathryn L. Lunetta
- , Felix R. Day
- & John R. B. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access The sperm of aging male bustards retards their offspring’s development
The sperm of aging male bustards retards their offspring’s development
Sperm from aging males may decline in quality, but it is unclear how aging affects the ability of males to produce successful offspring. Here, the authors show that paternal aging of captive long-lived houbara bustards reduces both the likelihood that eggs hatch and the rate at which chicks grow.
- Brian T. Preston
- , Michel Saint Jalme
- & Gabriele Sorci
-
Article |
 Steroid hormone signalling links reproduction to lifespan in dietary-restricted Caenorhabditis elegans
Steroid hormone signalling links reproduction to lifespan in dietary-restricted Caenorhabditis elegans
Dietary restriction increases the lifespan of many species, but often at the cost of reduced fertility. Here, Thondamal et al. show that the dietary restriction-mediated increase in lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegansdepends on the production of a steroid hormone and its inhibition of germline plasticity.
- Manjunatha Thondamal
- , Michael Witting
- & Hugo Aguilaniu
-
Article |
 Diminished hERG K+ channel activity facilitates strong human labour contractions but is dysregulated in obese women
Diminished hERG K+ channel activity facilitates strong human labour contractions but is dysregulated in obese women
Uterine muscle contracts rhythmically during labour but the underlying electrophysiological mechanisms are not fully understood. The authors of this study show that hERG1 potassium channels reduce human uterine contractions in pregnancy and are suppressed during labour in lean but not in obese women.
- Helena C. Parkington
- , Janet Stevenson
- & Roger Smith
-
Article |
 Dysregulation of hydrogen sulphide metabolism impairs oviductal transport of embryos
Dysregulation of hydrogen sulphide metabolism impairs oviductal transport of embryos
Enzymes required for the production of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) are expressed in mammalian reproductive tracts. Here, the authors show that production of H2S regulates contraction in excised human fallopian tube samples and is required for transport of the embryo through the fallopian tube in mice.
- Nannan Ning
- , Jianchun Zhu
- & Jingxin Li
-
Article |
 Dependence of fertility on kisspeptin–Gpr54 signaling at the GnRH neuron
Dependence of fertility on kisspeptin–Gpr54 signaling at the GnRH neuron
The kisspeptin receptor GPR54 is implicated in the maintenance of mammalian fertility. Kirilov et al.study GPR54 mutant mice and identify a subset of neurons in the brain expressing gonadotropin-releasing hormone as the critical site for kisspeptin action.
- Milen Kirilov
- , Jenny Clarkson
- & Allan E. Herbison
-
Article |
 Constitutively active Foxo3 in oocytes preserves ovarian reserve in mice
Constitutively active Foxo3 in oocytes preserves ovarian reserve in mice
The number of primordial follicles, which constitute the ovarian reserve, decreases with age. By overexpressing a constitutively active version of the transcription factor FOXO3, the authors increase the ovarian reserve and fertility in aging female mice.
- Emanuele Pelosi
- , Shakib Omari
- & Chris Ottolenghi
-
Article |
 A genetically female brain is required for a regular reproductive cycle in chicken brain chimeras
A genetically female brain is required for a regular reproductive cycle in chicken brain chimeras
Sexual dimorphism describes physical differences between males and females of the same species and is partly shaped by the action of hormones. Maekawa and colleagues construct mixed-sex chicken brain chimeras and find that the female reproductive cycle is largely destroyed in female chimeras with male brains.
- Fumihiko Maekawa
- , Miyano Sakurai
- & Hiroko Ohki-Hamazaki

 BRCA2 binding through a cryptic repeated motif to HSF2BP oligomers does not impact meiotic recombination
BRCA2 binding through a cryptic repeated motif to HSF2BP oligomers does not impact meiotic recombination